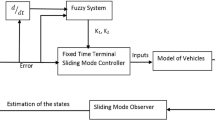
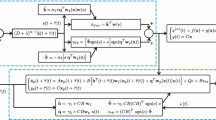
Abstract
In this paper, conventional gradient-descent-based adaptive fuzzy observer is improved by using the terminal sliding-mode theory for a class of nonlinear systems. The improvement is made in two ways: first, the switching term of the sliding-mode approach is added to the state of the observer. Second, the measurement error of the system is designed as the input of the observer instead of measured state. The stability of the observer and boundedness of the parameters are proved using Lyapunov approach. Contributions of the paper are summarized as follows: (i) the robustness and convergence properties of newly proposed observer are improved, (ii) the proposed adaptive fuzzy terminal sliding-mode observer, conventional adaptive fuzzy observer, adaptive neural-network observer, and Euler filtering approaches are compared in terms of their ability to estimate velocities of three real-time experimental systems reliably. The performance of the designed observers is discussed with root mean squared-error criterion where the proposed adaptive fuzzy terminal sliding-mode observer provided much accurate state estimation results than classical observers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luenberger, D.: Observers for multivariable systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 11(2), 190–197 (1966)
Thau, E.E.: Observing the state of nonlinear systems. Int. J. Control 17, 471–479 (1973)
Birk, J., Zeitz, M.: Extended-Luenberger observer for non-linear multivariable systems. Int. J. Control 47(6), 1823–1836 (1988)
Cox, H.: On the estimation of state variables and parameters for noisy dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 9(1), 5–12 (1964)
Simon, D.: Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H-Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken (2006)
Drakunov, S.V.: An adaptive quasioptimal filter with discontinuous parameters. Autom. Remote Control 44(9), 1167–1175 (1983)
Slotine, J.J.E., Hedrick, J.K., Misawa, E.A.: On sliding observers for nonlinear systems. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Control 109, 245–252 (1987)
Gauthier, J.P., Hammouri, H., Othman, S.: A simple observer for nonlinear systems applications to bioreactors. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 37(6), 875–880 (1992)
Tanaka, K., Wang, H.O.: Fuzzy regulators and fuzzy observers: alinear matrix inequality approach. In: Proceedings of the 36thIEEE Conference on Decision and Control, vol. 2, pp. 1315–1320, San Diego, California, 1997
Beyhan, S.: Runge–Kutta model-based nonlinear observer for synchronization and control of chaotic systems. ISA Trans. 52(4), 501–509 (2013)
Iplikci, S.: Runge–Kutta model-based adaptive predictive control mechanism for non-linear processes. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 35(2), 166–180 (2013)
Al-Hosani, K., Utkin, V.I.: Parameters estimation using sliding mode observer with shift operator. J. Frankl. Inst. 349(4), 1509–1525 (2012)
Spurgeon, S.K.: Sliding mode observers: a survey. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 39(8), 751–764 (2008)
Ahmed, M.S., Riyaz, S.H.: Dynamic observers—a neural net approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 9(1,2), 113–127 (2000)
Kim, Y.H., Lewis, F.L., Abdallah, C.T.: A dynamic recurrent neural-network-based adaptive observer for a class of nonlinear systems. Automatica 33(8), 1539–1543 (1997)
Park, JH., Yoon, PS., Park, GT.: Robust adaptive observer using fuzzy systems for uncertain nonlinear systems. In: The 10th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 3, pp. 749–752, The University of Melbourne, Australia, 2001
Boulkroune, A., Tadjine, M., M’Saad, M., Farza, M.: How to design a fuzzy adaptive controller based on observers for uncertain affine nonlinear systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 159(8), 926–948 (2008)
Leu, Y.-G., Lee, T.-T., Wang, W.-Y.: Observer-based adaptive fuzzy-neural control for unknown nonlinear dynamical systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 29(5), 583–591 (1999)
Lian, K.-Y., Hong, C.-W.: Current-sensorless flyback converters using integral T–S fuzzy approach. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 15(1), 66–74 (2013)
Wang, L.-K., Liu, X.-D.: Robust H\(_\infty\) fuzzy output feedback control for uncertain discrete-time nonlinear systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12(3), 218–226 (2010)
Zhang, L., Tong, S., Li, Y.: Adaptive fuzzy output-feedback control with prescribed performance for uncertain nonlinear systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 16(2), 212–221 (2014)
Lin, F.-C., Yang, S.-M.: Adaptive fuzzy logic-based velocity observer for servo motor drives. Mechatronics 13(3), 229–241 (2003)
Merry, R.J.E., van de Molengraft, M.J.G., Steinbuch, M.: Velocity and acceleration estimation for optical incremental encoders. Mechatronics 20(1), 20–26 (2010)
Feng, Y., Zheng, J., Xinghuo, Y., Truong, N.-V.: Hybrid terminal sliding-mode observer design method for a permanent-magnet synchronous motor control system. Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on 56(9), 3424–3431 (2009)
Tan, C.P., Yu, X., Man, Z.: Terminal sliding mode observers for a class of nonlinear systems. Automatica 46(8), 1401–1404 (2010)
Yuqiang, W., Xinghuo, Y., Man, Z.: Terminal sliding mode control design for uncertain dynamic systems. Syst. Control Lett. 34(5), 281–287 (1998)
Wang, L.X.: A Course in Fuzzy Systems and Control. Prentice-Hall Inc., London (1997)
Beyhan, S.: Adaptive dynamic neural-network observer design of velocity feedbacks. In: Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications (INISTA), 2012 International Symposium on, pages 1–5, Trabzon, Turkey, July 2012
Akçay, H., Ninness, B.: Orthonormal basis functions for modelling continuous-time systems. Signal Process. 77(3), 261–274 (1999)
Xinghuo, Y., Zhihong, M.: Fast terminal sliding-mode control design for nonlinear dynamical systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 49(2), 261–264 (2002)
Ionnou, P.A., Sun, J.: Robust Adaptive Control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1996)
Tan, C.P., Edwards, C.: Sliding mode observers for robust detection and reconstruction of actuator and sensor faults. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 13(5), 443–463 (2003)
Kim, Y.-T., Zenn Bien, Z.: Robust adaptive fuzzy control in the presence of external disturbance and approximation error. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 148(3), 377–393 (2004)
Quanser Inc. Quanser Inc., Canada, Rotary Flexible Joint User Manual, 2012
Feedback Inc. Digital Pendulum Control Experiments, 33-936s, Feedback Intruments ltd., 2006
Levant, A.: Robust exact differentiation via sliding mode technique. Automatica 34(3), 379–384 (1998)
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Delft Center for Systems and Control institute staff to collect experimental data from flexible-link transmission system. This paper is supported by a project of Pamukkale University Scientific Project Council (BAP) under grant number 2013BSP008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyhan, S. Adaptive Fuzzy Terminal Sliding-Mode Observer with Experimental Applications. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18, 585–594 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0102-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0102-8