Abstract
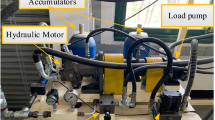
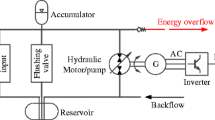
The hydraulic power take-off (HPTO) is considered as the most promising method to convert wave power to electrical power. This paper presents an experimental assessment of the power conversion of a wave energy converter using HPTO. Based on the experimental results, a modification of accumulator pre-charged pressure and a control strategy were proposed to improve the system performance. System design, the working principle and mathematical model of all components were described. The proposed method was verified based on both simulation and experimental tests. The results showed that the system always works at an optimal condition under different input wave conditions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johannes, F. (2007). A review of wave-energy extraction. Marine Structures, 20, 185–201.
Drew, B., Plummer, A. R., & Sahinkaya, M. N. (2009). A review of wave energy converter technology. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 223, 887–902.
Falcão, A. F. O. (2010). Wave energy utilization: A review of the technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 14, 899–918.
Iraide, L., Jon, A., Salvador, C., de Iñigo Martínez, A., & Iñigo, K. (2013). Review of wave energy technologies and the necessary power-equipment. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 27, 413–434.
Silvia, B., Adrià Moreno, M., Alessandro, A., Giuseppe, P., & Renata, A. (2013). Modeling of a point absorber for energy conversion in Italian seas. Energies, 6, 3033–3051.
Jusoh, M. A., Ibrahim, M. Z., Daud, M. Z., Albani, A., & Yusop, Z. M. (2019). Hydraulic power take-off concepts for wave energy conversion system: A review. Energies, 12, 4510.
Binh, P. C., Tri, N. M., Dung, D. T., Ahn, K. K., Kim, S. J., & Koo, W. (2016). Analysis, design and experiment investigation of a novel wave energy converter. IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 10, 460–469.
Dang, T. D., Nguyen, M. T., Phan, C. B., & Ahn, K. K. (2019). Development of a wave energy converter with mechanical power take-off via supplementary inertia control. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6, 497–509.
Dang, T. D., Phan, C. B., & Ahn, K. K. (2019). Design and Investigation of a novel point absorber on performance optimization mechanism for wave energy converter in heave mode. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6, 477–488.
Dang, T. D., Phan, C. B., & Ahn, K. K. (2019). Modeling and experimental investigation on performance of a wave energy converter with mechanical power take-off. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 6, 751–768.
Tri, N. M., Binh, P. C., & Ahn, K. K. (2018). Power take-off system based on continuously variable transmission configuration for wave energy converter. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 5, 89–101.
Ocean power technologies. https://www.oceanpowertechnologies.com. Accessed 2015.
Wave Star Energy. https://www.wavestarenergy.com. Accessed 2015
Choi, K. S., Yang, D. S., Park, S. Y., & Cho, B. H. (2012). Design and performance test of hydraulic PTO for wave energy converter. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 13(5), 795–801.
Falcão, A. F. O. (2017). Modeling and control of oscillating-body wave energy converters with hydraulic power take-off and gas accumulator. Ocean Engineering, 34, 2021–2032.
Ricci, P., Lopez, J., Santos, M., Ruiz-Minguela, P., Villate, J. L., Salcedo, F., et al. (2011). Control strategies for a wave energy converter connected to a hydraulic power takeoff. IET Renew Power Generation, 5, 234–244.
Joseba, L., Juan, C. A., Carlos, A., Patxi, E., Maider, S., & Pierpaolo, R. (2012). Design, construction and testing of a hydraulic power take-off for wave energy converters. Energies, 5, 2030–2052.
Do, H. T., Dinh, Q. T., Nguyen, M. T., Phan, C. B., Dang, T. D., et al. (2015). Effects of non-vertical linear motions of a hemispherical float wave energy converter. Ocean Engineering, 109, 430–438.
Do, H. T., Dinh, Q. T., Nguyen, M. T., Phan, C. B., Dang, T. D., et al. (2017). Proposition and experiment of a sliding angle self-tuning wave energy converter. Ocean Engineering, 132, 1–10.
Tri, N. M., Truong, D. Q., Binh, P. C., Dung, D. T., Lee, S., et al. (2016). A Novel control method to maximize the energy-harvesting capability of an adjustable slope angle wave energy converter. Renewable Energy, 97, 518–531.
Do, H. T., Dang, T. D., & Ahn, K. K. (2018). A multi-point-absorber wave-energy converter for the stabilization of output power. Ocean Engineering, 161, 337–349.
Ahn, K. K., Truong, D. Q., Tien, H. H., & Yoon, J. I. (2012). An innovative design of wave energy converter. Renewable Energy, 42, 186–194.
Truong, D. Q., & Ahn, K. K. (2014). Development of a novel point absorber in heave for wave energy conversion. Renewable Energy, 65, 183–191.
Cargo, C. J., Hillis, A. J., & Plummer, A. R. (2014). Optimisation and control of a hydraulic power take-off unit for a wave energy converter in irregular waves. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 228, 462–479.
Cargo, C. J., Plummer, A. R., Hillis, A. J., & Schlotter, M. (2012). Determination of optimal parameters for a hydraulic power take-off unit of a wave energy converter in regular waves. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 226, 98–111.
Cargo, C. J., Hillis, A. J., & Plummer, A. R. (2016). Strategies for active tuning of Wave Energy Converter hydraulic power take-off mechanisms. Renewable Energy, 94, 32–47.
Truong, D. Q., & Ahn, K. K. (2012). Wave prediction based on a modified grey model MGM(1,1) for real-time control of wave energy converters in irregular waves. Renewable Energy, 43, 242–255.
Falnes, J. (2002). Ocean waves and oscillating systems, linear interaction including wave-energy extraction. Cambridge: Cambridge University.
[Online] WAMIT, Inc version 7.0 user manual. (2015)https://www.wamit.com/manualupdate/history/V70_manual_old.pdf. Accessed 2015
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea (NRF-2020R1A2B5B03001480).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, T.D., Do, T.C. & Ahn, K.K. Experimental Assessment of the Power Conversion of a Wave Energy Converter Using Hydraulic Power Take-Off Mechanism. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 8, 1515–1527 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00261-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00261-z