Abstract
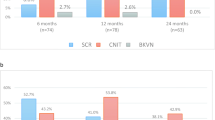
Subclinical rejection (SCR) has been variably associated with reduced graft survival, development and progression of interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy and chronic allograft nephropathy, but data are controversial concerning SCR treatment in terms of graft survival improvement. In this single-center retrospective study, we enrolled 174 adult kidney transplant recipients with a protocol biopsy performed at 30 days after transplantation to evaluate the incidence rate and risk factors for early SCR and its impact on 10-year graft survival. Five patients showed primary non function and were excluded. Among 159/169 (94.08 %) patients with stable graft function who underwent protocol biopsy, 17 (10.7 %) showed signs of SCR and were treated with low-dose intravenous (i.v.) steroids. Ten patients showed functional impairment, 8 (4.73 %) resulting as acute rejection. At multivariate analysis, donor age [odds ratio (OR) 1.04, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.01–1.09], and delayed graft function (DGF) (OR 1.08, 95 % CI 1.03–1.12) were significantly associated with SCR. The 10-year graft survival rate in the SCR group was similar to that in the normal-findings group (76.5 vs. 74.9 % respectively; p = 0.61). At multivariate Cox regression, acute [hazard ratio (HR) 5.22, 95 % CI 1.70–16.01], but not sub-clinical, rejection was independently associated with long-term graft failure. In conclusion, early protocol biopsy is a useful and safe tool to detect early SCR which seems not to affect the long-term survival. We suggest that this could be, probably, linked to early SCR treatment with low dose i.v. steroids.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, Bonsib SM, Castro MC, Cavallo T, Croker BP, Demetris AJ, Drachenberg CB, Fogo AB, Furness P, Gaber LW, Gibson IW, Glotz D, Goldberg JC, Grande J, Halloran PF, Hansen HE, Hartley B, Hayry PJ, Hill CM, Hoffman EO, Hunsicker LG, Lindblad AS, Yamaguchi Y et al (1999) The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int 55(2):713–723
Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL, O’Connell PJ, Allen RD, Chapman JR (2004) Natural history, risk factors, and impact of subclinical rejection in kidney transplantation. Transplantation 78(2):242–249
Rush D, Nickerson P, Gough J, McKenna R, Grimm P, Cheang M, Trpkov K, Solez K, Jeffery J (1998) Beneficial effects of treatment of early subclinical rejection: a randomized study. J Am Soc Nephrol 9(11):2129–2134
Nankivell BJ, Chapman JR (2006) The significance of subclinical rejection and the value of protocol biopsies. Am J Transplant 6(9):2006–2012
Shapiro R, Randhawa P, Jordan ML, Scantlebury VP, Vivas C, Jain A, Corry RJ, McCauley J, Johnston J, Donaldson J, Gray EA, Dvorchik I, Hakala TR, Fung JJ, Starzl TE (2001) An analysis of early renal transplant protocol biopsies–the high incidence of subclinical tubulitis. Am J Transplant 1(1):47–50
Miyagi M, Ishikawa Y, Mizuiri S, Aikawa A, Ohara T, Hasegawa A (2005) Significance of subclinical rejection in early renal allograft biopsies for chronic allograft dysfunction. Clin Transplant 19(4):456–465
Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL, O’Connell PJ, Allen RD, Chapman JR (2003) The natural history of chronic allograft nephropathy. N Engl J Med 349(24):2326–2333
Rush DN, Jeffery JR, Gough J (1995) Sequential protocol biopsies in renal transplant patients. Clinico-pathological correlations using the Banff schema. Transplantation 59(4):511–514
Shishido S, Asanuma H, Nakai H, Mori Y, Satoh H, Kamimaki I, Hataya H, Ikeda M, Honda M, Hasegawa A (2003) The impact of repeated subclinical acute rejection on the progression of chronic allograft nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(4):1046–1052
Seron D, Diaz-Gallo C, Grino JM, Castelao AM, Carrera M, Bover J, Alsina J (1991) Characterization of interstitial infiltrate in early renal allograft biopsies in patients with stable renal function. Transplant Proc 23(1 Pt 2):1267–1269
Choi BS, Shin MJ, Shin SJ, Kim YS, Choi YJ, Kim YS, Moon IS, Kim SY, Koh YB, Bang BK, Yang CW (2005) Clinical significance of an early protocol biopsy in living-donor renal transplantation: ten-year experience at a single center. Am J Transplant 5(6):1354–1360
Kanetsuna Y, Yamaguchi Y, Toma H, Tanabe K (2003) Histological evaluation of renal allograft protocol biopsies in the early period and 1 year after transplantation. Clin Transplant 17(Suppl 10):25–29
Rush D, Jeffery J, Trpkov K, Solez K, Gough J (1996) Effect of subclinical rejection on renal allograft histology and function at 6 months. Transplant Proc 28(1):494–495
Heilman RL, Devarapalli Y, Chakkera HA, Mekeel KL, Moss AA, Mulligan DC, Mazur MJ, Hamawi K, Williams JW, Reddy KS (2010) Impact of subclinical inflammation on the development of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant 10(3):563–570
Nankivell BJ, Fenton-Lee CA, Kuypers DR, Cheung E, Allen RD, O’Connell PJ, Chapman JR (2001) Effect of histological damage on long-term kidney transplant outcome. Transplantation 71(4):515–523
Rush DN, Karpinski ME, Nickerson P, Dancea S, Birk P, Jeffery JR (1999) Does subclinical rejection contribute to chronic rejection in renal transplant patients? Clin Transplant 13(6):441–446
Scholten EM, Rowshani AT, Cremers S, Bemelman FJ, Eikmans M, van Kan E, Mallat MJ, Florquin S, Surachno J, ten Berge IJ, Bajema IM, de Fijter JW (2006) Untreated rejection in 6-month protocol biopsies is not associated with fibrosis in serial biopsies or with loss of graft function. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(9):2622–2632
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group (2009) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant 9(Suppl 3):S1–S155
Vincenti F, Friman S, Scheuermann E, Rostaing L, Jenssen T, Campistol JM, Uchida K, Pescovitz MD, Marchetti P, Tuncer M, Citterio F, Wiecek A, Chadban S, El-Shahawy M, Budde K, Goto N (2007) Results of an international, randomized trial comparing glucose metabolism disorders and outcome with cyclosporine versus tacrolimus. Am J Transplant 7(6):1506–1514
Ekberg H, Tedesco-Silva H, Demirbas A, Vitko S, Nashan B, Gurkan A, Margreiter R, Hugo C, Grinyo JM, Frei U, Vanrenterghem Y, Daloze P, Halloran PF (2007) Reduced exposure to calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation. N Engl J Med 357(25):2562–2575
Ekberg H, Grinyo J, Nashan B, Vanrenterghem Y, Vincenti F, Voulgari A, Truman M, Nasmyth-Miller C, Rashford M (2007) Cyclosporine sparing with mycophenolate mofetil, daclizumab and corticosteroids in renal allograft recipients: the CAESAR Study. Am J Transplant 7(3):560–570
Thierry A, Thervet E, Vuiblet V, Goujon JM, Machet MC, Noel LH, Rioux-Leclercq N, Comoz F, Cordonnier C, Francois A, Marcellin L, Girardot-Seguin S, Touchard G (2011) Long-term impact of subclinical inflammation diagnosed by protocol biopsy one year after renal transplantation. Am J Transplant 11(10):2153–2161
Rush D, Arlen D, Boucher A, Busque S, Cockfield SM, Girardin C, Knoll G, Lachance JG, Landsberg D, Shapiro J, Shoker A, Yilmaz S (2007) Lack of benefit of early protocol biopsies in renal transplant patients receiving TAC and MMF: a randomized study. Am J Transplant 7(11):2538–2545
Roberts IS, Reddy S, Russell C, Davies DR, Friend PJ, Handa AI, Morris PJ (2004) Subclinical rejection and borderline changes in early protocol biopsy specimens after renal transplantation. Transplantation 77(8):1194–1198
Park JH, Yang CW, Kim YS, Lee SH, Choi YJ, Kim YS, Moon IS, Koh YB, Bang BK (2002) Comparisons of clinicopathological correlations between immediate and slow graft function in renal transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 16(Suppl 8):18–23
Schweitzer EJ, Drachenberg CB, Anderson L, Papadimetriou JC, Kuo PC, Johnson LB, Klassen DK, Hoehn-Saric E, Weir MR, Bartlett ST (1996) Significance of the Banff borderline biopsy. Am J Kidney Dis 28(4):585–588
Park JH, Yang CW, Kim YS, Moon IS, Chang YS, Koh YB, Bang BK (1999) Clinical impact of slow recovery of renal function in renal transplantation. Transplant Proc 31(7):2841–2842
Furness PN, Philpott CM, Chorbadjian MT, Nicholson ML, Bosmans JL, Corthouts BL, Bogers JJ, Schwarz A, Gwinner W, Haller H, Mengel M, Seron D, Moreso F, Canas C (2003) Protocol biopsy of the stable renal transplant: a multicenter study of methods and complication rates. Transplantation 76(6):969–973
Wilczek HE (1990) Percutaneous needle biopsy of the renal allograft. A clinical safety evaluation of 1129 biopsies. Transplantation 50(5):790–797
Rush DN, Grimm P, Gough J, Lipman M, Birk P, McKenna R, Nickerson P (1999) Prediction rejection: is early diagnosis achievable and important? Graft 2(Suppl. 2):s31–s35
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Armentano Filomena and Greco Angela for their nursing assistance in this study and all our Nephrology staff for their clinical assistance in this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gigliotti, P., Lofaro, D., Leone, F. et al. Early subclinical rejection treated with low dose i.v. steroids is not associated to graft survival impairment: 13-years’ experience at a single center. J Nephrol 29, 443–449 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-015-0206-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-015-0206-0