Abstract
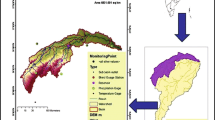
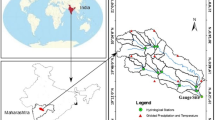
Tons river basin has a great significance to states Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh in India, concerning water resources aspects and the ecological balances. A hydrological modeling approach was used to identify the sensitive hydrological parameters of the basin through Sequential Uncertainty Fitting (SUFI-2) technique. SUFI-2 was used for the calibration of SOIL WATER ASSESSMENT TOOL (SWAT) model. It was calibrated for period (1979–2000) including 3 years as warm up (1979–1982), subsequently model was validated on 11 years of datasets (2001–2011). The percentage of observation covered by the 95PPU (p-factor) and the average thickness of the 95PPU band divided by the standard deviation of the measured data (r-factor), were taken into an account for performance evaluation of model. In calibration and validation the p-factor and the r-factor was obtained as 0.54, 0.76 and 0.68, 0.56 respectively. The coefficient of determination (R2), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), percent bias (PBIAS) and RMSE-observations standard deviation ratio (RSR) have been used for goodness of fit between observation and final best simulation. The R2, NSE, PBIAS and RSR are 0.74, 0.73, −3.55 and 0.54 respectively during the calibration whereas in validation period values are 0.75, 0.69, 18.55 and 0.56 respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour KC (2005) Calibration of hydrologic models: when is a model calibrated? In Zerger, A. and Argent, R.M. (eds) MODSIM 2005 International Congress on Modelling and Simulation. Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand, pp. 2449–12455.
Abbaspour KC (2015) SWAT-CUP: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs - A User Manual.
Abbaspour KC, Johnson A, van Genuchten M Th (2004) Estimating uncertain flow and transport parameters using a sequential uncertainty fitting procedure. Vadose Zone J 3(4), 1340–1352.
Abbaspour KC, Yang J, Maximov I, Siber R, Bogner K, Mieleitner J, Zobrist J, Srinivasan R (2007) Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J Hydrol 333:413–430
Abbaspour KC, Faramarzi M, Ghasemi SS, Yang H (2009) Assessing the impact of climate change on water resources in Iran. Water Resour Res 45:W10434. doi:10.1029/2008WR007615
Abbaspour KC, Rouholahnejad E, Vaghefi S, Srinivasan R, Yang H, Kløve B (2015) A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: Calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J Hydrol 5(24):733–752
Arnold JG, Fohrer N (2005).SWAT2000: Current capabilities and research opportunities in applied watershed modeling. Hydrol Proc 19(3): 563–572.
Arnold JG, Allen PM, Morgan D (2001) Hydrologic model for design of constructed wetlands. Wetlands 21(2):167–178
Arnold JG, Moriasi DN, Gassman PW, Abbaspour KC, et al., (2012) SWAT: model use, calibration, and validation. Am Soc Agri Biol Eng. 55(4): 1491–1508.
Beven K (2000) Rainfall-runoff modeling: the primer. Wiley, New York
Beven K, Binley A (1992) The future of distributed models: model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol Process 6:279–298
Bicknell BR, Imhoff JC, Kittle JL, Donigian AS, Johanson RC (1997) Hydrological simulation program–fortran, user’s manual for version 11: USA Environmental Protection Agency, National Exposure Research Laboratory, Athens, EPA/600/R-97/080, 755 p.
Biondi D, Freni G, Iacobellis V, Mascaro G, Montanari A (2012) Validation of hydrological models: conceptual basis, methodological approaches, and a proposal for a code of practice. Phys Chem Earth 42–44:70–76
Borah DK, Bera M (2004) Watershed–scale hydrologic and nonpoint–source pollution models: review of applications. American Society of Agricultural Engineers. ISSN 0001–235 47(3):789–803
Duan Q, Sorooshian S, Gupta VK (1992) Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour Res 28(4):1015–1031
Engel B, Storm D, White M, Arnold JG, Arabi M (2007) A hydrologic/water quality model application protocol. JAWRA, 43(5), 1223–1236.
Gassman PW, Reyes M, Green CH, Arnold JG (2007) The Soil and Water Assessment Tool: Historical development, applications, and future directions. Trans ASABE. 50(4): 1211–1250.
Gupta HV, Sorooshian S, Yapo PO (1999) Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J Hydrol Eng, 4(2), 135–143.
Gupta HV, Beven KJ, Wagener T (2006) Model calibration and uncertainty estimation. Encycl Hydrol Sci 11:131.
Gupta HV, Wagener T, Liu Y (2008) Reconciling theory with observations: Elements of a diagnostic approach to model evaluation. Hydrol Proc 22(18): 3802–3813.
Helton JC, Davisb FJ (2003) Latin hypercube sampling and the propagation of uncertainty in analyses of complex systems. Rel Eng System Saf 81(2003):23–69
Krause, P., Boyle, D., & Bäse, F. (2005) Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv Geosci, 5, 89–97.
Kuczera G, Parent E (1998) Monte Carlo assessment of parameter uncertainty in conceptual catchment models: the Metropolis algorithm. J Hydrol 211(1–4):69–85
McKay MD (1988) Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Using a Statistical Sample of Input Values. In: Ronen Y (ed) Uncertainty Analysis. CRC press, Inc, Boca Raton, pp 145–186
McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ (1979) A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 21:239–245
Mengistu DT, Sorteberg A (2012) Sensitivity of SWAT simulated streamflow to climatic changes within the Eastern Nile River basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(391–407):2012. doi:10.5194/hess-16-391-2012
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Binger RL, Harmel RD, Veith T (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50(3): 885–900.
Moriasi DN, Wilson BN, Douglas-Mankin KR, Arnold JG, Gowda PH (2012) Hydrologic and water quality models: use, calibration, and validation. Trans ASABE. 55(4): 1241–1247.
Moriasi DN, Gitau MW, Pai N, Daggupati P (2015) Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans ASABE. 58(6): 1763–1785. (doi:10.13031/trans.58.10715)
Narsimlu B, Gosain AK, Chahar BR, Singh SK, Srivastava PK (2015) SWAT model calibration and uncertainty analysis for streamflow prediction in the Kunwari River Basin, India, Using Sequential Uncertainty Fitting. Environ. Process. Doi:10.1007/s40710-015-0064-8.
Nash JE, Sutcliffe J (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models: part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry J, Williams J, King K (2005) Soil and Water Assessment Tool theoretical documentation version 2005 Texas, USA
Palosuo T, Kersebaum KC, Angulo C, Hlavinka P, Moriondo M, Olesen JE, Patil R, Ruget F, Rumbaur C, Takáč J, Trnka M, Bindi M, Caldag B, Ewert F, Ferrise R, Mirschel W, Saylan L, Siska B, Rötter R (2011) Simulation of winter wheat yield and its variability in different climates of Europe: A comparison of eight crop growth models. Eur J Agron 35(3):103–114
Patel D, Srivastava P (2013) Flood hazards mitigation analysis using remote sensing and GIS: correspondence with town planning scheme. Water Resour Manag 27:2353–2368. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0291-6.
Pfannerstill M, Guse B, Fohrer N (2014) Smart low flow signature metrics for an improved overall performance evaluation of hydrological models. J Hydrol 510:447–458
Rostamian R, Jaleh A, Afyuni M, Mousavi SF, Heidarpour M, Jalalian A, Abbaspour KC (2008) Application of a SWAT model for estimating runoff and sediment in two mountainous basins in central Iran. Hydrol Sci J 53:977–988
Santhi C, Arnold JG, Williams JR, Dugas WA, Srinivasan R, Hauck LM (2001) Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J Am Water Res Assoc 37(5):1169–1188
Schuol J, Abbaspour KC, Srinivasan R, Yang H (2008a) Modelling blue and green water availability in Africa at monthly intervals and subbasin level. Water Resources Res 44:W07406. doi:10.1029/2007WR006609
Schuol J, Abbaspour KC, Sarinivasan R, Yang H (2008b) Estimation of freshwater availability in the West African Subcontinent using the SWAT hydrologic model. J Hydrol 352(1–2):30–49.
Setegn G, Srinivasan R, Melesse AM, Dargahi B (2009) SWAT model application and prediction uncertainty analysis in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. 24:357–367. DOI:10.1002/hyp.7457.
Singh V, Bankar N, Salunkhe S, Bera AK, Sharma JR (2013) Hydrological stream flow modelling on Tungabhadra catchment: parameterization and uncertainty analysis using SWAT CUP. Curr Sci, VOL. 104, NO. 9
Sorooshian S (1983) Surface water hydrology: Online estimation. Rev Geophys 21(3):706–721
Spruill C, Workman S, Taraba J (2000) Simulation of daily and monthly stream discharge from small watersheds using the SWAT model. Trans ASAE 43:1431–1439.
Tolson BA, Shoemaker CA (2007) Cannonsville reservoir watershed SWAT2000 model development, calibration and validation. J Hydrol 337:68–86
Van Griensven A, Meixner T (2006) Methods to quantify and identify the sources of uncertainty for river basin water quality models. Water Sci Technol 53(1):51–59
Van Liew MW, Arnold JG, Garbrecht JD (2003) Hydrologic simulation on agricultural watersheds: Choosing between two models. Trans. ASAE 46(6): 1539–1551.
Van Griensven A, Meixner T, Srinivasan R, Grunwals S (2008) Fit-for-purpose analysis of uncertainty using split-sampling evaluations. Hydrol Sci J 53(5):1090–1103
Vrugt JA, Gupta HV, Bouten W, Sorooshian S (2003) A shuffled complex evolution metropolis algorithm for optimization and uncertainty assessment of hydrologic model parameters. Water Resources Res 39(8):1201. Doi:10.1029/2002WR001642
Wagener T, Gupta HV (2005) Model identification for hydrological forecasting under uncertainty. Stoch Env Res Risk A 19:378–387
Wagener T, Sivapalan M, McDonnell JJ, Hooper R, Lakshmi V, Liang X, Kumar P (2004) Predictions in ungauged basins (PUB): a catalyst for multi-disciplinary hydrology. Eos, Trans. AGU. 85(44): 451–452
Yang J, Reichert P, Abbaspour KC, Xia J, Yang H (2008) Comparing uncertainty analysis techniques for a SWAT application to the Chaohe Basin in China. J Hydrol 358:1–23
Yesuf HM, Melesse AM, Zeleke G, Alamirew T (2016) Streamflow prediction uncertainty analysis and verification of SWAT model in a tropical watershed. Environ Earth Sci 75:806.DOI:10.1007/s12665-016-5636-z.
Zeckoski RW, Smolen MD, Moriasi DN, Frankenberger JR, Feyereisen GW (2015) Hydrologic and water quality terminology as applied to modeling. Trans ASABE, 58(6), 1619–1635.
Zhang X, Srinivasan R, Bosch D (2009) Calibration and uncertainty analysis of the SWAT model using Genetic Algorithms and Bayesian Model Averaging. J Hydrol 374(2009):307–317
Zhang X, Srinivasan R, Liew MV (2010) On the use of multi-algorithm, genetically adaptive multi-objective method for multi-site calibration of the SWAT model. Hydrol Process 24:955–969
Zheng Y, Keller AA (2007) Uncertainty assessment in watershed-scale water quality modeling and management: 1. Framework and application of generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) approach. Water Resour Res 43: doi:10.1029/2006WR005345.
Zheng C, Hill MC, Cao G, Ma R (2012) MT3DMS: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE, 55(4), 1549–1559.
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is thankful to University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India for sponsoring major research project (MRP) [grant no. 42–74/2013 (SR)] to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Singh, S.K., Srivastava, P.K. et al. SWAT Model calibration and uncertainty analysis for streamflow prediction of the Tons River Basin, India, using Sequential Uncertainty Fitting (SUFI-2) algorithm. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 3, 30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0306-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0306-z