Abstract
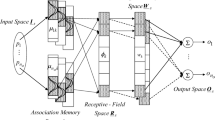
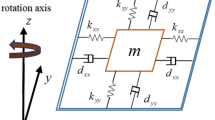
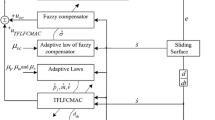
This paper aims to propose a design method of interval type-2 wavelet cerebellar model articulation controller (IT2WCMAC) and applies it to control uncertain nonlinear systems. The proposed controller incorporates an IT2WCMAC as the main controller to mimic an ideal controller, and a robust compensator is used to eliminate the approximation error between the IT2WCMAC and the ideal controller. The self-evolving algorithm is used to automatically construct the network structure from the blank rule-base. In the proposed control scheme, the steepest descent gradient algorithm is applied to online tune the network parameters, and a Lyapunov stability theorem is applied to guarantee the system’s stability. Moreover, the learning rates of the parameter adaptive laws can be optimized by the particle swarm optimization (PSO) to promote the parameter learning efficiency. Finally, the proposed control system is applied to control nonlinear chaotic systems to verify the control performance and to show the superiority of the proposed algorithm than the other control methods.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCulloch, W.S., Pitts, W.: A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 5, 115–133 (1943)
Hebb, D.: The organization of behavior. Wiley, New York (1949)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323, 533–536 (1986)
Gu, J., Pan, Y., Wang, H.: Research on the improvement of image edge detection algorithm based on artificial neural network. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 126, 2974–2978 (2015)
Chiang, H.-K., Fang, C.-C., Hsu, F.-J.: The neural sliding mode controller design of fan-plate system. Artif. Life Robot. 21, 49–56 (2016)
Han, Y.-Q.: Adaptive tracking control of nonlinear systems with dynamic uncertainties using neural network. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 49, 1391–1402 (2018)
He, W., Dong, Y.: Adaptive fuzzy neural network control for a constrained robot using impedance learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29, 1174–1186 (2018)
Zeng, G.-Q., Xie, X.-Q., Chen, M.-R., Weng, J.: Adaptive population extremal optimization-based PID neural network for multivariable nonlinear control systems. Swarm Evol. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.04.008
Fang, Y., Fei, J., Ma, K.: Model reference adaptive sliding mode control using RBF neural network for active power filter. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 73, 249–258 (2015)
Chen, L., Liu, M., Huang, X., Fu, S., Qiu, J.: Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for network-based nonlinear systems with actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26, 1311–1323 (2018)
Lin, C.-M., Lin, M.-H., Yeh, R.-G.: Synchronization of unified chaotic system via adaptive wavelet cerebellar model articulation controller. Neural Comput. Appl. 23(3–4), 965–973 (2013)
Lu, H.-C., Chuang, C.-Y.: Robust parametric CMAC with self-generating design for uncertain nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 74(4), 549–562 (2011)
Wang, J.-G., Tai, S.-C., Lin, C.-J.: The application of an interactively recurrent self-evolving fuzzy CMAC classifier on face detection in color images. Neural Comput. Appl. 29, 201–213 (2018)
Wang, J.-G., Tai, S.-C., Lin, C.-J.: Medical diagnosis applications using a novel interactively recurrent self-evolving fuzzy CMAC model. In: Proc. IJCNN, 2014, pp. 4092–4098
Guan, J.-S., Lin, L.-Y., Ji, G.L., Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L., Rudas, I.J.: Breast tumor computer-aided diagnosis using self-validating cerebellar model neural networks. Acta Polytechn. Hungarica 13, 39–52 (2016)
Lin, Y.Y., Liao, S.H., Chang, J.Y., Lin, C.T.: Simplified interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 25(5), 959–969 (2014)
Castillo, O., Martínez-Marroquín, R., Melin, P., Valdez, F., Soria, J.: Comparative study of bio-inspired algorithms applied to the optimization of type-1 and type-2 fuzzy controllers for an autonomous mobile robot. Inf. Sci. 192, 19–38 (2012)
Mendel, J.M.: A quantitative comparison of interval type-2 and type-1 fuzzy logic systems: first results. In: Proc. FUZZ-IEEE, 2010, pp. 1–8
Oh, S.-K., Jang, H.-J., Pedrycz, W.: A comparative experimental study of type-1/type-2 fuzzy cascade controller based on genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(9), 11217–11229 (2011)
Liang, Q., Mendel, J.M.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 8(5), 535–550 (2000)
Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L.: WCMAC-based control system design for nonlinear systems using PSO. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 33(2), 807–818 (2017)
Hsu, C.F., Lin, C.M., Lee, T.T.: Wavelet adaptive backstepping control for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 17(5), 1175–1183 (2006)
Mai, T., Wang, Y.: Adaptive force/motion control system based on recurrent fuzzy wavelet CMAC neural networks for condenser cleaning crawler-type mobile manipulator robot. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 22(5), 1973–1982 (2014)
Hung, Y.-C., Lin, F.-J., Hwang, J.-C., Chang, J.-K., Ruan, K.-C.: Wavelet fuzzy neural network with asymmetric membership function controller for electric power steering system via improved differential evolution. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30, 2350–2362 (2015)
Seo, Y., Kim, S., Kisi, O., Singh, V.P.: Daily water level forecasting using wavelet decomposition and artificial intelligence techniques. J. Hydrol. 520, 224–243 (2015)
Chui, C.K.: An introduction to wavelets. Academic Press, San Diego (2016)
Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L.: PSO-self-organizing interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for antilock braking systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(5), 1362–1374 (2017)
Lin, Y.-Y., Chang, J.-Y., Lin, C.-T.: Identification and prediction of dynamic systems using an interactively recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 24(2), 310–321 (2013)
Han, H., Wu, X., Liu, Z., Qiao, J.: Design of self-organizing intelligent controller using fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2017.2785812
Han, H.-G., Lin, Z.-L., Qiao, J.-F.: Modeling of nonlinear systems using the self-organizing fuzzy neural network with adaptive gradient algorithm. Neurocomputing 266(29), 566–578 (2017)
Chen, S.-Y., Liu, T.-S.: Intelligent tracking control of a PMLSM using self-evolving probabilistic fuzzy neural network. IET Electr. Power Appl. 11(6), 1043–1054 (2017)
Lin, C.-M., Le, T.-L., Huynh, T.-T.: Self-evolving function-link interval type-2 fuzzy neural network for nonlinear system identification and control. Neurocomputing 275, 2239–2250 (2018)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proc. IEEE conf. neural network, vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948 (1995)
Gao, W.-F., Liu, S.-Y.: A modified artificial bee colony algorithm. Comput. Oper. Res. 39(3), 687–697 (2012)
Zheng, Y.-J.: Water wave optimization: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic. Comput. Oper. Res. 55, 1–11 (2015)
Mirjalili, S.: The ant lion optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 83, 80–98 (2015)
Mirjalili, S.: Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl. Based Syst. 89, 228–249 (2015)
Du, K.-L., Swamy, M.: Ant colony optimization. In: Search and optimization by metaheuristics. Springer, 2016, pp. 191–199
Mirjalili, S., Lewis, A.: The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 95, 51–67 (2016)
Nagaraj, B., Murugananth, N.: A comparative study of PID controller tuning using GA, EP, PSO and ACO. In: Proc. ICCCCT, 2010, pp. 305–313
Le, T.-L., Lin, C.-M., Huynh, T.-T.: Self-evolving type-2 fuzzy brain emotional learning control design for chaotic systems using PSO. Appl. Soft Comput. 73, 418–433 (2018)
Hasanipanah, M., Amnieh, H.B., Arab, H., Zamzam, M.S.: Feasibility of PSO–ANFIS model to estimate rock fragmentation produced by mine blasting. Neural Comput. Appl. 30(4), 1015–1024 (2018)
Wu, L., Gao, H.: Sliding mode control of two-dimensional systems in Roesser model. IET Control Theory Appl. 2(4), 352–364 (2008)
Cui, R., Chen, L., Yang, C., Chen, M.: Extended state observer-based integral sliding mode control for an underwater robot with unknown disturbances and uncertain nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(8), 6785–6795 (2017)
Zheng, E.H., Xiong, J.J., Luo, J.L.: Second order sliding mode control for a quadrotor UAV. ISA Trans. 53(4), 1350–1356 (2014)
Mobayen, S., Tchier, F.: Synchronization of a class of uncertain chaotic systems with Lipschitz nonlinearities using state-feedback control design: a matrix inequality approach. Asian J. Control 20(1), 71–85 (2018)
Ditto, W., Munakata, T.: Principles and applications of chaotic systems. Commun. ACM 38(11), 96–102 (1995)
Chen, X., Park, J.H., Cao, J., Qiu, J.: Adaptive synchronization of multiple uncertain coupled chaotic systems via sliding mode control. Neurocomputing 273, 9–21 (2018)
Chen, S., Yu, S., Lü, J., Chen, G., He, J.: Design and FPGA-based realization of a chaotic secure video communication system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(9), 2359–2371 (2017)
Çavuşoğlu, Ü., Kaçar, S., Pehlivan, I., Zengin, A.: Secure image encryption algorithm design using a novel chaos based S-Box. Chaos Solitons Fractals 95, 92–101 (2017)
Lan, R., He, J., Wang, S., Gu, T., Luo, X.: Integrated chaotic systems for image encryption. Signal Process. 147, 133–145 (2018)
Ha, S., Liu, H., Li, S., Liu, A.: Backstepping-based adaptive fuzzy synchronization control for a class of fractional-order chaotic systems with input saturation. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00663-5
Pan, Y., Aranovskiy, S., Bobtsov, A., Yu, H.: Efficient learning from adaptive control under sufficient excitation. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/rnc.4541
Adetola, V., Guay, M.: Performance improvement in adaptive control of linearly parameterized nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 55(9), 2182–2186 (2010)
Lin, F.-J., Teng, L.-T., Chu, H.: A robust recurrent wavelet neural network controller with improved particle swarm optimization for linear synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(6), 3067–3078 (2008)
Slotine, J.-J.E., Li, W.: Applied nonlinear control. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1991)
Yan, J.-J., Shyu, K.-K., Lin, J.-S.: Adaptive variable structure control for uncertain chaotic systems containing dead-zone nonlinearity. Chaos Solitons Fractals 25(2), 347–355 (2005)
Lin, C.-M., Li, H.-Y.: Self-organizing adaptive wavelet CMAC backstepping control system design for nonlinear chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14(1), 206–223 (2013)
Lü, J., Chen, G., Cheng, D., Celikovsky, S.: Bridge the gap between the Lorenz system and the Chen system. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 12(12), 2917–2926 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support in part from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Republic of China under Grant MOST 106-2221-E-155-002-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, TL., Huynh, TT. & Lin, CM. Self-Evolving Interval Type-2 Wavelet Cerebellar Model Articulation Control Design for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems Using PSO. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 2524–2541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00735-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00735-6