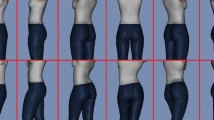
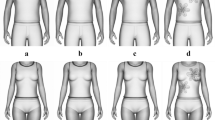
Abstract
Shoulder to hip ratio (SHR) is a sexually dimorphic trait in humans, yet no previous study has investigated the gazing behavior and perceived physical attractiveness of men and women in relation to men and women’s SHRs. Men and women are attentive to men’s upper body and consider higher SHRs as cues to masculinity, strength, and formidability. Moreover, while women’s shoulder width varies from one individual to another, to our knowledge no previous study has investigated perceived attractiveness and eye movement in relation to women’s SHR. Therefore, in the current study, we investigated attractiveness ratings and eye movements of both men and women to front- and back-posed male and female stimuli varying in SHR. Our results showed that men prefer more masculine ratios for men and less masculine ratios for women. However, the results also showed that women preferred an intermediate SHR for both men and women in the back view while their preference in the front view is not influenced by SHR. Eye movements showed that men viewed the chest region of other men in the front and back views of stimuli, and they had longer dwell time on chests of male stimuli with higher SHRs, while no significant difference was found for dwell time on chests of female stimuli varying in SHR. Also, no differences were observed for female participants in dwell time, for either chest regions of SHRs of male stimuli or for the chests of female stimuli. Altogether, the results of this study suggest that men more than women are attentive to variations in SHRs.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper.
Change history
11 July 2019
The original version of this article contained a mistake.
References
Andrews, T. M., Lukaszewski, A. W., Simmons, Z. L., & Bleske-Rechek, A. (2017). Cue-based estimates of reproductive value explain women’s body attractiveness. Evolution and Human Behavior, 38, 461–467.
Barbaro, N., Mogilski, J. K., Shackelford, T. K., & Pham, M. N. (2018). Men’s interest in allying with a previous combatant for future group combat. Human Nature, 29, 328–336.
Barber, N. (1995). The evolutionary psychology of physical attractiveness: sexual selection and human morphology. Ethology and Sociobiology, 16, 395–424.
Bovet, J., Lao, J., Bartholomée, O., Caldara, R., & Raymond, M. (2016). Mapping female bodily features of attractiveness. Scientific Reports, 6, 18551.
Braun, M. F., & Bryan, A. (2006). Female waist-to-hip and male waist-to-shoulder ratios as determinants of romantic partner desirability. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 23(5), 805–819.
Brooks, R. C., Shelly, J. P., Jordan, L. A., & Dixson, B. J. (2015). The multivariate evolution of female body shape in an artificial digital ecosystem. Evolution and Human Behavior, 36(5), 351–358.
Butovskaya, M., Sorokowska, A., Karwowski, M., Sabiniewicz, A., Fedenok, J., Dronova, D., Negasheva, M., Selivanova, E., & Sorokowski, P. (2017). Waist-to-hip ratio, body-mass index, age and number of children in seven traditional societies. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1622.
Buunk, B. P., & Dijkstra, P. (2005). A narrow waist versus broad shoulders: sex and age differences in the jealousy-evoking characteristics of a rival’s body build. Personality and Individual Differences, 39(2), 379–389.
Dixson, A. F., Halliwell, G., East, R., Wignarajah, P., & Anderson, M. J. (2003). Masculine somatotype and hirsuteness as determinants of sexual attractiveness to women. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 32(1), 29–39.
Dixson, B. J., Dixson, A. F., Li, B., & Anderson, M. J. (2007a). Studies of human physique and sexual attractiveness: sexual preferences of men and women in China. American Journal of Human Biology, 19(1), 88–95.
Dixson, B. J., Dixson, A. F., Morgan, B., & Anderson, M. J. (2007b). Human physique and sexual attractiveness: sexual preferences of men and women in Bakossiland, Cameroon. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 36(3), 369–375.
Dixson, B. J., Dixson, A. F., Bishop, P. J., & Parish, A. (2010a). Human physique and sexual attractiveness in men and women: a New Zealand–US comparative study. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 39(3), 798–806.
Dixson, B. J., Grimshaw, G. M., Linklater, W. L., & Dixson, A. F. (2010b). Watching the hourglass. Human Nature, 21(4), 355–370.
Dixson, B. J., Grimshaw, G. M., Linklater, W. L., & Dixson, A. F. (2011). Eye-tracking of men’s preferences for waist-to-hip ratio and breast size of women. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 40(1), 43–50.
Dixson, B. J., Grimshaw, G. M., Ormsby, D. K., & Dixson, A. F. (2014). Eye-tracking women’s preferences for men’s somatotypes. Evolution and Human Behavior, 35(2), 73–79.
Doyle, J. F., & Pazhoohi, F. (2012). Natural and augmented breasts: is what is not natural most attractive? Human Ethology Bulletin, 27, 4014.
Dural, S., Cetinkaya, H., & Gulbetekin, E. (2008). The role of the waist to hip ratio in evaluation of female physical attractiveness: eye-tracker data. Turkish Journal of Psychology, 23, 75–91.
Durkee, P. K., Goetz, A. T., & Lukaszewski, A. W. (2018). Formidability assessment mechanisms: examining their speed and automaticity. Evolution and Human Behavior, 39(2), 170-178.
Durkee, P. K., Polo, P., Muñoz-Reyes, J. A., Rodríguez-Ruiz, C., Losada-Pérez, M., Fernández-Martínez, A. B., Turiégano, E., Buss, D. M. & Pita, M. (2019). Men’s bodily attractiveness: Muscles as fitness indicators. Evolutionary Psychology, 17(2), 1474704919852918.
Fan, J., Dai, W., Liu, F., & Wu, J. (2005). Visual perception of male body attractiveness. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 272(1560), 219–226.
Feierman, J. R. (2010). Pedophilia: its relationship to the homosexualities and the Roman Catholic Church, Part I. Antonianum, LXXXV, 451–177.
Frederick, D. A., & Haselton, M. G. (2007). Why is muscularity sexy? Tests of the fitness indicator hypothesis. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 33(8), 1167–1183.
Frederick, D. A., Buchanan, G. M., Sadehgi-Azar, L., Peplau, L. A., Haselton, M. G., Berezovskaya, A., & Lipinski, R. E. (2007). Desiring the muscular ideal: men’s body satisfaction in the United States, Ukraine, and Ghana. Psychology of Men & Masculinity, 8(2), 103–117.
Furnham, A., & Nordling, R. (1998). Cross-cultural differences in preferences for specific male and female body shapes. Personality and Individual Differences, 25(4), 635–648.
Furnham, A., & Swami, V. (2007). Perception of female buttocks and breast size in profile. Social Behavior and Personality an International Journal, 35, 1–8.
Garza, R., & Byrd-Craven, J. (2019). Fertility status in visual processing of men’s attractiveness. Evolutionary Psychological Science, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40806-019-00190-4
Garza, R., Heredia, R. R., & Cieślicka, A. B. (2016). Male and female perception of physical attractiveness: an eye movement study. Evolutionary Psychology, 14(1), 1474704916631614.
Garza, R., Heredia, R. R., & Cieślicka, A. B. (2017). An eye tracking examination of men’s attractiveness by conceptive risk women. Evolutionary Psychology, 15(1), 1474704917690741.
Grammer, K., Fink, B., Møller, A. P., & Thornhill, R. (2003). Darwinian aesthetics: sexual selection and the biology of beauty. Biological Reviews, 78(3), 385–407.
Grillot, R. L., Simmons, Z. L., Lukaszewski, A. W., & Roney, J. R. (2014). Hormonal and morphological predictors of women’s body attractiveness. Evolution and Human Behavior, 35, 176–183.
Havlíček, J., Třebický, V., Valentova, J. V., Kleisner, K., Akoko, R. M., Fialová, J., et al. (2017). Men’s preferences for women’s breast size and shape in four cultures. Evolution and Human Behavior, 38, 217–226.
Hewig, J., Trippe, R. H., Hecht, H., Straube, T., & Miltner, W. H. (2008). Gender differences for specific body regions when looking at men and women. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 32, 67–78.
Hill, A. K., Hunt, J., Welling, L. L., Cárdenas, R. A., Rotella, M. A., Wheatley, J. R., et al. (2013). Quantifying the strength and form of sexual selection on men’s traits. Evolution and Human Behavior, 34(5), 334–341.
Hönekopp, J., Rudolph, U., Beier, L., Liebert, A., & Müller, C. (2007). Physical attractiveness of face and body as indicators of physical fitness in men. Evolution and Human Behavior, 28(2), 106–111.
Horvath, T. (1981). Physical attractiveness: the influence of selected torso parameters. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 10(1), 21–24.
Hughes, S. M., & Gallup, G. G. (2003). Sex differences in morphological predictors of sexual behavior: shoulder to hip and waist to hip ratios. Evolution and Human Behavior, 24(3), 173–178.
Jünger, J., Kordsmeyer, T. L., Gerlach, T. M., & Penke, L. (2018). Fertile women evaluate male bodies as more attractive, regardless of masculinity. Evolution and Human Behavior, 39(4), 412–423.
Kasperk, C., Helmboldt, A., Börcsök, I., Heuthe, S., Cloos, O., Niethard, F., & Ziegler, R. (1997). Skeletal site-dependent expression of the androgen receptor in human osteoblastic cell populations. Calcified Tissue International, 61(6), 464–473.
Kordsmeyer, T. L., Hunt, J., Puts, D. A., Ostner, J., & Penke, L. (2018). The relative importance of intra-and intersexual selection on human male sexually dimorphic traits. Evolution and Human Behavior, 39(4), 424–436.
Lassek, W. D., & Gaulin, S. J. C. (2009). Costs and benefits of fat-free muscle mass in men: relationships to mating success, dietary requirements, and native immunity. Evolution and Human Behavior, 30, 322–328.
Lassek, W. D., & Gaulin, S. J. (2016). What makes Jessica Rabbit sexy? Contrasting roles of waist and hip size. Evolutionary Psychology, 14(2), 1474704916643459.
Marcinkowska, U. M., Kozlov, M. V., Cai, H., Contreras-Garduno, J., Dixson, B. J., Oana, G. A., Kaminski, G., Li, N. P., Lyons, M. T., Onyishi, I. E., Prasai, K., Pazhoohi, F., Prokop, P., Rosales Cardozo, S. L., Sydney, N., Yong, J. C., & Rantala, M. J. (2014). Cross-cultural variation in men’s preference for sexual dimorphism in women’s faces. Biology Letters, 10(4), 20130850.
Marcinkowska, U. M., Rantala, M. J., Lee, A. J., Kozlov, M. V., Aavik, T., Cai, H., Contreras-Garduño, J., David, O. A., Kaminski, G., Li, N. P., Onyishi, I. E., Prasai, K., Pazhoohi, F., Prokop, P., Cardozo, S. L. R., Sydney, N., Taniguchi, H., Krams, I., & Dixson, B. J. W. (2019). Women’s preferences for men’s facial masculinity are strongest under favorable ecological conditions. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 3387.
Massar, K., & Buunk, A. P. (2009). Rivals in the mind’s eye: jealous responses after subliminal exposure to body shapes. Personality and Individual Differences, 46(2), 129–134.
Mautz, B. S., Wong, B. B., Peters, R. A., & Jennions, M. D. (2013). Penis size interacts with body shape and height to influence male attractiveness. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(17), 6925–6930.
Pazhoohi, F., & Liddle, J. R. (2012). Identifying feminine and masculine ranges for waist-to-hip ratio. Journal of Social, Evolutionary, and Cultural Psychology, 6(2), 227–232.
Pazhoohi, F., Hosseinchari, M., & Doyle, J. F. (2012). Iranian men’s waist-to-hip ratios, shoulder-to-hip ratios, body esteem and self-efficacy. Journal of Evolutionary Psychology, 10(2), 61–67.
Pazhoohi, F., Silva, C., Lamas, J., Mouta, S., Santos, J., & Arantes, J. (2018). The effect of height and shoulder-to-hip ratio on interpersonal space in virtual environment. Psychological Research, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-017-0968-1
Price, E. M., Kang, J., Dunn, J., & Hopkins, S. (2011). Muscularity and attractiveness as predictors of human egalitarianism. Personality and Individual Differences., 50, 636–640.
Price, M. E., Sheehy-Skeffington, J., Sidnaius, J., & Pound, N. (2017). Is sociopolitical egalitarinsim related to bodily and facial formidability in men? Evolution and Human Behavior, 38, 626–634.
Sell, A., Lukazsewski, A. W., & Townsley, M. (2017). Cues of upper body strength account for most of the variance in men’s bodily attractiveness. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 284, 1–8.
Singh, D. (1993) Adaptive significance of female physical attractiveness: Role of waist-to-hip ratio. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 65(2):293-307.
Singh, D. (1994). Is thin really beautiful and good? Relationship between waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and female attractiveness. Personality & Individual Differences, 16(1), 123-132.
Singh, D., & Young, R. K. (1995). Body weight, waist-to-hip ratio, breasts, and hips: Role in judgments of female attractiveness and desirability for relationships. Ethology & Sociobiology, 16(6), 483-507.
Skuballa, I. T., Fortunski, C., & Renkl, A. (2015). An eye movement pre-training fosters the comprehension of processes and functions in technical systems. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 598.
Suschinsky, K. D., Elias, L. J., & Krupp, D. B. (2007). Looking for Ms. Right: Allocating attention to facilitate mate choice decisions. Evolutionary Psychology, 5(2), 147470490700500214.
Tovée, M. J., Maisey, D. S., Vale, E. L., & Cornelissen, P. L. (1999). Characteristics of male attractiveness for women. The Lancet, 353(9163), 1500.
Wenzlaff, F., Briken, P., & Dekker, A. (2016). Video-based eye tracking in sex research: a systematic literature review. The Journal of Sex Research, 53(8), 1008–1019.
Funding
This study was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology and the Portuguese Ministry of Science, Technology and Higher Education through national funds and co-financed by FEDER through COMPETE2020 under the PT2020 Partnership Agreement (POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007653). FP receives funding from FCT Portugal through grant PD/BD/114366/2016. AM receives funding from FCT Portugal through grants PTDC/DTP-EPI/0412/2012 and PEST-C/FIS/UI607/2011. JA receives funding from FCT Portugal through grants PTDC/MHC-PCN/4589/2012 and IF/01298/2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pazhoohi, F., Garza, R., Doyle, J.F. et al. Sex Differences for Preferences of Shoulder to Hip Ratio in Men and Women: an Eye Tracking Study. Evolutionary Psychological Science 5, 405–415 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40806-019-00198-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40806-019-00198-w