Abstract
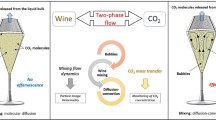
This study investigated the influence of the number of nucleation sites on the evolution of the dissolved CO2 concentration of beer contained in an etched glass comprising 0 to 70 etchings. Four identically shaped glasses were studied, three etched and one non-etched. We followed the temporal evolution of the liquid (i.e., beer) and gaseous (i.e., CO2) phases of the beer for each of them. The gaseous phase is monitored by measuring the evolution of the dissolved CO2 concentration in the beer once poured into the glass. Particle image velocimetry (PIV) techniques are used to quantify the mixing dynamics of the beer during the tasting. The results show that the CO2 concentration decreases approximately 3.7 times faster in the glass with 70 etchings than in the unetched glass. This study suggests a close link between the number of nucleation sites and the release of dissolved CO2 by different mechanisms: bubble bursting, molecular diffusion, and mass convection-diffusion, the latter being increased by liquid mixing mechanisms. On the one hand, too many bubbles will bother the consumer by causing a chemical sting and will quickly deplete the beer in dissolved gas. On the other hand, too few bubbles will not allow conveying the aromas to the surface and the consumer will judge the beer as too bland and not visually flattering, hence the need to find a compromise.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bamforth C (2000) J Inst Brew 106:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2050-0416.2000.tb00062.x
Prins JT, Van Marle (1999) Foam formation in beer: some physics behind it. In: Proc Eur Brew Conv Congr Foam Symp. Amsterdam, Verlag Hans Carl, Getränke-Fachverlag: Nürnberg, pp. 26–36
Donadini G, Fumi MD, de Faveri MD (2011) J Inst Brew 117:523–533. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2050-0416.2011.tb00500.x
Ono M, Hashimoto S, Kakudo Y, Nagami K, Kumada J (1983) J Am Soc Brew Chem 41:19–23. https://doi.org/10.1094/ASBCJ-41-0019
Liger-Belair G (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:2788–2802. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf048259e
Clark R, Linforth R, Bealin-Kelly F, Hort J (2011) J Inst Brew 117:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2050-0416.2011.tb00446.x
Meilgaard MC (1982) J Agric Food Chem 30:1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00114a002
Liger-Belair G, Conreux A, Villaume S, Cilindre C (2013) Food Res Int 54:516–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.07.048
Tominaga T, Guimbertau G, Dubourdieu D (2003) J Agric Food Chem 51:1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020755k
Shafer NE, Zare RN (1991) Phys Today 44:48–52. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.881294
Polidori G, Beaumont F, Jeandet P, Liger-Belair G (2009) J Vis 12:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181866
Beaumont F, Popa C, Liger-Belair G, Polidori G (2012) JFV. 19 doi:https://doi.org/10.1615/JFlowVis ImageProc.2013005152
Beaumont F, Liger-Belair G, Polidori G (2015) Exp Fluids 56:170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2040-5
Beaumont F, Bogard F, Murer S, Polidori G (2022) Dynamics. 2, 326–335 https://doi.org/10.3390/dynamics2040018
Chandrashekar J, Yarmolinsky D, Von Buchholtz L, Oka Y, Sly W, Ryba NJ et al (2009) Science 326:443–445. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.11746
Dunkel T, Hofmann (2010) Angew Chem Int Ed 49:2975–2977. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200906978
Liger-Belair G et al (2008) Anal Chim Acta 621:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.10.054
Padet J (2005) in Convection thermique et massique: Principes généraux (Techniques de l’Ingénieur, p. 23
Perret DA, Bonhommeau G, Liger-Belair T, Cours A, Alijah (2014) J Phys Chem B 118:1839–1847. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp410998f
Beaumont F, Cilindre C, Abdi E, Maman M, Polidori G (2019) Curr Res Nutr Food Sci J 7:227–235. https://doi.org/10.12944/CRNFSJ.7.1.22
Liger-Belair G, Cilindre C (2021) ACS Omega 6:9672–9679. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00256
Beaumont F, Liger-Belair G, Bailly Y, Polidori G (2016) Exp Fluids 57:85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-016-2180-2
Polidori G, Beaumont F, Jeandet P, Liger-Belair G (2008) J Vis 11:184–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03181703
Buch M, Rakib M, Stambouli (2008) in Transfert de matière - Cinétique du transfert de matière entre deux phases, (Ed. Techniques Ingénieur,
Brogioli D, Vailati A (2000) Phys Rev E 63:012105. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.63.012105
Beaumont F, Liger-Belair G, Polidori G (2019) Acta Mech 230:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2311-3
Beaumont F, Liger-Belair G, Polidori G (2016) J Food Eng 188:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.05.012
Saint-Eve et al (2010) Food Quality and Preference. 21, 1026–1033 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2010.05.021
Pozo-Bayón M, Santos M, Martín-Álvarez PJ, Reineccius G (2009) Flavour Fragr J 24:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.1934
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with Ethical Standards
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Beaumont, F., Bogard, F., Murer, S. et al. New Insights on the Effect of Forced Laser-Etched Nucleation on the Unsteady Evolution of Two-Phase Flow in a Beer Glass. Exp Tech 48, 31–39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-023-00644-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-023-00644-2