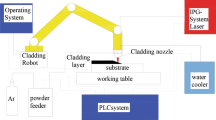
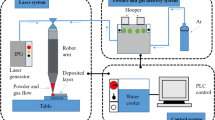
Abstract
Laser cladding is an environmentally friendly and reliable surface modification technology. The quality characteristics of the coating are directly affected by the process parameters of laser cladding. The reasonable selection of process parameters is essential to obtain high-quality coating. In this study, the single-track 15-5PH alloy coating was fabricated on the surface of 12Cr13 stainless steel. In view of the hybrid Genetic Algorithm and Ant Colony Optimization (GA-ACO) can effectively improve the prediction ability and robustness of Random Forest Regression (RFR), a prediction method of cladding layer quality characteristics based on GA-ACO-RFR was proposed. The fast non-dominated ranking genetic algorithm with elite strategy by introducing the Gaussian distribution crossover operator (GNSGA-II) was used to optimize the process parameters of laser cladding. The results showed that the multi-objective optimization method of laser cladding process parameters proposed in this paper can obtain high-quality laser cladding coating. This work demonstrated the potential of the proposed method in laser cladding process prediction and optimization.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu, L., Xue, P., Lan, Q., Meng, G., Ren, Y., Yang, Z., Xu, P., & Liu, Z. (2021). Recent research and development status of laser cladding: A review. Optics & Laser Technology, 138, 106915.
Satyavathi Yedida, V. V., & Vasudev, H. (2022). A review on the development of thermal barrier coatings by using thermal spray techniques. Materials Today: Proceedings, 50, 1458–1464.
Yu, X., Hou, Y., Ren, X., Sun, C., & Wang, M. (2022). Research progress on the removal, recovery and direct high-value materialization of valuable metal elements in electroplating/electroless plating waste solution. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 46, 102577.
Scheuer, C., Ristiano, J., Cardoso, R. P., & Brunatto, S. F. (2021). Sequential low-temperature plasma-assisted thermochemical treatments of the AISI 420 martensitic stainless steel. Surface and Coatings Technology, 421, 127459.
Yao, X. X., Ge, P., Li, J. Y., Wang, Y. F., Li, T., Liu, W. W., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Controlling the solidification process parameters of direct energy deposition additive manufacturing considering laser and powder properties. Computational Materials Science, 182, 109788.
Tebaay, L. M., Hahn, M., & Tekkaya, A. E. (2020). Distortion and dilution behavior for laser metal deposition onto thin sheet metals. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 7, 625–634.
Guo, C., He, S., Yue, H., Li, Q., & Hao, G. (2021). Prediction modelling and process optimization for forming multi-layer cladding structures with laser directed energy deposition. Optics & Laser Technology, 134, 106607.
Gao, M., Li, L., Wang, Q., Ma, Z., Li, X., & Liu, Z. (2022). Integration of additive manufacturing in casting: advances, challenges, and prospects. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 9, 305–322.
Du, Y., Zhou, Z., He, G., & Xu, L. (2022). Multi-parameter optimization of laser cladding 15–5PH using TOPSIS-GRA based on combined weighting method. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 31, 1934–1948.
Ma, M., Xiong, W., Lian, Y., Han, D., Zhao, C., & Zhang, J. (2020). Modeling and optimization for laser cladding via multi-objective quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Surface and Coatings Technology, 381, 125129.
Meng, G., Zhu, L., Zhang, J., Yang, Z., & Xue, P. (2021). Statistical analysis and multi-objective process optimization of laser cladding TiC-Inconel718 composite coating. Optik, 240, 166828.
Chen, T., Wu, W., Li, W., & Liu, D. (2019). Laser cladding of nanoparticle TiC ceramic powder: Effects of process parameters on the quality characteristics of the coatings and its prediction model. Optics & Laser Technology, 116, 345–355.
Wu, D., Hu, M., Huang, Y., Zhang, P., & Yu, Z. (2021). In situ monitoring and penetration prediction of plasma arc welding based on welder intelligence-enhanced deep random forest fusion. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 66, 153–165.
Song, C., Liu, L., Yang, Y., & Weng, C. (2020). Prediction on geometrical characteristics of laser energy deposition based on regression equation and neural network. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53, 89–96.
Pant, P., & Chatterjee, D. (2020). Prediction of clad characteristics using ANN and combined PSO-ANN algorithms in laser metal deposition process. Surfaces and Interfaces, 21, 100699.
Ilanlou, M., Shoja Razavi, R., Nourollahi, A., Hosseini, S., & Haghighat, S. (2022). Prediction of the geometric characteristics of the laser cladding of Inconel 718 on the Inconel 738 substrate via genetic algorithm and linear regression. Optics & Laser Technology, 156, 108507.
Saini, J., Dutta, M., & Marques, G. (2022). A novel application of fuzzy inference system optimized with particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm for PM10 prediction. Soft Computing, 26, 9573–9586.
Bakhtiyari, A. N., Wang, Z., Wang, L., & Zheng, H. (2021). A review on applications of artificial intelligence in modeling and optimization of laser beam machining. Optics & Laser Technology, 135, 106721.
Mohammed, S., Zhang, Z., & Kovacevic, R. (2020). Optimization of processing parameters in fiber laser cladding. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 111, 2553–2568.
Chakraborty, S. S., & Dutta, S. (2019). Estimation of dilution in laser cladding based on energy balance approach using regression analysis. Sādhanā, 44, 150.
Feng, Y., Pang, X., Feng, K., Feng, Y., & Li, Z. (2022). A method for evaluating the crack resistance and predicting the preheating temperature of high hardness coating prepared by laser cladding. Surface and Coatings Technology, 432, 128076.
Chang, C., Wu, K., Han, C., Tsai, T., Liu, S., & Lin, J. (2022). Establishment of the model widely valid for the melting and vaporization zones in selective laser melting printings via experimental verifications. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 9, 143–162.
Murat, F., Kaymaz, İ, Şensoy, A. T., & Korkmaz, İH. (2022). Determining the optimum process parameters of selective laser melting via particle swarm optimization based on the response surface method. Metals and Materials International. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01205-9
Li, C., Huang, J., Wang, K., Chen, Z., & Liu, Q. (2019). Optimization of processing parameters of laser skin welding in vitro combining the response surface methodology with NSGA- II. Infrared Physics & Technology, 103, 103067.
Peng, S., Li, T., Zhao, J., Lv, S., Tan, G. Z., Dong, M., & Zhang, H. (2019). Towards energy and material efficient laser cladding process: Modeling and optimization using a hybrid TS-GEP algorithm and the NSGA-II. Journal of Cleaner Production, 227, 58–69.
Jiang, X., Tian, Z., Liu, W., Tian, G., Gao, Y., Xing, F., Suo, Y., & Song, B. (2022). An energy-efficient method of laser remanufacturing process. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 52, 102201.
Liu, Y., Shen, W., Man, Y., Liu, Z., & Seferlis, P. (2019). Optimal scheduling ratio of recycling waste paper with NSGAII based on deinked-pulp properties prediction. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 132, 74–83.
García Moreno, A. I., Alvarado Orozco, J. M., IbarraMedina, J., & Martínez Franco, E. (2021). Ex-situ porosity classification in metallic components by laser metal deposition: A machine learning-based approach. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 62, 523–534.
Nemati, S., Basiri, M. E., Ghasem-Aghaee, N., & Aghdam, M. H. (2009). A novel ACO–GA hybrid algorithm for feature selection in protein function prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 12086–12094.
Anand, R. S., Jawahar, C. P., Solomon, A. B., & David, S. (2021). Prediction of Al2O3/R134a nanorefrigerant based modified thermosyphon performance using random forest algorithm. Materials Today: Proceedings, 47, 6585–6589.
Yang, N., Song, Z., Hofmann, H., & Sun, J. (2022). Robust State of Health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using convolutional neural network and random forest. Journal of Energy Storage, 48, 103857.
Nunes Miranda, E., Henrique Groenner Barbosa, B., Henrique Godinho Silva, S., Augusto Ussi Monti, C., Yue Phin Tng, D., & Rezende Gomide, L. (2022). Variable selection for estimating individual tree height using genetic algorithm and random forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 504, 119828.
Li, S., Li, S., Liu, D., Zou, R., & Yang, Z. (2022). Hardness prediction of high entropy alloys with machine learning and material descriptors selection by improved genetic algorithm. Computational Materials Science, 205, 111185.
Ma, Y., Mao, Z., Wang, T., Qin, J., Ding, W., & Meng, X. (2020). Obstacle avoidance path planning of unmanned submarine vehicle in ocean current environment based on improved firework-ant colony algorithm. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 87, 106773.
Zhang, J., Shi, S., Jiang, W., Shi, T., & Ji, S. (2019). Simulation analysis of temperature field and process optimization of laser cladding based on internal wire feeding of three beams. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 46, 122–129.
Wu, S., Liu, Z., Huang, X., Wu, Y., & Gong, Y. (2021). Process parameter optimization and EBSD analysis of Ni60A-25% WC laser cladding. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 101, 105675.
Zhou, Z., Qiu, F., Zheng, F., & Ye, M. (2022). Neural network joint capacity-power control strategy based on NSGAII-BP for interference suppression in LEO satellite uplinks. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 102, 108093.
Tan, W., Yuan, X., Yang, Y., & Wu, L. (2022). Multi-objective casting production scheduling problem by a neighborhood structure enhanced discrete NSGA-II: An application from real-world workshop. Soft Computing, 26, 8911–8928.
Zhang, M., Luo, W., & Wang, X. (2009). A normal distribution crossover for ε-MOEA. Journal of Software, 20, 305–314.
Deliktaş, D. (2022). Self-adaptive memetic algorithms for multi-objective single machine learning-effect scheduling problems with release times. Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 34, 748–784.
de Melo, S. A., Pereira, R. B. D., da Silva Reis, A. F., Lauro, C. H., & Brandão, L. C. (2022). Multi-objective evolutionary optimization of unsupervised latent variables of turning process. Applied Soft Computing, 120, 108713.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Innovative Research Group of Universities in Chongqing (Grant No. CXQT21024), the “Lump-sum System” Project of Chongqing Talent Plan (cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0056), the Chongqing Talent Program (Grant No. CQYC20210302226), the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission of China (Grant No. KJZD-K202000801), and the Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (Grant No. 20JS020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, G., Du, Y., Liang, Q. et al. Modeling and Optimization Method of Laser Cladding Based on GA-ACO-RFR and GNSGA-II. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 10, 1207–1222 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00492-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00492-2