Abstract
Background
Magnesium deficiency is common in patients with chronic kidney diseases (CKD) due to restricted magnesium intake and impaired magnesium reabsorption. Based on pathophysiological risk factors influencing kidney magnesium reabsorption, a magnesium depletion score (MDS) was developed. Using MDS as a novel indicator for assessing body magnesium status, we hypothesized that it was associated with clinical prognosis.
Methods
We conducted a prospective population-based cohort study using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2014 to explore the impact of MDS on the clinical outcomes of CKD patients. Propensity score-matched analyses were conducted to increase comparability. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and the secondary outcomes were cardiovascular-cause and cancer-cause mortality.
Results
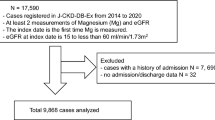
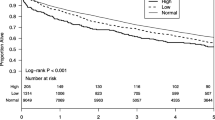
After propensity score matching, 3294 CKD patients were divided into 2 groups: MDS ≤ 2 (N = 1647), and MDS > 2 (N = 1647). During a median follow-up of 75 months, Kaplan–Meier analyses showed that MDS > 2 was associated with worse 5- and 10-year overall survival (78.5% vs 73.4%; 53.1% vs 43.1%, P < 0.001). After adjusting for confounding variables, MDS was found to be an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality (HR:1.34, 95% CI 1.20–1.50, P < 0.001). MDS > 2 was also associated with higher cardiovascular-cause mortality (16.2% VS 11.6%, P = 0.005). Multivariate competing risk analysis revealed that MDS > 2 was an independent risk factor (HR: 1.33, 95% CI 1.06–1.66, P = 0.012). Subgroup analyses reported that MDS > 2 increased all-cause mortality and cardiovascular-cause mortality only in patients with inadequate magnesium intake (P < 0.001, P < 0.001) but not in those with adequate intake (P = 0.068, P = 0.920).
Conclusions
A magnesium depletion score > 2 was independently associated with higher long-term cardiovascular-cause and all-cause mortality in CKD patients.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration (2020) Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 395(10225):709–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P (2017) Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 389(10075):1238–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32064-5
Bello AK, Alrukhaimi M, Ashuntantang GE, Basnet S, Rotter RC, Douthat WG, Kazancioglu R, Köttgen A, Nangaku M, Powe NR, White SL, Wheeler DC, Moe O (2017) Complications of chronic kidney disease: current state, knowledge gaps, and strategy for action. Kidney Int Suppl (2011) 7(2):122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kisu.2017.07.007
Luyckx VA, Tuttle KR, Garcia-Garcia G, Gharbi MB, Heerspink HJL, Johnson DW, Liu ZH, Massy ZA, Moe O, Nelson RG, Sola L, Wheeler DC, White SL (2017) Reducing major risk factors for chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 7(2):71–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kisu.2017.07.003
Covic A, Vervloet M, Massy ZA, Torres PU, Goldsmith D, Brandenburg V, Mazzaferro S, Evenepoel P, Bover J, Apetrii M, Cozzolino M (2018) Bone and mineral disorders in chronic kidney disease: implications for cardiovascular health and ageing in the general population. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 6(4):319–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30310-8
Floege J, Kronenberg F, Froissart M (2011) Mortality in chronic kidney disease and mineral metabolism. JAMA 306(2):159. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.948 (author reply 159-60)
Massy ZA, Drüeke TB (2015) Magnesium and cardiovascular complications of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 11(7):432–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.74
Oka T, Hamano T, Sakaguchi Y, Yamaguchi S, Kubota K, Senda M, Yonemoto S, Shimada K, Matsumoto A, Hashimoto N, Mori D, Monden C, Takahashi A, Obi Y, Yamamoto R, Takabatake Y, Kaimori JY, Moriyama T, Horio M, Matsui I, Isaka Y (2019) Proteinuria-associated renal magnesium wasting leads to hypomagnesemia: a common electrolyte abnormality in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34(7):1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy119
Arnaud MJ (2008) Update on the assessment of magnesium status. Br J Nutr 99(Suppl 3):S24-36. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711450800682X
Tong GM, Rude RK (2005) Magnesium deficiency in critical illness. J Intensive Care Med 20(1):3–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066604271539
Fang X, Liang C, Li M, Montgomery S, Fall K, Aaseth J, Cao Y (2016) Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake and cardiovascular mortality: a systematic review and dose-based meta-regression analysis of prospective studies. J Trace Elem Med Biol 38:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.03.014
Xu T, Sun Y, Xu T, Zhang Y (2013) Magnesium intake and cardiovascular disease mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Cardiol 167(6):3044–3047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.11.090
Ellison DH, Maeoka Y, McCormick JA (2021) Molecular mechanisms of renal magnesium reabsorption. J Am Soc Nephrol 32(9):2125–2136. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2021010042
Blaine J, Chonchol M, Levi M (2015) Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 10(7):1257–1272. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.09750913 (Epub 2014 Oct 6. Erratum in: Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Oct 7;10(10):1886-7)
William JH, Danziger J (2016) Magnesium deficiency and proton-pump inhibitor use: a clinical review. J Clin Pharmacol 56(6):660–668
Fan L, Zhu X, Rosanoff A, Costello RB, Yu C, Ness R, Seidner DL, Murff HJ, Roumie CL, Shrubsole MJ, Dai Q (2021) magnesium depletion score (MDS) predicts risk of systemic inflammation and cardiovascular mortality among US adults. J Nutr. 151(8):2226–2235. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxab138
Ahluwalia N, Dwyer J, Terry A, Moshfegh A, Johnson C (2016) Update on NHANES dietary data: focus on collection, release, analytical considerations, and uses to inform public policy. Adv Nutr 7(1):121–134. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.009258
Pfeiffer CM, Lacher DA, Schleicher RL, Johnson CL, Yetley EA (2017) Challenges and lessons learned in generating and interpreting NHANES nutritional biomarker data. Adv Nutr 8(2):290–307. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.014076
Gor D, Gerber BS, Walton SM et al (2020May) Antidiabetic drug use trends in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Diabetes 12(5):385–395
Institute of Medicine (1997) Dietary reference intakes: calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, vitamin D, and flouride. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Azem R, Daou R, Bassil E, Anvari EM, Taliercio JJ, Arrigain S, Schold JD, Vachharajani T, Nally J, Na Khoul GN (2020) Serum magnesium, mortality and disease progression in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol 21(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-020-1713-3
Yuan Q, Xie Y, Peng Z, Wang J, Zhou Q, Xiao X, Wang W, Huang L, Tang W, Li X, Zhang L, Wang F, Zhao MH, Tao L, He K, Wanggou S, Xu H, C-STRIDE study group (2021) Urinary magnesium predicts risk of cardiovascular disease in Chronic Kidney Disease stage 1–4 patients. Clin Nutr. 40(4):2394–2400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.036
Bressendorff I, Hansen D, Schou M, Silver B, Pasch A, Bouchelouche P, Pedersen L, Rasmussen LM, Brandi L (2016) Oral magnesium supplementation in chronic kidney disease stages 3 and 4: efficacy, safety, and effect on serum calcification propensity-a prospective randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial. Kidney Int Rep 2(3):380–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2016.12.008
Diaz-Tocados JM, Peralta-Ramirez A, Rodríguez-Ortiz ME, Raya AI, Lopez I, Pineda C, Herencia C et al (2017) Dietary magnesium supplementation prevents and reverses vascular and soft tissue calcifications in uremic rats. Kidney Int 92:1084–1099
Sarrafzadegan N, Khosravi-Boroujeni H, Lotfizadeh M, Pourmogaddas A, Salehi-Abargouei A (2016) Magnesium status and the metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition 32(4):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2015.09.014
Artunc F, Schleicher E, Weigert C, Fritsche A, Stefan N, Häring HU (2016) The impact of insulin resistance on the kidney and vasculature. Nat Rev Nephrol 12(12):721–737
Spoto B, Pisano A, Zoccali C (2016) Insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 311(6):F1087–F1108
López-Baltanás R, Encarnación Rodríguez-Ortiz M, Canalejo A, Díaz-Tocados JM, Herencia C, Leiva-Cepas F, Torres-Peña JD, Ortíz-Morales A, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Rodríguez M, Almadén Y (2021) Magnesium supplementation reduces inflammation in rats with induced chronic kidney disease. Eur J Clin Invest 51(8):e13561. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.13561
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by grants from 1.3.5 Project for Disciplines of Excellence-Clinical Research Incubation Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (2021HXFH007). The funders had no role in study design, data collection or analysis, preparation of the manuscript, or the decision to publish.
Conflict of interest disclosures (for all authors)
None.
Ethics Approval Statement
This study involved secondary data analysis of a nationally representative publicly available dataset. The study we conducted was exempt from institutional review for this reason.
Data availability
All data are publicly available at [https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/Default.aspx].
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, S., Zhou, Z., Lin, T. et al. Magnesium Depletion Score is Associated with Long-Term Mortality in Chronic Kidney Diseases: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. J Nephrol 36, 755–765 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-022-01489-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-022-01489-5