Abstract
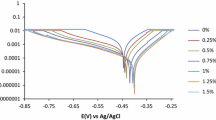
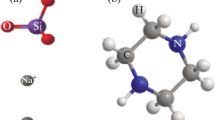
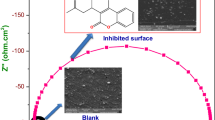
Analysis of the synergistic effect of sodium molybdenum oxide and vanillin on the corrosion inhibition of high carbon steel and 3CR12 ferritic stainless steel in 2M HCl solution was done through coupon measurement, potentiodynamic polarization test and IR spectroscopy. Results show the admixture compound inhibited the corrosion of both steels, but performed more effectively on 3CR12 ferritic steel with average inhibition efficiency above 90% while the average inhibition efficiency of the compound on carbon steel was around 75%. Polarization studies showed mixed inhibiting properties of the compound on the carbon steel and anodic corrosion inhibition on the ferritic steel. The compound adsorbed over the entire carbon steel surface, but selectively precipitates at anodic sites on the stainless steel surface due to the passivation characteristics of the steel. Chemisorption mechanism was determined from thermodynamic calculations to be the mode of inhibition on the steels through the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Infrared spectroscopy exposed the presence of the functional groups and bonds such as alcohols, phenols, primary and secondary amines and amides within the compound responsible for corrosion inhibition.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia-Arriaga V, Alvarez-Ramirez J, Amaya Sosa ME (2010) H2S and O2 influence on the corrosion of carbon steel immersed in a solution containing 3M diethanolamine. Corros Sci 52(7):2268–2279. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2010.03.016
Ramesh S, Rajeswari S, Maruthamuthu S (2003) Effect of inhibitors and biocide on corrosion control of mild steel in natural aqueous environment. Mater Lett 57(29):4547–4554. doi:10.1016/S0167-577X(03),00360-4
Jackson J, Finsgar M (2014) Application of corrosion inhibitors for steels in acidic media for the oil and gas industry: a review. Corros Sci 86:17–41. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2014.04.044
Bockris JOM, Yang B (1991) Mechanism of corrosion inhibition of iron in acid solution by acetylenic alcohols. J Electrochem Soc 138:2237–2252
Kertit S, Elkholy A, Aride J, Srhiri A, Ben Bachir A, Etman M (1989) Chemical and electrochemical inhibition studies of corrosion and hydrogen surface embrittlement. I. Fe0.78B0.13Si0.09 amorphous alloy in molar HCl. J Appl Electrochem 19(1):83–89. doi:10.1007/BF01039394
Edrah S, Hasan SK (2010) Studies on thiourea derivatives as corrosion inhibitor for aluminum in sodium hydroxide Solution. J Appl Sci Res 6(8):1045–1049
Bazzi L, Salghi R, Bouchtart A, El Alami Z, Kertit S (2002) The inhibition effect of inorganic compounds on the corrosion of the 3003 aluminium alloy in the presence of sodium chloride. Rev Met Paris 99(2):189–197. doi:10.1051/metal:2002192
Atmani F, Lahem D, Poelman M, Buess-Herman C, Olivier MG (2013) Mild steel corrosion in chloride environment: effect of surface preparation and influence of inorganic inhibitors. Corros Eng, Sci Technol 48(1):9–18. doi:10.1179/1743278212Y.0000000037
Yufei K, Fang C, Ao X (2013) Molybdate-based corrosion inhibitor system for carbon steel in sea ice melt-water. Desalin Water Treat 51(16–18):3133–3137. doi:10.1080/19443994.2012.749006
Lizlovs EA (1976) Molybdates as corrosion inhibitors in the presence of chlorides. Corrosion 32(7):263–266. doi:10.5006/0010-9312-32.7.263
Lia X, Dengb S, Fua H (2010) Adsorption and inhibition effect of vanillin on cold rolled steel in 3.0M H3PO4. Prog Org Coat 67(4):420–426. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2009.12.006
Loto RT (2016) Electrochemical analysis of the corrosion inhibition properties of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde on low carbon steel in dilute acid media. Cogent Eng 3:1242107. doi:10.1080/23311916.2016.1242107
Pryor MJ, Cohen M (1953) The inhibition of the corrosion of iron by some anodic inhibitors. J Electrochem Soc 100(5):203–215. doi:10.1149/1.2781106
Emregüla KC, Hayvalıb M (2004) Studies on the effect of vanillin and protocatechualdehyde on the corrosion of steel in hydrochloric acid. Mater Chem Phys 83(2–3):209–216
Standard practice for preparing, cleaning, and evaluating corrosion test specimens. https://www.astm.org/Standards/G1.htm. Accessed 12 Jan 2017
Standard practice for laboratory immersion corrosion testing of metals. https://www.astm.org/DATABASE.CART/HISTORICAL/G31-72R04.htm. Accessed 12 Jan 2017
Venkatesan P, Anand B, Matheswaran P (2009) Influence of formazan derivatives on corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Eur J Chem 6(S1):S438–S444. doi:10.1155/2009/507383
Abbasova VM, Abd El-Lateefa HM, Aliyevaa LI, Qasimova EE, Ismayilova IT, Khalaf MM (2013) A study of the corrosion inhibition of mild steel C1018 in CO2-saturated brine using some novel surfactants based on corn oil. Egypt J Pet 4(22):451–470. doi:10.1016/j.ejpe.2013.11.002
Sethi T, Chaturvedi A, Mathur RK (2007) Corrosion inhibitory effects of some Schiff’s bases on mild steel in acid media. J Chil Chem Soc 52(3):1206–1213. doi:10.4067/S0717-97072007000300003
Standard Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polarization Resistance Measurements. https://www.astm.org/Standards/G59.htm. Accessed 12 Jan 2017
Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements. https://www.astm.org/Standards/G102.htm. Accessed 12 Jan 2017
Ahmad K (2006) Principles of corrosion engineering and corrosion control. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK
Choi Y, Nesic S, Ling S (2011) Effect of H2S on the CO2 corrosion of carbon steel in acidic solutions. Electrochim Acta 56(4):1752–1760. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.08.049
Okamoto G, Shibata T, Sato N (1969) Reports of Asahi glass foundation for industrial technology, vol 15. Asahi Glass Foundation for Industrial Technology, Tokyo, pp 207–230
Thompson SC. Molybdates: an alternative to hexavalent chromates in corrosion prevention and control. http://infohouse.p2ric.org/ref/29/28424.pdf. Accessed 14 January 2017
Trabanelli G, Carassiti V (1970) Advances in corrosion science and technology, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, p 147
Desimonea MP, Grundmeier G, Gordilloc G, Simison SN (2011) Amphiphilic amido-amine as an effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel exposed to CO2 saturated solution: polarization, EIS and PM-IRRAS studies. Electrochim Acta 56(8):2990–2998. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.01.009
Bockris JOM, Swinkels DAJ (1964) Adsorption of n-decylamine on solid metal electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 111(6):736–743. doi:10.1149/1.2426222
Li X, Dengb S, Fua H, Lia T (2009) Adsorption and inhibition effect of 6-benzylaminopurine on cold rolled steel in 1.0M HCl. Electrochim Acta 54(16):4089–4098. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.02.084
Sahin M, Bilgic S, Yilmaz H (2002) The inhibition effects of some cyclic nitrogen compounds on the corrosion of the steel in NaCl mediums. Appl Surf Sci 195(1–4):1–7. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(01),00783-8
Bentley AJ, Earwakera LG, Farr JPG, Saremi M, Seeney AM (1986) Molybdates in aqueous corrosion inhibition III. Effects of molybdate in the anodic filming of steel. Polyhedron 5(1–2):547–550. doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(00),84962-1
Sakashita M, Sato N (1977) The effect of molybdate anion on the ion-selectivity of hydrous ferric oxide films in chloride solutions. Corros Sci 17(6):473–486. doi:10.1016/0010-938X(77),90003-8
Susai RS, Mary R, Noreen A, Ramaraj R (2002) Synergistic corrosion inhibition by the sodium dodecylsulphate–Zn2+ system. Corros Sci 44(10):2243–2252. doi:10.1016/S0010-938X(02),00052-5
Sahin M, Bilgiç S, Yılmaz H (2002) The inhibition effects of some cyclic nitrogen compounds on the corrosion of the steel in NaCl mediums. Appl Surf Sci 195(104):1–7. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(01),00783-8
Roque JM, Pandiyan T, Cruz J, Garcia-Ochoa E (2008) DFT and electrochemical studies of tris(benzimidazole-2-ylmethyl)amine as an efficient corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel surface. Corros Sci 50(3):614–624. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2007.11.012
Benali O, Larabi L, Traisnel M, Gengembre L, Harek Y (2007) Electrochemical, theoretical and XPS studies of 2-mercapto-1-methylimidazole adsorption on carbon steel in 1M HClO4. Appl Surf Sci 253(14):6130–6139. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.01.075
Kellou-Kerkouche F, Benchettara A, Amara S (2008) Effect of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate on the corrosion inhibition of Fe–1Ti–20C alloy in 0.5M H2SO4. Mater Chem Phys 110(1):26–33. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.01.005
Selvi JA, Rajendran S, Ganga SV, Amalraj JA, Narayanasamy B (2009) Corrosion inhibition by beet root extract. Port Electrochim Acta 27(1):1–11
Rajendran S, Paulraj J, Rengan P, Jeyasundari J, Manivannan M (2013) Corrosion resistance of 18 carat gold in artificial saliva in presence of d-glucose. Eur Chem Bull 2(6):389–392
Fushimi K, Seo M (2001) Initiation of a local breakdown of passive film on iron due to chloride ions generated by a liquid-phase ion-gun for local breakdown. J Electrochem Soc 148(11):B450–B456. doi:10.1149/1.1407832
Fushimi K, Azumi K, Seo M (2000) Use of a liquid-phase ion-gun for local breakdown of the passive film on iron. J Electrochem Soc 147(2):552–557. doi:10.1149/1.1393231
Heusler KE, Fisher L (1976) Kinetics of pit initiation at passive iron. Mater Corros 27(8):551–556. doi:10.1002/maco.19760270802
Shibata T (1990) Stochastic studies of passivity breakdown. Corros Sci 31:413–423. doi:10.1016/0010-938X(90)90140-Z
Sato N (1976) Stochastic process of chloride-pit generation in passive stainless steel. J Electrochem Soc 123(8):1197–1199. doi:10.1149/1.2133034
Aramaki K, Node Y, Nishihara H (1990) Adsorption and corrosion inhibition effect of polar organic compounds on iron in 1M HClO4 containing SH−. J Electrochem Soc 137:1354–1358. doi:10.1149/1.2086673
Ateya B, El-Anadouli BE, El-Nizamy F (1984) The adsorption of thiourea on mild steel. Corros Sci 24(6):509–515. doi:10.1016/0010-938X(84),90033-7
Dhar HP, Conway BE, Joshi KM (1973) On the form of adsorption isotherms for substitutional adsorption of molecules of different sizes. Electrochim Acta 18(11):789–798. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(73),85030-3
Abiola OK (2006) Adsorption of 3-(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidyl methyl)-4-methyl thiazolium chloride on mild steel. Corros Sci 48(10):3078–3090. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2005.12.001
Bockris JOM (1970) Modern electrochemistry, vol 2. Macdonald Ltd., London, p 772
Ateya B, El-Anadouli BE, El-Nizamy F (1984) The adsorption of thiourea on mild steel. Corros Sci 24(6):509–515
Donnely B, Downie TC, Grzeskowiak R, Hamburg HR, Short D (1978) The effect of electronic delocalization in organic groups in substituted thiocarbonyl RCSNH2 and related compounds on inhibition efficiency. Corros Sci 18(2):109–116
Benali O, Benmehdi H, Hasnaoui O, Selles C, Salghi R (2013) Green corrosion inhibitor: Inhibitive action of tannin extract of Chamaerops humilis plant for the corrosion of mild steel in 0.5M H2SO4. J Mater Environ Sci 4(1):127–138
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Covenant University for the sponsorship of the research and provision of research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loto, R.T. Comparative Analysis of the Synergistic Effect of Sodium Molybdenum Oxide and Vanillin on the Corrosion Inhibition of 3CR12 Ferritic Stainless Steel and High Carbon Steel in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid. J Bio Tribo Corros 3, 17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-017-0077-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-017-0077-0