Abstract
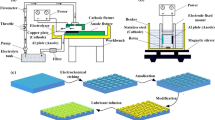
In this work, we present a simple technique for green fabrication of slippery liquid-infused surface (SLIS) with anti-friction property on various metallic substrates using wire electrical discharge machining. Micro-crater structures were successfully obtained, and the surface had excellent liquid-repellent property after modification and infusion of silicone oil. A wide range of liquids including water, juice, coffee, tea, vinegar, albumin, glycerol, and ketchup could easily slid down the surface tilted at an angle of 10° without leaving any trace. The influences of the number of cutting step on the morphology and wettability of the surface were studied comprehensively. Further, the tribological properties of the surface were analyzed and the results showed that the SLIS had a decrease of 73.2% in friction coefficient as compared to that of the smooth surface. By studying the morphology of the worn surfaces, it is found that the SLIS had slight abrasive wear behavior. To demonstrate the precision processing ability of this technology, we fabricated slippery sub-millimeter-scale asymmetric bump arrays, and the experiment results showed that the asymmetric bump arrays had excellent water harvesting ability at low temperatures. This kind of environment-friendly precision machining technology will promote the practical applications of metallic functional materials.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, M. J., Wang, S. T., & Jiang, L. (2017). Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nature Reviews Materials, 2, 17036.
Si, Y. F., Dong, Z. C., & Jiang, L. (2018). Bioinspired designs of superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic materials. ACS Central Science, 4, 1102–1112.
Kreder, M. J., Alvarenga, J., Kim, P., & Aizenberg, J. (2016). Design of anti-icing surfaces: Smooth, textured or slippery? Nature Reviews Materials, 1, 15003.
Kang, B., Sung, J., & So, H. (2021). Realization of superhydrophobic surfaces based on three-dimensional printing technology. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 8, 47–55.
Barthwal, S., & Lim, S. H. (2020). Robust and chemically stable superhydrophobic aluminum-alloy surface with enhanced corrosion-resistance properties. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 7, 481–492.
Jung, K. K., Jung, Y., Park, B. G., Choi, C. J., & Ko, J. S. (2021). Super wear resistant nanostructured superhydrophobic surface. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-021-00325-8
Wong, T. S., Kang, S. H., Tang, S. K. Y., Smythe, E. J., Hatton, B. D., Grinthal, A., & Aizenberg, J. (2011). Bioinspired self-repairing slippery surfaces with pressure-stable omniphobicity. Nature, 477, 443–447.
Wu, X. H., & Chen, Z. (2018). A mechanically robust transparent coating for anti-icing and self-cleaning applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6, 16043–16052.
Epstein, A. K., Wong, T. S., Belisle, R. A., Boggs, E. M., & Aizenberg, J. (2012). Liquid-infused structured surfaces with exceptional anti-biofouling performance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 13182–13187.
Zhou, X., Lee, Y. Y., Chong, K. S. L., & He, C. B. (2018). Superhydrophobic and slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces formed by the self-assembly of a hybrid ABC triblock copolymer and their antifouling performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 6, 440–448.
Xiao, L. L., Li, J. S., Mieszkin, S., Di Fino, A., Clare, A. S., Callow, M. E., Callow, J. A., Grunze, M., Rosenhahn, A., & Levkin, P. A. (2013). Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces showing marine antibiofouling properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5, 10074–10080.
Kim, P., Wong, T. S., Alvarenga, J., Kreder, M. J., Adorno-Martinez, W. E., & Aizenberg, J. (2012). Liquid-infused nanostructured surfaces with extreme anti-ice and anti-frost performance. ACS Nano, 6, 6569–6577.
Wilson, P. W., Lu, W. Z., Xu, H. J., Kim, P., Kreder, M. J., Alvarenga, J., & Aizenberg, J. (2013). Inhibition of ice nucleation by slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces (SLIPS). Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 15, 581–585.
Juuti, P., Haapanen, J., Stenroos, C., Niemela-Anttonen, H., Harra, J., Koivuluoto, H., Teisala, H., Lahti, J., Tuominen, M., Kuusipalo, J., Vuoristo, P., & Makela, J. M. (2017). Achieving a slippery, liquid-infused porous surface with anti-icing properties by direct deposition of flame synthesized aerosol nanoparticles on a thermally fragile substrate. Applied Physics Letters, 110, 161603.
Zhang, J. L., Gu, C. D., & Tu, J. P. (2017). Robust slippery coating with superior corrosion resistance and anti-icing performance for AZ31B Mg alloy protection. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 11247–11257.
Tuo, Y. J., Zhang, H. F., Chen, W. P., & Liu, X. W. (2017). Corrosion protection application of slippery liquid-infused porous surface based on aluminum foil. Applied Surface Science, 423, 365–374.
Wang, P., Lu, Z., & Zhang, D. (2015). Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces fabricated on aluminum as a barrier to corrosion induced by sulfate reducing bacteria. Corrosion Science, 93, 159–166.
Qiu, R., Zhang, Q., Wang, P., Jiang, L. N., Hou, J., Guo, W. M., & Zhang, H. X. (2014). Fabrication of slippery liquid-infused porous surface based on carbon fiber with enhanced corrosion inhibition property. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspectsis, 453, 132–141.
Wang, Y., Zhang, H. F., Liu, X. W., & Zhou, Z. P. (2016). Slippery liquid-infused substrates: A versatile preparation, unique anti-wetting and drag-reduction effect on water. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 4, 2524–2529.
Hemeda, A. A., & Tafreshi, H. V. (2016). Liquid-infused surfaces with trapped air (LISTA) for drag force reduction. Langmuir, 32, 2955–2962.
Park, K. C., Kim, P., Grinthal, A., He, N., Fox, D., Weaver, J. C., & Aizenberg, J. (2016). Condensation on slippery asymmetric bumps. Nature, 531, 78–82.
Luo, H., Lu, Y., Yin, S. H., Huang, S., Song, J. L., Chen, F. Z., Chen, F. J., Carmalt, C. J., & Parkin, I. P. (2018). Robust platform for water harvesting and directional transport. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6, 5635–5643.
Manna, U., & Lynn, D. M. (2015). Fabrication of liquid-infused surfaces using reactive polymer multilayers: Principles for manipulating the behaviors and mobilities of aqueous fluids on slippery liquid interfaces. Advanced Materials, 27, 3007–3012.
Yong, J. L., Chen, F., Yang, Q., Fang, Y., Huo, J. L., Zhang, J. Z., & Hou, X. (2017). Nepenthes inspired design of self-repairing omniphobic slippery liquid infused porous surface (SLIPS) by femtosecond laser direct writing. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 4, 1700552.
Luo, J. T. T., Geraldi, N. R. R., Guan, J. H. H., Mchale, G., Wells, G. G. G., & Fu, Y. Q. Q. (2017). Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces and droplet transportation by surface acoustic waves. Physical Review Applied, 7, 014017.
Chen, X. C., Ren, K. F., Wang, J., Lei, W. X., & Ji, J. (2017). Infusing lubricant onto erasable microstructured surfaces toward guided sliding of liquid droplets. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 1959–1967.
Wang, N., Xiong, D. S., Lu, Y., Pan, S., Wang, K., Deng, Y. L., & Shi, Y. (2016). Design and fabrication of the lyophobic slippery surface and its application in anti-icing. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120, 11054–11059.
Gao, X. Y., & Guo, Z. G. (2017). Mechanical stability, corrosion resistance of superhydrophobic steel and repairable durability of its slippery surface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 512, 239–248.
Wang, N., Xiong, D. S., Pan, S., Deng, Y. L., & Shi, Y. (2016). Fabrication of superhydrophobic and lyophobic slippery surface on steel substrate. Applied Surface Science, 387, 1219–1224.
Wang, P., Zhang, D., Lu, Z., & Sun, S. M. (2016). Fabrication of slippery lubricant-infused porous surface for inhibition of microbially influenced corrosion. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8, 1120–1127.
Doll, K., Fadeeva, E., Schaeske, J., Ehmke, T., Winkel, A., Heisterkamp, A., Chichkov, B. N., Stiesch, M., & Stumpp, N. S. (2017). Development of laser-structured liquid-infused titanium with strong biofilm-repellent properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 9359–9368.
Bae, W. G., Song, K. Y., Rahmawan, Y., Chu, C. N., Kim, D., Chung do, K., & Suh, K. Y. (2012). One-step process for superhydrophobic metallic surfaces by wire electrical discharge machining. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4, 3685–3691.
Liu, Y., Moevius, L., Xu, X., Qian, T., Yeomans, J. M., & Wang, Z. (2014). Pancake bouncing on superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature Physics, 10, 515–519.
Liu, C., Liu, Q., Jin, R., Lin, Z., & Xu, Y. (2020). Mechanism analysis and durability evaluation of anti-icing property of superhydrophobic surface. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 156, 119768.
Zhou, C. L., Wu, X. Y., Lu, Y. J., Wu, W., Zhao, H., & Li, L. J. (2018). Fabrication of hydrophobic Ti3SiC2 surface with micro-grooved structures by wire electrical discharge machining. Ceramics International, 44, 18227–18234.
Wang, H., Chi, G., Wang, Y., Yu, F., & Wang, Z. (2019). Fabrication of superhydrophobic metallic surface on the electrical discharge machining basement. Applied Surface Science, 478, 110–118.
Chen, Z., Yan, Z., Zhou, H., Han, F., & Yan, H. (2021). One-step fabrication of the wear-resistant superhydrophobic structure on SiCp/Al composite surface by WEDM. Surface & Coatings Technology, 409, 126876.
Kojima, A., Natsu, W., & Kunieda, M. (2008). Spectroscopic measurement of arc plasma diameter in EDM. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 57, 203–207.
Pérez, R., Carron, J., Rappaz, M., Walder, G., Revaz, B., & Flukiger, R. (2007). Measurement and metallurgical modeling of the thermal impact of EDM discharges on steel. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Electromachining, pp. 17–22.
Wang, Y., Yao, S. W., Ding, Z. J., Wu, C. Z., & Xiong, W. (2021). Machining characteristics of USV-MF complex assisted WEDM-LS based on multi-physical coupling. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 8, 387–404.
Salvati, E., & Korsunsky, A. M. (2020). Micro-scale measurement & FEM modelling of residual stresses in AA6082-T6 Al alloy generated by wire EDM cutting. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 275, 116373.
Tang, J. J., & Yang, X. D. (2018). Simulation investigation of thermal phase transformation and residual stress in single pulse EDM of Ti-6Al-4V. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 51, 135308.
Zouaghi, S., Six, T., Bellayer, S., Moradi, S., Hatzikiriakos, S. G., Dargent, T., Thomy, V., Coffinier, Y., Andre, C., Delaplace, G., & Jimenez, M. (2017). Antifouling biomimetic liquid-infused stainless steel: Application to dairy industrial processing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 26565–26573.
Ma, Q., Wang, W., & Dong, G. N. (2019). Facile fabrication of biomimetic liquid-infused slippery surface on carbon steel and its self-cleaning, anti-corrosion, anti-frosting and tribological properties. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 577, 17–26.
Luo, H., Yin, S. H., Huang, S., Chen, F. J., Tang, Q. C., & Li, X. J. (2019). Fabrication of slippery Zn surface with improved water-impellent, condensation and anti-icing properties. Applied Surface Science, 470, 1139–1147.
Ouyang, Y. B., Zhao, J., Qiu, R., Hu, S. G., Chen, M., & Wang, P. (2019). Liquid-infused superhydrophobic dendritic silver matrix: A bio-inspired strategy to prohibit biofouling on titanium. Surface & Coatings Technology, 367, 148–155.
Yao, W. H., Chen, Y. H., Wu, L., Zhang, J. K., & Pan, F. S. (2022). Effective corrosion and wear protection of slippery liquid-infused porous surface on AZ31 Mg alloy. Surface & Coatings Technology, 429, 127953.
Yang, Z. C., He, X. Y., Chang, J. F., Bai, X. Q., Cao, P., & Yuan, C. Q. (2021). Fabrication of biomimetic slippery liquid-infused porous surface on 5086 aluminum alloy with excellent antifouling performance. Surface and Interface Analysis, 53, 147–155.
Qiu, Z. H., Qiu, R., Xiao, Y. M., Zheng, J. Y., & Lin, C. G. (2018). Slippery liquid-infused porous surface fabricated on CuZn: A barrier to abiotic seawater corrosion and microbiologically induced corrosion. Applied Surface Science, 457, 468–476.
Bai, S. F., Liu, X. H., Xu, L. K., Xuan, J. J., Liu, Y. R., Shao, Y., Xin, Y. L., Li, X. B., & Fan, L. (2022). Enhancement of corrosion resistance and lubricating performance of electrodeposited Ni-Co coating composited with mesoporous silica nanoparticles and silicone oil impregnation. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 282, 125929.
Jambor, M., Kajanek, D., Fintova, S., Broncek, J., Hadzima, B., Guagliano, M., & Bagherifard, S. (2021). Directing surface functions by inducing ordered and irregular morphologies at single and two-tiered length scales. Advanced Engineering Materials, 23, 2001057.
Rowthu, S., & Hoffmann, P. (2018). Perfluoropolyether impregnated mesoporous alumina composites overcome the dewetting-tribological properties trade-off. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10, 10560–10570.
Wakuda, M., Yamauchi, Y., Kanzaki, S., & Yasuda, Y. (2003). Effect of surface texturing on friction reduction between ceramic and steel materials under lubricated sliding contact. Wear, 254, 356–363.
Chen, F. Y., Ying, J. M., Wang, Y. F., Du, S. Y., Liu, Z. P., & Huang, Q. (2016). Effects of graphene content on the microstructure and properties of copper matrix composites. Carbon, 96, 836–842.
Bowden, F. P., & Tabor, D. (2001). The friction and lubrication of solids. Oxford University Press.
Fan, H. Z., Zhang, Y. S., Hu, T. C., Song, J. J., Ding, Q., & Hu, L. T. (2015). Surface composition-lubrication design of Al2O3/Ni laminated composites—Part I: Tribological synergy effect of micro-dimpled texture and diamond-like carbon films in a water environment. Tribology International, 85, 142–151.
Golchin, A., Wikner, A., & Emami, N. (2016). An investigation into tribological behaviour of multi-walled carbon nanotube/graphene oxide reinforced UHMWPE in water lubricated contacts. Tribology International, 95, 156–161.
Tang, J. Z., Ding, Q., Zhang, S. W., & Hu, L. T. (2016). The fracture mechanism and the corresponding optimization strategy for nonhydrogenated amorphous carbon film in dimethyl silicone oil. Surface & Coatings Technology, 307, 941–950.
Quan, X., Hu, M., Gao, X. M., Fu, Y. L., Weng, L. J., Wang, D. S., Jiang, D., & Sun, J. Y. (2016). Friction and wear performance of dual lubrication systems combining WS2-MoS2 composite film and low volatility oils under vacuum condition. Tribology International, 99, 57–66.
Andersson, P., Koskinen, J., Varjus, S. E., Gerbig, Y., Haefke, H., Georgiou, S., Zhmud, B., & Buss, W. (2007). Microlubrication effect by laser-textured steel surfaces. Wear, 262, 369–379.
Huang, W., Jiang, L., Zhou, C. X., & Wang, X. L. (2012). The lubricant retaining effect of micro-dimples on the sliding surface of PDMS. Tribology International, 52, 87–93.
Cao, M., Yu, C., Xiao, X., Zhang, B., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Ma, H., Cui, X., Li, Z., & Jiang, L. (2018). Bioinspired pressure-tolerant asymmetric slippery surface for continuous self-transport of gas bubbles in aqueous environment. ACS Nano, 12, 2048–2055.
Ghosh, A., Ganguly, R., Schutzius, T. M., & Megaridis, C. M. (2014). Wettability patterning for high-rate, pumpless fluid transport on open, non-planar microfluidic platforms. Lab on a Chip, 14, 1538–1550.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U19A20103), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M661184), and the Jilin Province Scientific and Technological Development Program (No. YDZJ202101ZYTS025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, Z., Cheng, Y., Xu, J. et al. Green Fabrication of Anti-friction Slippery Liquid-Infused Metallic Surface with Sub-millimeter-Scale Asymmetric Bump Arrays and Its Application. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 10, 1281–1298 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00463-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-022-00463-7