Abstract
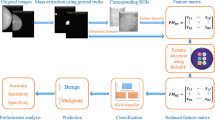
Mammographic risk analysis is an important task for assessing the likelihood of a woman developing breast cancer. It has attracted much attention in recent years as it can be used as an early risk indicator when screening patients. In this paper, a kernel-based fuzzy-rough nearest-neighbour approach to classification is employed to address the issue of the assessment of mammographic risk. Four different breast tissue density assessment metrics are employed to support this study, and the performance of the proposed approach is compared with alternative nearest-neighbour-based classifiers and other popular learning classification techniques. Systematic experimental results show that the work employed here generally improves the classification performance over the others, measured using criteria such as classification accuracy rate, root mean squared error and the kappa statistics. This demonstrates the potential of kernel-based fuzzy-rough nearest-neighbour classification as a robust and reliable tool for mammographic risk analysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The relevant WEKA software can be download from https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/2043486/weka.jar.
References
World Health Organization, “Breast cancer: prevention and control,” from: http://www.who.int/cancer/detection/breastcancer/en/. Accessed Aug 2014
World Cancer Research Fund International, “Breast cancer,” from: http://www.wcrf.org/cancer _statistics/data_specific_cancers/breast_cancer_statistics.php. Accessed Aug 2014
World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. “Latest world cancer statistics: Global cancer burden rises to 14.1 million new cases in 2012: Marked increase in breast cancers must be addressed,” from: www.iarc.fr/en/media-centre/pr/2013/pdfs/pr223_E.pdf, Accessed Aug 2014
Tortajada, M., Oliver, A., Martí, R., Ganau, S., Tortajada, L., Sentís, M., Freixenet, J., Zwiggelaar, R.: Breast peripheral area correction in digital mammograms. Comput. Biol. Med. 50, 32–40 (2014)
Tesic, V., Kolaric, B., Znaor, A., Kuna, S.K., Brkljacic, B.: Mammographic density and estimation of breast cancer risk in intermediate risk population. Breast J. 19(1), 71–78 (2013)
Wang, A., Vachon, C., Brandt, K., Ghosh, K.: Breast density and breast cancer risk: a practical review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 89(4), 548–557 (2014)
Qu, Y., Shang, C., Wu, W., Shen, Q.: Evolutionary fuzzy extreme learning machine for mammographic risk analysis. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 13(4), 282–291 (2011)
Strange, H., Chen, Z., Denton, E., Zwiggelaar, R.: Modelling mammographic microcalcification clusters using persistent mereotopology. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 47, 157–163 (2014)
He, W., Denton, E., Zwiggelaar, R.: A study on mammographic image modelling and classification using multiple databases, in Breast Imaging, pp. 696–701 (2014)
Pfeiffer, P.: Concepts of Probability Theory. Courier Dover Publications, Mineola (2013)
Neapolitan, R.: Probabilistic reasoning in expert systems: theory and algorithms, Create Space Independent Publishing Platform (2012)
Han, B., Davis, L.: Density-based multifeature background subtraction with support vector machine. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(5), 1017–1023 (2012)
Aggarwal, C., Zhai, C.: Mining Text Data. The Springer Publishing Co., New York (2012)
Karimi, K., Hamilton, H.: Finding temporal relations: Causal Bayesian networks vs. C4.5, Foundations of Intelligent Systems, pp. 266–273 (2010)
Qin, B., Xia, Y., Prabhakar, S.: Rule induction for uncertain data. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 29(1), 103–130 (2011)
Lejarraga, T., Dutt, V., Gonzalez, C.: Instance-based learning: a general model of repeated binary choice. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 25(2), 143–153 (2012)
Jiang, S., Pang, G., Wu, M., Kuang, L.: An improved K-nearest-neighbor algorithm for text categorization. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(1), 1503–1509 (2012)
Qu, Y., Shang, C., Shen, Q., Mac Parthaláin, N., Wu,W.: Kernel-based fuzzy-rough nearest neighbour classification. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 1523–1529 (2011)
Jensen, R., Shen, Q.: New approaches to fuzzy-rough feature selection. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17(4), 824–838 (2009)
Maji, S., Berg, A., Malik, J.: Efficient classification for additive kernel SVMs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(1), 66–77 (2013)
Wolfe, J.: Risk for breast cancer development determined by mammographic parenchymal pattern. Cancer 37, 2486–2492 (1976)
Boyd, N., Byng, J., Jong, R., Fishell, E., Little, L., Miller, A., Lockwood, G., Tritchler, D., Yaffe, M.: Quantitative classification of mammographic densities and breast cancer risk: results from the canadian national breast screening study. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 87(9), 670–675 (1995)
Tabár, L., Tot, T., Dean, P.: The Art and Science of Early Detection with Mammography. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart (2005)
American College of Radiology: Illustrated Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System BIRADS, 3rd ed. (1998)
Pawlak, Z.: Rough Sets: Theoretical Aspects of Reasoning About Data. Kluwer Academic Publishing, Dordrecht (1991)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Putting rough sets and fuzzy sets together. In: Slowinski, R. (ed.) Intelligent Decision Support, pp. 203–232. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1992)
Radzikowska, A., Kerre, E.: A comparative study of fuzzy rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 126(2), 137–155 (2002)
Cornelis, C., De Cock, M., Radzikowska, A.: Vaguely quantified rough sets, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4482, pp. 87–94 (2007)
Keller, J., Gray, M., Givens, J.: A fuzzy k-nearest neighbor algorithm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 15(2), 580–588 (1985)
Sarkar, M.: Fuzzy-rough nearest neighbors algorithm. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 158, 2123–2152 (2007)
Sun, L., Li, C.: A fast and scalable fuzzy-rough nearest neighbor algorithm. WRI Glob. Congr. Intell. Syst. 4, 311–314 (2009)
Bian, H., Mazlack, L.: Fuzzy-rough nearest-neighbor classification approach. In: Proceeding of the 22nd International Conference of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society, pp. 500–505 (2003)
Babu, V., Viswanath, P.: Rough-fuzzy weighted k-nearest leader classifier for large data sets. Pattern Recogn. 42(9), 1719–1731 (2009)
Jensen, R., Cornelis, C.: Fuzzy-rough nearest neighbour classification and prediction. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 412(42), 5871–5884 (2011)
Genton, M.: Classes of kernels for machine learning: a statistics perspective. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2, 299–312 (2001)
Moser, B.: On the T-transitivity of kernels. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 157, 1787–1796 (2006)
Hu, Q., Chen, D., Yu, D., Pedrycz, W.: Kernelised fuzzy rough sets. In: 4th International Conference, Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology, pp. 304–311 (2009)
Jensen, R., Cornelis, C.: Fuzzy-rough instance selection. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 1776–1782 (2010)
Qu, Y., Shen, Q., Mac Parthaláin, N., Shang, C., Wu, W.: Fuzzy similarity-based nearest-neighbour classification as alternatives to their fuzzy-rough parallels. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 54(1), 184–195 (2013)
Suckling, J., Partner, J., Dance, D., Astley, S.,Hutt, I., Boggis, C., Ricketts, I., Stamatakis, E., Cerneaz, N., Kok, S., Betal, D., Taylor, P., Savage, J.: The mammographic image analysis society digital mammogram database. In: International Workshop on Digital Mammography, pp. 211–221 (1994)
Oliver, A., Freixenet, J., Marti, R., Pont, J., Perez, E., Denton, E., Zwiggelaar, R.: A novel breast tissue density classification methodology. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 12(1), 55–65 (2008)
Lam, P., Vacek, P., Geller, B., Muss, H.: The association of increased weight, body mass index, and tissue density with the risk of breast carcinoma in vermont. Cancer 89, 369–375 (2000)
Hall, M.: Correlation-based feature selection for discrete and numeric class machine learning. PhD thesis, University of Waikato (2000)
Kleene, S.: Introduction to Metamathematics. Van Nostrand, New York (1952)
Dienes, S.: On an implication function in many-valued systems of logic. J. Symb. Log. 14(2), 95–97 (1949)
D. Rajnarayan and D. Wolpert, “Bias-variance trade-offs: novel applications,” Encyclopedia of Machine Learning, pp. 101–110, 2010
Cohen, J.: A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 20(1), 37–46 (1960)
Mac Parthaláin, N., Jensen, R.: Unsupervised fuzzy-rough set-based dimensionality reduction. Inf. Sci. 229, 106–121 (2013)
Jensen, R., Shen, Q.: Computational Intelligence and Feature Selection: Rough and Fuzzy Approaches. IEEE Press and Wiley, Hoboken (2008)
Shang, C., Barnes, D.: Fuzzy-rough feature selection aided support vector machines for Mars image classification. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 117(3), 202–213 (2013)
Fu, X., Shen, Q.: Fuzzy complex numbers and their application for classifiers performance evaluation. Pattern Recogn. 44(7), 1403–1417 (2011)
Boongoen, T., Shang, C., Iam-On, N., Shen, Q.: Extending data reliability measure to a filter approach for soft subspace clustering. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 40, 6 (2011)
Boongoen, T., Shen, Q.: Nearest-neighbor guided evaluation of data reliability and its applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 40(6), 1622–1633 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61272171), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 3132014094, 3132013335, 3132013325) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2013M541213). The authors would like to thank the support provided by Aberystwyth University and by the colleagues in the Advanced Reasoning Group with the Department of Computer Science, Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Computer Science at Aberystwyth University, UK. The authors are also grateful to the reviewers for their constructive comments which have helped improve this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Shang, C., Shen, Q. et al. Kernel-based Fuzzy-rough Nearest-neighbour Classification for Mammographic Risk Analysis. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 17, 471–483 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0044-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0044-1