Abstract
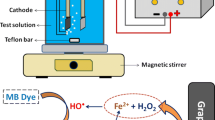
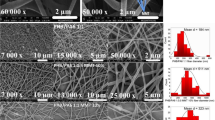
Electrospun membranes act as a support so that the iron (III) ions can be immobilized on polymer substrates to create heterogeneous Fenton catalysts with high activity, low iron leaching and improved stability without generating iron hydroxide sludge. In this study, functionalization of electrospun polyurethane (PU) is done using triethanolamine (TEA) and used as a novel support for heterogeneous Fenton catalyst. The fabricated membranes were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to analyze the effective doping of ferric chloride (FeCl3) and amine compounds properly into the fibrous electrospun PU. The porous nature and increased wettability resulted in improved adsorption and further degradation. The composite microfibrous membrane showed highly efficient degradation of 98% for chromium, 93% for methyl orange (MO) and 89% for methylene blue (MB) using the Fenton reaction reported for the first time. Experimental conditions were optimized at a pH of 3 for chromium (Cr(III)) and MO, and at a pH of 11 for MB, with an initial concentration of 10 ppm, catalyst loading of 2 g/L and temperature of 50 ℃. From the detailed kinetics study, data fitted well the first order reaction kinetics, and the membranes were successfully reused for five cycles after regeneration.
Highlights
-
Electrospun PU is functionalised with TEA and used as a novel support for heterogeneous Fenton catalysis.
-
High efficiency removal of Cr(III), MB, and MO using f-PU/FeCl3 was achieved within 180 min.
-
Electrospun f-PU membrane improved the porous nature and wettability compared to PU membrane.
-
The membranes showed good recyclability.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abdel-Mottaleb MM, Khalil A, Osman TA, Khattab A (2019) Removal of hexavalent chromium by electrospun PAN/GO decorated ZnO. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 98:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.06.025
Akhi Y, Irani M, Olya ME (2016) Simultaneous degradation of phenol and paracetamol using carbon/MWCNT/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers during photo-like-Fenton process. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 63:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.028
Alam SN, Sharma N, Kumar L (2017) Synthesis of Graphene Oxide (GO) by modified hummers method and its thermal reduction to obtain Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)*. Graphene 06(01):1–18. https://doi.org/10.4236/graphene.2017.61001
Ali AE (2003) Low spin iron (III)-Triethanolamine complex characterization and physico-chemical studies. Science Direct Working Paper No S1574-0331(04)70695-5. Available at SSRN: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2979819
Ayodamope EO (2015) Oxidative degradation of methylene blue using fenton reagent. Int J Sci Eng Res 6(11). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319629691_Oxidative_Degradation_of_Methylene_Blue_Using_Fenton_Reagent
Bagbi Y, Solanki PR, Pandey A (2019) Electrospun nanofibrous filtration membranes for heavy metals and dye removal. Nanoscale materials in water purification. Elsevier, pp 275–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813926-4.00015-X
Cai Y, Wang Q, Wei Q, You Q, Huang F, Song L (2010) Structure, thermal, and antibacterial properties of polyacrylonitrile/ferric chloride nanocomposite fibers by electrospinning. Int J Polym Anal Charact 15(2):110–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236660903525083
Chavan R, Bhat N, Parit S, Narasimharao K, Devan RS, Patil RB (2023) Development of magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst for enhanced Fenton and photo-Fenton degradation of MB and Cr (VI) photo-reduction. Mater Chem Phys 293:126964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126964
Golbaz S, Jafari AJ, Kalantari RR (2013) The study of Fenton oxidation process efficiency in the simultaneous removal of phenol, cyanide, and chromium (VI) from synthetic wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 51(28–30):5761–5767. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.760108
Habiba U, Lee JL, Joo TC, Ang BC, Afifi AM (2019) Degradation of methyl orange and congo red by using chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/TiO2 electrospun nanofibrous membrane. Int J Biol Macromol 131:821–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.132
Jafari AJ, Golbaz S, Kalantary R (2014) Treatment of hexavalent chromium by using a combined Fenton and chemical precipitation process. J Water Reuse Desalin 3(4):373–380. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2013.113
Jatoi AW (2020) Polyurethane nanofibers incorporated with ZnAg composite nanoparticles for antibacterial wound dressing applications. Comp Comm 19:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.03.004
Jiang X, Luo H, Yin Y, Zhou W (2017) Facile synthesis of MoS2/reduced graphene oxide composites for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 7(39):24149–24156. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA03531D
Khatri M, Qureshi UA, Ahmed F, Khatri Z, Kim IS (2019) Dyeing of electrospun nanofibers. In: Barhoum A, Bechelany M, Makhlouf A (eds) Handbook of nanofibers. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42789-8_55-1
Khatri M, Hussain N, El-Ghazali S (2020) Ultrasonic-assisted dyeing of silk fibroin nanofibers: an energy-efficient coloration at room temperature. Appl Nanosci 10:917–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01191-2
Laiju AR, Sivasankar T, Nidheesh PV (2014) Iron-loaded mangosteen as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the treatment of landfill leachate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(18):10900–10907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2883-y
Li CJ, Li YJ, Wang JN, Cheng J (2013) PA6@FexOy nanofibrous membrane preparation and its strong Cr (VI)-removal performance. Chem Eng J 220:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.060
Lu W, Duan C, Zhang Y, Gao K, Dai L, Shen M (2021) Cellulose-based electrospun nanofiber membrane with core-sheath structure and robust photocatalytic activity for simultaneous and efficient oil emulsions separation, dye degradation and Cr (VI) reduction. Carbohydr Polym 258:117676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117676
Luong THV, Nguyen THT, Nguyen BV, Nguyen NK, Nguyen TQC, Dang GH (2022) Efficient degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue in aqueous solution using a novel Fenton-like catalyst of CuCo-ZIFs. Green Process Synth 11(1):71–83. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2022-0006
Mohamed A, Yousef S, Ali S, Sriubas M, Varnagiris S, Tuckute S (2021) Highly efficient visible light photodegradation of Cr (VI) using electrospun mwcnts-Fe3O4@pes nanofibers. Catalysts 11(7):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11070868
Nidheesh PV (2015) Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the abatement of organic pollutants from aqueous solution: a review. RSC Adv 5:40552–40577. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA02023A
Park CH, Kang SJ, Tijing LD, Pant HR, Kim CS (2013) Inductive heating of electrospun Fe2O3/polyurethane composite mat under high-frequency magnetic field. Ceram Int 39(8):9785–9790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.05.042
Pervez M N, Stylios G K, Buonerba A, Hasan S W, Cai Y J, Zhao Y P (2021) Ultrasound-assisted Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue using electrospun nanofibrous membranes. CEST2021 1–4. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnc2021.00211
Renu AM, Agarwal M, Singh K (2023) Simultaneous removal of heavy metals and dye from wastewater: modelling and experimental study. Water Sci Technol 87(1):193–217. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.410
Saeed K, Haider S, Oh TJ, Park SY (2008) Preparation of amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile (PAN-oxime) nanofibers and their applications to metal ions adsorption. J Memb Sci 322(2):400–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.05.062
Sagitha P, Reshmi CR, Sundaran SP, Binoy A, Mishra N, Sujith A (2018) In-vitro evaluation on drug release kinetics and antibacterial activity of dextran modified polyurethane fibrous membrane. Int J Biol Macromol 126:717–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.155
Sun C, Feng X (2017) Enhancing the performance of PVDF membranes by hydrophilic surface modification via amine treatment. Sep Purif Technol 185:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.05.022
Sundaran SP, Reshmi CR, Sagitha P, Sujith A (2020) Polyurethane nanofibrous membranes decorated with reduced graphene oxide-TiO2 for photocatalytic templates in water purification. J Mater Sci 55(14):5892–5907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04414-y
Wang J, Pan K, He Q, Cao B (2013) Polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole core/shell nanofiber mat for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 244–245:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.020
Wang Q, Shao Z, Jiang J, Liu Y, Wang X, Li W, Zheng G (2022) One-step preparation of PVDF/GO electrospun nanofibrous membrane for high-efficient adsorption of Cr (VI). Nanomaterials 12(18):3115. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183115
Yan E, Cao M, Jiang J, Gao J, Jiang C, Ba X, Yang X, Zhang D (2017) A novel adsorbent based on magnetic Fe3O4 contained polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofibers for chromium (VI) removal. Solid State Sci 72:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2017.08.014
Youssef NA, Shaban SA, Ibrahim FA, Mahmoud AS (2016) Degradation of methyl orange using Fenton catalytic reaction. Egypt J Pet 25(3):317–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.07.017
Zhang Q, Fang W, Wang M, Tian T, Li G, Zhao Y (2022) Titanium dioxide nanofibers modified with iron oxide for the heterogeneous Fenton reaction. Ceram Int 48:25183–25190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.181
Zhao X, Dong Y, Cheng B, Kang W (2013) Removal of textile dyes from aqueous solution by heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction using modified PAN nanofiber Fe complex as catalyst. Int J Photoenergy. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/820165
Zhao D, Gao X, Wu C, Xie R, Feng S, Chen C (2016) Facile preparation of amino functionalized graphene oxide decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the adsorption of Cr (VI). Appl Surf Sci 384:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.022
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the “All India Council for technical education” (AICTE-8-41/FDC/RPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Parvathy Pavithran: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing and original draft preparation.
Ria Mariam John: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation
Dr. Soney. C. George: Supervision, review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Nikhi Maria Raju: Supervision, Writing, review & editing, Project administration
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pavithran, P., John, R.M., George, S.C. et al. Highly Efficient Removal of Chromium, Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Using Electrospun Polyurethane as a Support in Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction. Environ. Process. 11, 17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-024-00697-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-024-00697-4