Abstract
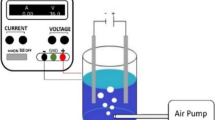
The production of biodiesel is an energy and water-intensive process that produces wastewater with high concentrations of COD, BOD, and FOG. Conventional treatment processes are not capable of treating contaminants and pollutants in biodiesel wastewater to satisfactory concentrations, and hence, advanced treatment processes are necessary. Untreated discharge of biodiesel wastewater results in additional costs during the production of biodiesel when penalties and fines are applied. In this research, a lab-scale integrated treatment process was used to investigate the successful abatement of contaminants, COD, BOD and FOG, present in industrial biodiesel wastewater. The integrated treatment process consisted of three consecutive steps: acidification, electrochemical oxidation, and adsorption. Acidification as a pre-treatment occurred at a pH of 2. Electrochemical oxidation using IrO2-Ta2O5/Ti anodes at a current density of 1 mA/cm2 and NaCl concentration of 0.08 M was followed by three consecutive adsorption stages using Chitosan powder at a concentration of 4.5 g/L. The experimental results show that the integrated treatment process could reduce COD, BOD and FOG levels by 94%, 86% and 95%, respectively. The treated effluent complies with local industrial effluent discharge standards, which could be disposed of safely without further treatment.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad AL, Sumathi S, Hameed BH (2005) Adsorption of residue oil from palm oil mill effluent using powder and flake chitosan: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Water Res 39:2483–2494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.03.035
Aksoyoglu S (1989) Sorption of U(VI) on granite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem Artic 134:393–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02278276
Almomani F, Baranova EA (2012) Electro-oxidation of two reactive azo dyes on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Water Sci Technol 66:465–471. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.180
Bhatt AS, Sakaria PL, Vasudevan M, Pawar PR, Sudheesh N, Bajaj HC, Mody HM (2012) Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous medium by organoclays: equilibrium modelling, kinetic and thermodynamic exploration. RSC Adv 2:8663. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra20347b
Bouberka AKZ, Kameche FSM, Derriche Z (2007) Adsorption study of an industrial dye by an organic clay. 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-007-9016-6
Chavalparit O, Ongwandee M (2009) Optimizing electrocoagulation process for the treatment of biodiesel wastewater using response surface methodology. J Environ Sci 21:1491–1496. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62445-6
Chiou MS, Li HY (2002) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan beads. J Hazard Mater 93:233–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00030-4
Coledam DAC, Aquino JM, Rocha-Filho RC, Bocchi N, Biaggio SR (2014) Influence of chloride-mediated oxidation on the electrochemical degradation of the direct black 22 dye using boron-doped diamond and β-PbO2 anodes. Quim Nova 37:1312–1317. https://doi.org/10.5935/0100-4042.20140219
Comninellis C (1994) Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants. Electrochim Acta 39:1857–1862
Costa NM, Silva VM, Damaceno G, Sousa RMF, Richter EM, Machado AEH, Trovó AG (2017) Integrating coagulation-flocculation and UV-C or H2O2/UV-C as alternatives for pre- or complete treatment of biodiesel effluents. J Environ Manag 203:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.07.069
Daud NM, Rozaimah S, Abdullah S, Hasan HA, Yaakob Z (2014) Production of biodiesel and its wastewater treatment technologies : a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 94:487–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.10.009
Daud Z, Awang H, Abdul Latif AA, Nasir N, Ridzuana MH, Ahmad Z (2015) Suspended solid, colour, COD and oil and grease removal from biodiesel wastewater by coagulation and flocculation processes. Procedia - Soc Behav Sci 195:2407–2411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.06.234
De Marques Neto JO, Bellato CR, Milagres JL, Pessoa KD, de Alvarenga ES (2013) Preparation and evaluation of chitosan beads immobilized with iron(III) for the removal of as(III) and as(V) from water. J Braz Chem Soc 24:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532013000100017
Dewil R, Mantzavinos D, Poulios I, Rodrigo MA (2017) New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Manag 195:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.010
Fajardo AS, Seca HF, Martins RC (2017) Electrochemical oxidation of phenolic wastewaters using a batch-stirred reactor with NaCl electrolyte and Ti/RuO2 anodes. J Electroanal Chem 785:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.12.033
Fazal MA, Haseeb ASMA, Masjuki HH (2011) Biodiesel feasibility study: an evaluation of material compatibility; performance; emission and engine durability. Renew Sust Energ Rev 15:1314–1324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2010.10.004
Foley T, Thornton K, Dixon RK (2015) REN21. 2015. Renewables 2015 Global Status Report
Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E (2011) Mineralization of the recalcitrant oxalic and oxamic acids by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using a boron-doped diamond anode. Water Res 45:2975–2984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.017
Garcia-Segura S, Ocon JD, Chong MN (2018) Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents — a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 113:48–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.014
Haseeb ASMA, Fazal MA, Jahirul MI, Masjuki HH (2011) Compatibility of automotive materials in biodiesel: a review. Fuel 90:922–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2010.10.042
Huang CA, Yang SW, Chen CZ, Hsu F-Y (2017) Electrochemical behaviour of IrO2 -Ta2 O5 /Ti anodes prepared with different surface pretreatments of Ti substrate. Surf Coatings Technol 320:270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.01.005
Jaruwat P, Kongjao S, Hunsom M (2010) Management of biodiesel wastewater by the combined processes of chemical recovery and electrochemical treatment. Energy Convers Manag 51:531–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.10.018
Kilislioglu A, Bilgin B (2003) Thermodynamic and kinetic investigations of uranium adsorption on amberlite IR-118H resin. Appl Radiat Isot 58:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(02)00316-0
Laus R, Costa TG, Szpoganicz B, Fávere VT (2010) Adsorption and desorption of cu(II), cd(II) and Pb(II) ions using chitosan crosslinked with epichlorohydrin-triphosphate as the adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 183:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.016
Ltaïef AH, D’Angelo A, Ammar S, Gadri A, Galia A, Scialdone O (2017) Electrochemical treatment of aqueous solutions of catechol by various electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: effect of the process and of operating parameters. J Electroanal Chem 796:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.04.033
Moreira FC, Boaventura RAR, Brillas E, Vilar VJP (2017) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl Catal B Environ 202:217–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.037
Ngamlerdpokin K, Kumjadpai S, Chatanon P (2011) Remediation of biodiesel wastewater by chemical- and electro-coagulation: a comparative study. J Environ Manag 92:2454–2460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.05.006
Özcan AS, Erdem B, Özcan A (2004) Adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto Na – bentonite and DTMA – bentonite. 280:44–54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.07.035
Ozcan A, Ozcan A, Tunali S (2005) Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of copper(II) ions onto seeds of. J Hazard Mater 124:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.05.007
Palomino Romero JA, Cardoso Junior FSS, Figueiredo RT, Silva DP, Cavalcanti EB (2013) Treatment of biodiesel wastewater by combined electroflotation and electrooxidation processes. Sep Sci Technol 48:2073–2079. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.779712
Pitakpoolsil W, Hunsom M (2013) Adsorption of pollutants from biodiesel wastewater using chitosan flakes. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44:963–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.02.009
Rajkumar D, Palanivelu K (2004) Electrochemical treatment of industrial wastewater. J Hazard Mater 113:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.05.039
Rajkumar D, Kim JG, Palanivelu K (2005) Indirect electrochemical oxidation of phenol in the presence of chloride for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng Technol 28:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.200407002
Rattanapan C, Sawain A, Suksaroj T, Suksaroj C (2011) Enhanced efficiency of dissolved air flotation for biodiesel wastewater treatment by acidification and coagulation processes. Desalination 280:370–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.07.018
Ruhsing Pan J, Huang C, Chen S, Chung YC (1999) Evaluation of a modified chitosan biopolymer for coagulation of colloidal particles. Colloids Surface A Physicochem Eng Asp 147:359–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00588-3
Sakkayawong N, Thiravetyan P, Nakbanpote W (2005) Adsorption mechanism of synthetic reactive dye wastewater by chitosan. J Colloid Interface Sci 286:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.01.020
Santos MRG, Goulart MOF, Tonholo J, Zanta CLPS (2006) The application of electrochemical technology to the remediation of oily wastewater. Chemosphere 64:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.036
Sharma NK, Philip L (2016) Combined biological and photocatalytic treatment of real coke oven wastewater. Chem Eng J 295:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.031
Siles JA, Martin MA, Chica AF, Martin A (2010) Anaerobic co-digestion of glycerol and wastewater derived from biodiesel manufacturing. Bioresour Technol 101:6315–6321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.042
Sokker HH, El-Sawy NM, Hassan MA, El-Anadouli BE (2011) Adsorption of crude oil from aqueous solution by hydrogel of chitosan-based polyacrylamide prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization. J Hazard Mater 190:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.055
Suehara K, Kawamoto Y, Fujii E (2005) Biological treatment of wastewater discharged from biodiesel fuel production plant with alkali-catalyzed transesterification. J Biosci Bioeng 100:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.100.437
Sukkasem C, Laehlah S, Hniman A (2011) Upflow bio-filter circuit (UBFC): biocatalyst microbial fuel cell (MFC) configuration and application to biodiesel wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 102:10363–10370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.007
Thirugnanasambandham K, Sivakumar V, Prakash Maran J, Kandasamy S (2014) Chitosan-based grey wastewater treatment-a statistical design approach. Carbohydr Polym 99:593–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.058
Vázquez I, Rodríguez-Iglesias J, Marañón E, Castrillon L, Alvarez M (2007) Removal of residual phenols from coke wastewater by adsorption. J Hazard Mater 147:395–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.019
Veljković VB, Stamenković OS, Tasić MB (2014) The wastewater treatment in the biodiesel production with alkali-catalyzed transesterification. Renew Sust Energ Rev 32:40–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.007
Wu W, Huang Z-H, Lim T-T (2014) Recent development of mixed metal oxide anodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants in water. Appl Catal A Gen 480:58–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.04.035
Xu X, Cheng Y, Zhang T (2016) Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater using interior micro-electrolysis/Fenton oxidation-coagulation and biological degradation. Chemosphere 152:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.100
Yan Z, Zhao Y, Zhang Z (2015) A study on the performance of IrO2-Ta2O5 coated anodes with surface-treated Ti substrates. Electrochim Acta 157:345–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.01.005
Acknowledgements
The National Research Foundation (NRF) of South Africa for the student scholarship. NMT Electrodes (PTY) Ltd., Durban, South Africa, for supplying the IrO2–Ta2O5 anodes used in the electrochemical cell. The biodiesel producing company in Cape Town, South Africa, that supplied the industrial biodiesel wastewater effluent, used in this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myburgh, D.P., Aziz, M., Roman, F. et al. Removal of COD from Industrial Biodiesel Wastewater Using an Integrated Process: Electrochemical-Oxidation with IrO2-Ta2O5/Ti Anodes and Chitosan Powder as an Adsorbent. Environ. Process. 6, 819–840 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00401-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00401-x