Abstract
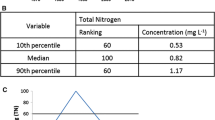
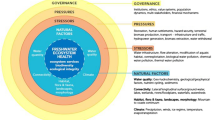
Lake Ecosystems have experienced a significant loss of their ecological value due to various human activities. It has been recognized that the continued alteration of freshwater biodiversity is not sustainable, and also, it has been realized that less modified freshwater ecosystems provide significant economic and social benefits to society. In Greece, changes in land and water management, driven by the increase in agricultural production and the urban expansion, have created multiple stressors on lentic ecosystems which cannot be ignored any longer. The objective of the present study is to describe some of these stressors, and to identify their impacts on Greek lakes. We collected an extensive dataset from twelve natural lakes using several metrics, also suggested by the Water Framework Directive (WFD), along with specific ecohydrological characteristics. Our results demonstrate severe impact on water quality and quantity with consequence to the lake’s functions, and extended eutrophication in almost all lakes. The Greek lakes have been subjected to various hydromorphological alterations, which affect their metabolism, while the aforementioned effects are further maximized due to particularities of the Mediterranean climate. The set up of good management practices through multipurpose management plans are also discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexakis D, Tsihrintzis V, Tsakiris G, Gikas G (2016) Suitability of water quality indices for application in lakes in the Mediterranean. Water Resour Manag 30:1621–1633. doi:10.1007/s11269-016-1240-y
Beklioglu M, Romo S, Kagalou I, Ouintana X, Becares E (2007) State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 584:317–326. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-0577-x
Chorus I, Bartram J (1999) Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. UNESCO, WHO and UNEP by E&FN Spon, London and New York
Crist E, Cafaro P (2012) Life on the brink: environmentalists confront overexploitation. University of Georgia Press, Athens, Georgia, USA
EASAC (European Academies Science Advisory Council) (2009) Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity in Europe. EASAC Policy report.http://www.easac.eu/fileadmin/PDF_s/reports_statements/Ecosystems.pdf.Accessed February 2009
EEA (2012) European waters — assessment of status and pressures. EEA report 8/2012. http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/european-waters-assessment-2012. Accessed 13 Nov 2012
ETC./ICM (2012) Ecological and chemical status and pressures in European waters. Thematic assessment on ecological and chemical status and pressures. ETC.-ICM Technical Report 1/2012. Prague: European Topic Centre on Inland, Coastal and Marine waters.http://icm.eionet.europa.eu/ETC_Reports/EcoChemStatusPressInEurWaters_201211. Accessed 13 Nov 2012
ETC./ICM (2015) European Freshwater Ecosystem Assessment: Cross-walk Between the Water Framework Directive and Habitats Directive Types, Status and Pressures. ETC./ICM Technical Report 2/2015. Magdeburg: European Topic Centre on inland, coastal and marine waters, 176 pp
European Commission (2000) Water Framework Directive: Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities, L327/1, Luxembourg
European Commission (2009) Guidance Document on Eutrophication Assessment in the Context of European Water Policy, Luxembourg
Grantham T, Merenlender A, Resh V (2010) Climatic influences and anthropogenic stressors: an integrated framework for streamflow management in Mediterranean-climate California, U.S.A. Freshw Biol 55:188–204. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02379.x
Jeppesen E, Jensen P, Sondergaard E, Lauridsen T, Pedersen J, Jensen L (1997) Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 342:151–161. doi:10.1023/A:1017046130329
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Meerhoff M, Lauridsen TL, Jensen JP (2007) Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction — some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia 584:239–252. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6399-2_22
Jeppesen E, Brucet S, Naselli-Flores L, Papastergiadou E, Stefanidis K, Nõges T, Nõges P, Attayde JL, Zohary T, Coppens J, Bucak T, Fernandes Menezes R, Sousa Freitas FR, Kernan M, Søndergaard M, Beklioğlu M (2015) Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 750:201–227. doi:10.1007/s10750-014-2169-x
Joint Research Centre [JRC] (2014) Water Framework Directive, Intercalibration Technical Report, Luxembourg, Publications Office by European Union
Kagalou I (2010) Classification and management issues of Greek lakes under the European Water Framework Directive: a DPSIR approach. J Environ Monit 12:2207–2215. doi:10.1039/c0em00212g
Kagalou I, Leonardos I (2009) Typology, classification and management issues of Greek lakes: implication of the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). Environ Monit Assess 150:469–484. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0245-2
Maberly S, Elliot J (2012) Insights from long-term studies in the Windermere catchment: external stressors, internal interactions and the structure and function of lake ecosystems. Freshw Biol 57:233–243. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02718.x
Maltby E, Ormerod SJ (2011) Freshwaters – Openwaters, Wetlands and Floodplains. In: The UK National Ecosystem Assessment Technical Report, pp. 285 295–360. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: synthesis. Island Press, Washington
Ministry of Environment (2011): Joint Ministerial Decision No. 140384 (FEK 2017B) /9-9-2011, Athens, Greece (in Greek)
Moustaka-Gouni M, Michaloudi E, Sommer U (2014) Modifying the PEG model for Mediterranean lakes – no biological winter and strong fish predation. Freshw Biol 59:1136–1144. doi:10.1111/fwb.12335
Noges T (2009) Relationships between morphometry, geographic location and water quality parameters of European lakes. Hydrobiologia 633:33–43. doi:10.1007/s10750-009-9874-x
Ntislidou Ch. (2014) Physical and chemical variables from several lakes. Using benthic invertebrate taxa for lake ecological status assessment (in preparation)
Ormerod S, Dobson M, Hildrew A, Townsend C (2010) Multiple stressors in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw Biol 55:1–4. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02395.x
Quinn G, Keough M (2002) Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tsakiris G (2015) The status of the European waters in 2015: a review. Environ Process 2:543–557. doi:10.1007/s40710-015-0079-1
Wallace JS, Acreman MC, Sullivan CA (2003) The sharing of water between society and ecosystems: from conflict to catchment-based co-management. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358:2011–2026. doi:10.1098/rstb.2003.1383
Acknowledgments
An initial version of this paper has been presented at the 9th World Congress of the European Water Resources Association (EWRA) “Water Resources Management in a Changing World: Challenges and Opportunities”, Istanbul, Turkey, June 10–13, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Latinopoulos, D., Ntislidou, C. & Kagalou, I. Multipurpose Plans for the Sustainability of the Greek Lakes: Emphasis on Multiple Stressors. Environ. Process. 3, 589–602 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0152-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0152-4