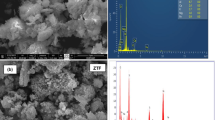
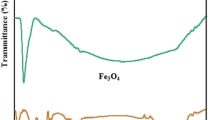
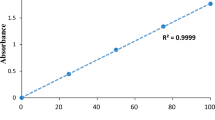
Abstract
In this study, the anionic azo dye was taken out of an aqueous solution using the batch adsorption approach. Zeolite NaX and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents were employed. The effects of the variables such as initial azo dye concentration (5–45 mg/L), shaking rotary speed (100–200 rpm), pH (2–10) and contact time (10–140 min) were examined with both doses of adsorbents (0.1–0.5 g) Zeolite NaX and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. The outcomes showed that good removal efficiencies were attained for both adsorbents Zeolite NaX and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles, with values of 72.34% and 99.99%, respectively. The ideal values for both adsorbents were achieved, including pH of 2, initial azo dye concentration of 5 mg/L, shaking speed of 180 rpm, contact period of 120 min and adsorbent dose of 0.3 g of Zeolite NaX and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. The results demonstrated that when the Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isotherm adsorption models were compared, the Langmuir isotherm adsorption model showed a higher correlation coefficient R2 for Zeolite NaX and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles of 0.9958 and 0.9767, respectively. Zeolite NaX and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle adsorption rates were found to support pseudo-first-order kinetics with strong correlation R2 values of 0.9894 and 0.9728, respectively. The findings indicate that Zeolite NaX has a lower dye removal efficiency than Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles under the same working conditions.
Highlights
-
The NaX and Fe3O4 adsorbents were used to remove the anionic azo dye successfully.
-
A maximum azo dye removal was achieved on Fe3O4 nanoparticles adsorbent.
-
Fe3O4 was found very active for removal of azo dye compounds from wastewater.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data and material are presented in the main paper.
References
Abbood NS, Ali NS, Khader EH, Majdi HS, Albayati TM, Saady NM (2023) Photocatalytic degradation of cefotaxime pharmaceutical compounds onto a modified nanocatalyst. Res on Chem Inter 49:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-022-04879-3
Akolekar D, Chaffee A, Howe RF (1997) The transformation of kaolin to low-silica X zeolite. Zeol 19:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-2449(97)00132-2
Alamrani WA, Hanafiah MA, Mohammed AH (2022) A comprehensive review of anionic azo dyes adsorption on surface-functionalised silicas. Environ Sci and Poll Res 29:76565–76610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23062-0
Alardhi SM, Alrubaye JM, Albayati TM (2020) Removal of methyl green dye from simulated waste water using hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane. In IOP Conf Series: Mat Sci and Eng 928:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/928/5/052020
Albayati TM, Doyle AM (2013) Shape-selective adsorption of substituted aniline pollutants from wastewater. Adsor Sci and Tech 31:459–468
Albayati TM, Doyle AM (2014) Purification of aniline and nitrosubstituted aniline contaminants from aqueous solution using beta zeolite. Chem Bulg J Sci Educ 23:105–114
Ali NS, Jabbar NM, Alardhi SM, Majdi HS, Albayati TM (2022a) Adsorption of methyl violet dye onto a prepared bio-adsorbent from date seeds: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Heli 8:10276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10276
Ali NS, Kalash KR, Ahmed AN, Albayati TM (2022b) Performance of a solar photocatalysis reactor as pretreatment for wastewater via UV, UV/TiO2, and UV/H2O2 to control membrane fouling. Sci Rep 12:16772–16782. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20984-0
Aljaaf HJ, Ali NS, Alardhi SM, Albayati TM (2022) Implementing eggplant peels as an efficient bio-adsorbent for treatment of oily domestic wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 245:226–237. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.27986
Atiyah NA, Albayati TM, Atiya MA (2022a) Functionalization of mesoporous MCM-41 for the delivery of curcumin as an anti-inflammatory therapy. Adv Powder Tech 33:103417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.103417
Atiyah NA, Albayati TM, Atiya MA (2022b) Interaction behavior of curcumin encapsulated onto functionalized SBA-15 as an efficient carrier and release in drug delivery. J of Mol Struc 1260:132879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132879
Azari A, Nabizadeh R, Mahvi AH, Nasseri S (2021) Magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes-loaded alginate for treatment of industrial dye manufacturing effluent: adsorption modelling and process optimisation by central composite face-central design. Inter J of Environ Analy Chem 14:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1877279
Banerjee S, Chattopadhyaya MC (2017) Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low cost agricultural by-product. Arab J of Chem 10:1629–1638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.06.005
Chawla S, Uppal H, Yadav M, Bahadur N, Singh N (2017) Zinc peroxide nanomaterial as an adsorbent for removal of Congo red dye from waste water. Ecotox and environ saf 135:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.09.017
Chiu YH, Chang TFM, Chen CY, Sone M, Hsu YJ (2019) Mechanistic insights into photodegradation of organic dyes using heterostructure photocatalysts. Catal 9:398–430. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050430
Chukwuemeka-Okorie HO, Ekuma FK, Akpomie KG, Nnaji JC, Okereafor AG (2021) Adsorption of tartrazine and sunset yellow anionic dyes onto activated carbon derived from cassava sievate biomass. Appl Water Sci 11:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01357-w
Filipkowska U, Jozwiak T, Rodziewicz J, Kuciejewska J (2013) Application of maize silage as a biosorbent for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. Rocz Ochr Srodo 15:2324–2338
Firmino PI, da Silva ME, Cervantes FJ, dos Santos AB (2010) Colour removal of dyes from synthetic and real textile wastewaters in one-and two-stage anaerobic systems. Bioreso Tech 101:7773–7779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.050
Fu J, Wen T, Wang Q, Zhang XW, Zeng QF, An SQ, Zhu HL (2010) Degradation of active brilliant red X-3B by a microwave discharge electrodeless lamp in the presence of activated carbon. Environ tech 31:771–779. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593331003646620
Ho YS (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J of haz mat 136:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Joshi PA, Mhatre KJ (2015) Microbial efficiency to degrade Carbol fuchsin and malachite green dyes. Adv in Appl Sci Res 6:85–88
Kadhum ST, Alkindi GY, Albayati TM (2021) Determination of chemical oxygen demand for phenolic compounds from oil refinery wastewater implementing different methods. Desalin and Water Treat 231:44–53. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27443
Kannan N, Meenakshisundaram M (2002) Adsorption of Congo Red on various activated carbons. A comparative study. Water air and soil poll 138:289–305. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015551413378
Kannan N, Veemaraj T (2009) Removal of lead (II) ions by adsorption ontobamboo dust and commercial activated Carbons-A comparative study. E-J of Chem 6:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/515178
Kannan N, Xavier A (2001) New composite mixed adsorbents for the removal of acetic acid by adsorption from aqueous solutions-a comparative study. Toxi and Environ Chem 79:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240109358979
Khader EH, Mohammed TJ, Adnan SW (2021) Reduction of oil and COD from produced water by activated carbon, zeolite, and mixed adsorbents in a fixed-bed column. Desalin waterTreat 227:216–227. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27295
Khader EH, Abbood NS, Albyati TN, Mohammed TJ (2022a) Performance evaluation of integral process for treatment of oilfield wastewater. In AIP Conf Pro 2443:030035. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0091914
Khader EH, Mohammed TJ, Mirghaffari N, Salman AD, Juzsakova T, Abdullah TA (2022b) Removal of organic pollutants from produced water by batch adsorption treatment. Clean Tech and Environ Policy 24:713–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02159-z
Khanday WA, Marrakchi F, Asif M, Hameed BH (2017) Mesoporous zeolite–activated carbon composite from oil palm ash as an effective adsorbent for methylene blue. J of the Tai Inst of Chem Eng 70:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.10.029
Kim J, Bak GH, Yoo DY, Lee YI, Lee YG, Chon K (2023) Functionalization of pine sawdust biochars with Mg/Al layered double hydroxides to enhance adsorption capacity of synthetic azo dyes: adsorption mechanisms and reusability. Heli 9:14142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14142
Labiod K, Hazourli S, Bendaia M, Tlili M, AitBara A, Graine R, Meradi H, Rather SU (2022) Removal of Azo Dye Carmoisine by Adsorption process on Diatomite. Adsor Sci and Tech 2022:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9517605
Liu Y, Liu L, Shan J, Zhang J (2015) Electrodeposition of palladium and reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites on foam-nickel electrode for electrocatalytic hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. J of haz mat 290:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.016
Lotito AM, De SM, Di IC, Bergna G (2014) Textile wastewater treatment: aerobic granular sludge vs activated sludge systems. Water Res 54:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.01.055
Marrakchi F, Ahmed MJ, Khanday WA, Asif M, Hameed BH (2017) Mesoporous-activated carbon prepared from chitosan flakes via single-step sodium hydroxide activation for the adsorption of methylene blue. Int J Biol Macromol 98:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.119
Metin S, Çifçi D (2023) Chemical industry wastewater treatment by coagulation combined with Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. J of Chem Tech and Biotech 7:7321–7332. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.7321
Munagapati VS, Kim DS (2016) Adsorption of anionic azo dye Congo Red from aqueous solution by Cationic Modified Orange Peel Powder. J of Mol Liq 220:540–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.04.119
Murat M, Amokrane A, Bastide JP, Montanaro L (1992) Synthesis of zeolites from thermally activated kaolinite. Some observations on nucleation and growth. Clay Min 27:119–130
Muslim WA, Albayati TM, Al-Nasri SK (2022) Decontamination of actual radioactive wastewater containing 137Cs using bentonite as a natural adsorbent: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Sci Rep 12:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18202-y
Nazifa TH, Saady NM, Bazan C, Zendehboudi S, Aftab A, Albayati TM (2021) Anaerobic digestion of blood from slaughtered livestock: a review. Ener 14:5641–5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14185666
Ouassif H, Moujahid EM, Lahkale R, Sadik R, Bouragba FZ, Diouri M (2020) Zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxide: high efficient removal by adsorption of tartrazine dye from aqueous solution. Surf and Interf 18:100401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100401
Oukebdane K, Necer IL, Didi MA (2022) Binary comparative study adsorption of anionic and cationic azo-dyes on Fe3O4-Bentonite magnetic nanocomposite: kinetics, equilibrium, mechanism and thermodynamic study. Silic 14:9555–9568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-022-01710-x
Pasalari H, Ghaffari HR, Mahvi AH, Pourshabanian M, Azari A (2017) Activated carbon derived from date stone as natural adsorbent for phenol removal from aqueous solution. Desalin and Water Treat 72:406–417. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20686
Ramimoghadam D, Bagheri S, Abd Hamid SB (2014) Progress in electrochemical synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J of Magnetism and Magnetic Mat 368:207–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.05.015
Saad A, Bakas I, Piquemal JY, Nowak S, Abderrabba M, Chehimi MM (2016) Mesoporous silica/polyacrylamide composite: preparation by UV-graft photopolymerization, characterization and use as hg (II) adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci 367:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.134
Salazar JM, Lectez S, Gauvin C, Macaud M, Bellat JP, Weber G, Bezverkhyy I, Simon JM (2017) Adsorption of hydrogen isotopes in the zeolite NaX: experiments and simulations. Inter J of Hydr Ener 42:13099–13110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.222
Santos SC, Boaventura RA (2015) Treatment of a simulated textile wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) with addition of a low-cost adsorbent. J of haz mat 291:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.074
Selvaraj V, Karthika TS, Mansiya C, Alagar M (2021) An over review on recently developed techniques, mechanisms and intermediate involved in the advanced azo dye degradation for industrial applications. J Mol Struct 1224:129195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129195
Solanki S, Sinha S, Bisaria K, Singh R, Saxena R (2022) Accurate data prediction by fuzzy inference model for adsorption of hazardous azo dyes by novel algal doped magnetic chitosan bionanocomposite. Environ Res 214:113844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113844
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Chao HP (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water res 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Uppal S, Arora A, Gautam S, Singh S, Choudhary RJ, Mehta SK (2019) Magnetically retrievable Ce-doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles as scaffolds for the removal of azo dyes. RSC adv 9:23129–23141. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA03252E
Vieira ML, Martinez MS, Santos GB, Dotto GL, Pinto LA (2018) Azo dyes adsorption in fixed bed column packed with different deacetylation degrees chitosan coated glass beads. J of Environ Chem Eng 6:3233–3241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.059
Yadav S, Asthana A, Chakraborty R, Jain B, Singh AK, Carabineiro SA, Susan MA (2020) Cationic dye removal using novel magnetic/activated charcoal/β-cyclodextrin/alginate polymer nanocomposite. Nanomat 10:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010170
Yesilada O, Birhanli E, Geckil H (2018) Bioremediation and decolorization of textile dyes by white rot fungi and laccase enzymes. Mycor and environ sustain 2:121–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77386-5_5
Yin H, Qiu P, Qian Y, Kong Z, Zheng X, Tang Z, Guo H (2019) Textile wastewater treatment for water reuse: a case study. Proc 7:1–34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010034
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Technology- Iraq.Baghdad, Iraq.
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors are contributed effectively in this paper; all experimental work was achieved by E. H., and R. H. with help of T. M., the writing paper as original draft preparation. T. M. was responsible about the idea of the paper as a supervisor and Writing- Reviewing and Editing paper with revision as well with help of N. S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khader, E.H., Khudhur, R.H., Abbood, N.S. et al. Decolourisation of Anionic Azo Dye in Industrial Wastewater Using Adsorption Process: Investigating Operating Parameters. Environ. Process. 10, 34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00646-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-023-00646-7