Abstract
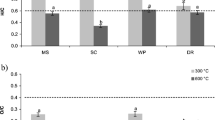
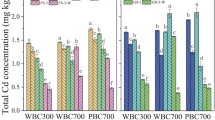
The aim of this paper was to investigate the remediation effect of polyethyleneimine-modified biochar (PBC400) on Cd-contaminated soil. Biochar was prepared from tobacco straws, and polyethyleneimine (PEI) was loaded on the biochar surface to produce PBC400. The prepared PBC400 was characterized by Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses. During the soil incubation, soil samples were collected three times at 30, 60 and 90 days, and the physical and chemical properties of soil and the contents of heavy metals were determined after natural drying. When the PBC400 addition amount was 3% and the soil was cultured for 90 days, the remediation effect was optimal. The pH increased by 0.52 units, the cation exchange capacity (CEC), available phosphorus and potassium contents increased by 30%, 43% and 39%, respectively, the available Cd content in the soil decreased by 54.36%, the weak acid extractable Cd content decreased by 35.36%, and the residual Cd content increased by 184.67%. The results indicate that PBC400 can be used to remediate heavy metal-contaminated soil and reduce the bioavailability, migration, and transformation ability of Cd.
Highlights
Biochar and polyethyleneimine-modified biochar (PBC400) improved the physical and chemical properties of soils.
PBC400 had the best remediation effect on Cd-contaminated soil.
The lowest content of available Cd was for PBC400 addition of 3% and soil cultured for 90 days.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad M, Ok YS, Rajapaksha AU et al (2016) Lead and copper immobilization in a shooting range soil using soybean stover- and pine needle-derived biochars: Chemical, microbial and spectroscopic assessments. J Hazard Mater 301:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.029
Alam I, Alam M, Khan A et al (2021) Biochar supplementation regulates growth and heavy metal accumulation in tomato grown in contaminated soils. Physiol Plant 173(1):340–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/PPL.13414
Amin A (2022) Effects of three different acidic biochars on carbon emission and quality indicators of poorly fertile soil during 8 months of incubation. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22(1):36–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42729-021-00631-9
Awad M, Liu ZZ, Skalicky M et al (2021) Fractionation of heavy metals in multi-contaminated soil treated with biochar using the sequential extraction procedure. Biomolecules 11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOM11030448
Blenis N, Hue N, Maaz TM et al (2023) Biochar production, modification, and its uses in soil remediation: a review. Sustainability 15(4):15043442. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU15043442
Bousdra T, Papadimou SG, Golia EE (2023) The use of biochar in the remediation of pb, cd, and cu-contaminated soils. The impact of biochar feedstock and preparation conditions on its remediation capacity. Land 12(2):1202038. https://doi.org/10.3390/LAND12020383
Bucatariu F, Zaharia MM, Petrila LM et al (2022) Sand/polyethyleneimine composite microparticles: eco-friendly, high selective and efficient heavy metal ion catchers. Colloids Surf A 649:129540. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2022.129540
Chandra S, Medha I, Bhattacharya J et al (2022) Effect of the co-application of Eucalyptus Wood Biochar and Chemical Fertilizer for the remediation of Multimetal (Cr, Zn, Ni, and Co) contaminated soil. Sustainability 14(12):14127266. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU14127266
Chen Z, Wang YF, Zeng J et al (2022) Chitosan/polyethyleneimine magnetic hydrogels for adsorption of heavy metal ions. Iran Polym J 31(10):1273–1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-022-01075-3
El-Nemr MA, Abdelmonem NM, Ismail IMA et al (2020) Ozone and ammonium hydroxide modification of Biochar prepared from Pisum sativum peels improves the adsorption of copper (II) from an aqueous medium. Environ Processes 7(3):973–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00455-2
Fan SX, Zuo JC, Dong HY (2020) Changes in Soil Properties and Bacterial Community composition with Biochar Amendment after six years. Agronomy 10(5):10050746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10050746
Gholami L, Rahimi G (2023) The efficiency of potato peel biochar for the adsorption and immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediation 25(2):263–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2022.2073962
Haddad SA, Lemanowicz J (2021) Benefits of corn-cob biochar to the microbial and enzymatic activity of soybean plants grown in soils contaminated with heavy metals. Energies 14(18):14185763. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14185763
Huang LK, Wang Q, Zhou QY et al (2020) Cadmium uptake from soil and transport by leafy vegetables: a meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 264:114677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114677
Huang YM, Wang B, Lv JP et al (2022) Facile synthesis of sodium lignosulfonate/polyethyleneimine/sodium alginate beads with ultra-high adsorption capacity for cr(VI) removal from water. J Hazard Mater 436:129270. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2022.129270
Jabli M, Sebeia N, El-Ghoul Y et al (2023) Chemical modification of microcrystalline cellulose with polyethyleneimine and hydrazine: characterization and evaluation of its adsorption power toward anionic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 229:210–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.309
Jia J, Luan SJ, Wu AH (2014) Adsorption and application of heavy metal ions by polyethyleneimine. Polym Bull 1134–44. https://doi.org/10.14028/j.cnki.1003-3726.2014.11.005
Jin XC, Xiang ZY, Liu QG et al (2017) Polyethyleneimine-bacterial cellulose bioadsorbent for effective removal of copper and lead ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 244:844–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.072
Karimi A, Moezzi A, Chorom M, Enayatizamir N (2019) Chemical fractions and availability of Zn in a calcareous soil in response to biochar amendments. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19(4):851–864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00084-1
Kharazian P, Fernandez-Ondono E, Jimenez MN et al (2022) Pinus halepensis in Contaminated Mining Sites: study of the transfer of Metals in the plant-soil system using the BCR Procedure. Toxics 10(12):10120728. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120728
Li LL, Jia ZL, Ma H et al (2019) The effect of two different biochars on remediation of Cd-contaminated soil and cd uptake by Lolium perenne. Environ Geochem Health 41(5):2067–2080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00257-y
Li TT, Tong ZH, Gao B et al (2020) Polyethyleneimine-modified biochar for enhanced phosphate adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(7):7420–7429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07053-2
Li A, Xie H, Qiu Y et al (2022) Resource utilization of rice husk biomass: Preparation of MgO flake-modified biochar for simultaneous removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution and polluted soil. Environ Pollut 310:119869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119869
Linam F, McCoach K, Limmer MA et al (2021) Contrasting effects of rice husk pyrolysis temperature on silicon dissolution and retention of cadmium (cd) and dimethylarsinic acid (DMA). Sci Total Environ 765:144428. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.144428
Liu Z, Nan Z, Zhao C et al (2018) Potato absorption and phytoavailability of cd, Ni, Cu, Zn and Pb in sierozem soils amended with municipal sludge compost. J Arid Land 10(4):638–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-018-0062-6
Liu HJ, Zhou YC, Yang YB et al (2019) Synthesis of polyethylenimine/graphene oxide for the adsorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 471:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.231
Liu M, Sun FX, Lv YZ et al (2021) Remediation of arsenic-contaminated soil by nano-zirconia modified biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(48):68792–68803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15362-8
Mei C, Wang H, Cai KZ et al (2022) Characterization of soil microbial community activity and structure for reducing available cd by rice straw biochar and Bacillus cereus RC-1. Sci Total Environ 839:156202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156202
Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources (2014) National Soil Pollution Survey [R]. http://www.gov.cn/foot/site1/20140417/782bcb88840814ba158d01.pdf 2023.5.18
Nazari S, Rahimi G, Nezhad A (2019) Effectiveness of native and citric acid-enriched biochar of Chickpea straw in cd and pb sorption in an acidic soil. J Environ Chem Eng 7(3):103064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103064
Nazeer M, Khan MJ, Muhammad D et al (2023) Biochar application stabilized the heavy metals in coal mined soil. Can J Soil Sci 0073. https://doi.org/10.1139/CJSS-2022-0073
Pandey D, Daverey A, Dutta K et al (2022) Enhanced adsorption of Congo red dye onto polyethyleneimine-impregnated biochar derived from pine needles. Environ Monit Assess 194(12):880. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-022-10563-1
Pawar RR, Lalhmunsiama, Kim M et al (2018) Efficient removal of hazardous lead, cadmium, and arsenic from aqueous environment by iron oxide modified clay-activated carbon composite beads. Appl Clay Sci 162:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.06.014
Plohl O, Finsgar M, Gyergyek S et al (2019) Efficient copper removal from an aqueous anvironment using a novel and hybrid nanoadsorbent based on derived-polyethyleneimine linked to silica magnetic nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 9(2):9020209. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020209
Rajapaksha AU, Chen SS, Tsang DCW et al (2016) Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: potential and implication of biochar modification. Chemosphere 148:276–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.01.043
Rasuli F, Owliaie H, Najafi-Ghiri M et al (2022) Effect of biochar on potassium fractions and plant-available P, Fe, Zn, Mn and Cu concentrations of calcareous soils. Arid Land Research and Management 36(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324982.2021.1936689
Riva L, Fiorati A, Punta C (2021) Synthesis and application of cellulose-polyethyleneimine composites and nanocomposites: a concise review. Materials 14(3):14030473. https://doi.org/10.3390/MA14030473
Scotti C, Bertora C, Valagussa M et al (2022) Agroenvironmental Performances of Biochar Application in the Mineral and Organic fertilization strategies of a maize-ryegrass forage system. Agriculture-Basel 12(7):925–925. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRICULTURE12070925
Shakoor MB, Ali S, Rizwan M et al (2020) A review of biochar-based sorbents for separation of heavy metals from water. Int J Phytoremediation 22(2):111–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1647405
Shi Y, Zhao ZZ, Zhong Y et al (2022) Synergistic effect of floatable hydroxyapatite-modified biochar adsorption and low-level CaCl2 leaching on cd removal from paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 807(02):150872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150872
Siddika A, Islam MM, Parveen Z et al (2023) Remediation of chromium (VI) from contaminated agricultural soil using modified Biochars. Environ Manage 71(4):809–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-022-01731-7
Song DL, Xi XY, Zheng Q et al (2019) Soil nutrient and microbial activity responses to two years after maize straw biochar application in a calcareous soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.073
Su J, Weng X, Luo ZJ et al (2023) Impact of Biochar on Soil Properties, Pore Water Properties, and available cadmium. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107(3):544–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00128-021-03259-8
Sun LJ, Gong PY, Sun YF et al (2022) Modified chicken manure biochar enhanced the adsorption for Cd2+ in aqueous and immobilization of cd in contaminated agricultural soil. Sci Total Environ 851:158252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158252
Tanis I, Kostarellou E, Karatasos K (2021) Molecular dynamics simulations of hyperbranched poly (ethylene imine)-graphene oxide nanocomposites as dye adsorbents for water purification. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(40):22874–22884. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP02461B
Tian HR, Huang C, Wang P et al (2023) Enhanced elimination of cr(VI) from aqueous media by polyethyleneimine modified corn straw biochar supported sulfide nanoscale zero valent iron: performance and mechanism. Bioresour Technol 369:128452. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2022.128452
Wang X, Liu Q, Liu JY et al (2017) 3D self-assembly polyethyleneimine modified graphene oxide hydrogel for the extraction of uranium from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 426:1063–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.203
Wang G, Cheng XL, Zeng YC et al (2020a) Effects of some parameters on the removal of cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions by polyethyleneimine-sodium xanthogenate. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17(12):4733–4744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02798-7
Wang X, Feng JH, Cai YW et al (2020b) Porous biochar modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI) for effective enrichment of U(VI) in aqueous solution. Sci Total Environ 708(C):134575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134575
Wu M, Wei JS, Sun HD et al (2016) Improvement of Acid Soil by Plant materials and Biochar. Chin J Trop Crops 37(12):2276–2282
Xiao WW, Lin GB, He XM et al (2022) Interactions among heavy metal bioaccessibility, soil properties and microbial community in phyto-remediated soils nearby an abandoned realgar mine. Chemosphere 286:131638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131638
Xie XL, Gao HL, Luo X et al (2019) Polyethyleneimine modified activated carbon for adsorption of cd(II) in aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 7(3):103183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103183
Xu WF, Liu X, Tang KW (2022) Adsorption of hydroquinone and pb(II) from water by beta-cyclodextrin/polyethyleneimine bi-functional polymer. Carbohydr Polym 294:119806. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2022.119806
Yadav M, Jadeja R, Thakore S (2022) An Ecofriendly Approach for Methylene Blue and lead (II) adsorption onto Functionalized Citrus limetta Bioadsorbent. Environ Processes 9:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-022-00583-x
Yan R, Feng W (2020) Effect of vegetation on soil bacteria and their potential functions for ecological restoration in the Hulun Buir Sandy Land, China. J Arid Land 12(3):473–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-020-0011-z
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiment: Haihua Li, Yuanyuan Qu; Biochar preparation: Zhichen Wang, Minghao Xie; Original draft preparation: Haihua Li, Yuanyuan Qu, Zhichen Wang, and Minghao Xie; Review and editing: Haihua Li, Yuanyuan Qu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate and publish
All authors agree with the content and gave explicit consent to submit.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Qu, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Remediation of Cd-Contaminated Soil by Polyethyleneimine-Modified Biochar. Environ. Process. 10, 29 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00647-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00647-6