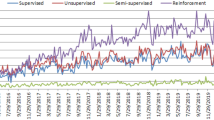
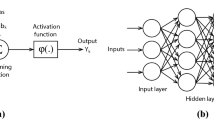
Abstract
In several earlier papers, the author defined and detailed the concept of a servgood, which can be thought of as a physical good or product enveloped by a services-oriented layer that makes the good smarter or more adaptable and customizable for a particular use. Adding another layer of physical sensors could then enhance its smartness and intelligence, especially if it were to be connected with other servgoods—thus, constituting an Internet of Things (IoT) or servgoods. More importantly, real-time decision making is central to the Internet of Things; it is about decision informatics and embraces the advanced technologies of sensing (i.e., Big Data), processing (i.e., real-time analytics), reacting (i.e., real-time decision-making), and learning (i.e., deep learning). Indeed, real-time decision making (RTDM) is becoming an integral aspect of IoT and artificial intelligence (AI), including its improving abilities at voice and video recognition, speech and predictive synthesis, and language and social-media understanding. These three key and mutually supportive technologies—IoT, RTDM, and AI—are considered herein, including their progress to date.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson RD (2016) It’s going to kill us and other myths about the future of AI. Information Technology and Innovation Foundation
Bifet A (2013) Mining big data in real time. Informatica 37:15–20
Carr N (2010) The shallows: what the internet is doing to our brains. Norton, New York
Castro D, New J (2016) The promise of artificial intelligence. Center for Data Innovation
Dreyfus H (1972) What computers can’t do. MIT Press, New York
Hattori H, Nakajima Y, Ishida T (2011) Learning from humans: agent modeling with individual human behaviors. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern A 41(1):1–9
Hendler J, Mulvehill AM (2016) Social machines: the coming collision of artificial intelligence, social networking, and humanity. Apress, New York
Lavalle S, Lesser E, Shockley R, Hopkins MS, Kruschwitz N (2011) Big data, analytics and the path from insights to value. MIT Sloan Manag Rev 52(2):21–31
Manyika J, Chui M, Bughin J, Brown B, Dobbs R, Roxbury C, Byers AH (2011) Big data: the next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. McKinsey Global Institute, New York
Maxim Integrated (2015) The bright new outlook for LEDs: new drivers. New Possibilities. Commercial Application Note
MIT (2016) The 50 smartest companies in 2016. MIT Technol Rev 117(2):27–46
McCarthy J, Minsky ML, Rochester N, Shannon CE (1955) A proposal for the Dartmouth research project on artificial intelligence. Republished in 2006. AI Mag 27(4):11–14
Minsky M (1960) Steps toward artificial intelligence. Republished in 2006, AI Magazine 27(4):109 ff
Mlodinow L (2012) Subliminal: how your unconscious mind rules your behavior. Pantheon Books, New York
Perry T (2015) Temporary tattoos can replace today’s biomedical sensors. IEEE Spectr 34–39:84–85
Porter ME, Heppelmann JE (2014) How smart, connected products are transforming competition. Harvard Rev 102(1):1–23
Ross PE (2015) Diabetes has a new enemy: robo-pancreas. IEEE Spectr 40–43:87
Siegel E (2013) Predictive analytics: the power to predict who will click, buy, lie, or die. Wiley, New York
Silver D, Huang A, Maddison CJ, Guez A, Sifre L, Van den Driessche G, Schrittwieser J, Antonoglou I, Panneershelvam V, Lanctot M, Dieleman S, Grewe D, Nham J, Kalchbrenner N, Sutskever I, Lillicrap T, Leach M, Kavukcuoglu K, Graepel T, Hassabis D (2016) Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529:484–489
Taleb NN (2010) The black swan, 2nd edn. Random House Inc, New York
Tien JM (2003) Toward a decision informatics paradigm: a real-time information based approach to decision making. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C 33(1):102–113
Tien JM (2011) Manufacturing and services: from mass production to mass customization. J Syst Sci Syst Eng 20(2):129–154
Tien JM (2012) The next industrial revolution: integrated services and goods. J Syst Sci Syst Eng 21(3):257–296
Tien JM (2014) Overview of big data: a US perspective. Bridge 44(4):12–19
Tien JM (2015) Internet of connected servgoods: considerations, consequences and concerns. J Syst Eng 24(2):130–167
Tien JM (2017) The sputnik of servgoods: autonomous vehicles. J Syst Eng 26(2):10–38
Tien JM, Berg D (2003) A case for service systems engineering. J Syst Eng 12(1):13–39
Tien JM, Cahn MF (1981) An evaluation of the wilmington management of demand program. National Institute of Justice, Washington
Turing A (1950) Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind 50:433–460
Zikopoulos PC, Eaton C, DeRoos D, Deutsch T, Lapis G (2012) Understanding big data: analytics for enterprise class hadoop and streaming data. The McGraw-Hill Companies, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tien, J.M. Internet of Things, Real-Time Decision Making, and Artificial Intelligence. Ann. Data. Sci. 4, 149–178 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-017-0112-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-017-0112-5