Abstract
Background
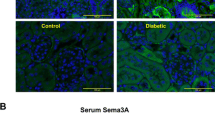
Semaphorins are guidance proteins implicated in several processes such as angiogenesis, organogenesis, cell migration, and cytokine release. Experimental studies showed that semaphorin-3a (SEMA3A) administration induces transient massive proteinuria, podocyte foot process effacement and endothelial cell damage in healthy animals. While SEMA3A signaling has been demonstrated to be mechanistically involved in experimental diabetic glomerulopathy and in acute kidney injury, to date its role in human chronic kidney disease (CKD) has not been investigated.
Methods
To test the hypothesis that SEMA3A may play a role in human CKD, we performed a cross-sectional, nested, case–control study on 151 matched hypertensive patients with and without CKD. SEMA3A was quantified in the urine (USEMA) by ELISA. Glomerular filtration rate was estimated (eGFR) by the CKD-EPI formula and albuminuria was measured as albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR).
Results
USEMA levels were positively correlated with urine ACR (p = 0.001) and serum creatinine (p < 0.001). USEMA was higher in patients with both components of renal damage as compared to those with only one and those with normal renal function (p < 0.007 and <0.001, respectively). The presence of increased USEMA levels (i.e. top quartile) entailed a fourfold higher risk of combined renal damage (p < 0.001) and an almost twofold higher risk of macroalbuminuria (p = 0.005) or of reduced eGFR, even adjusting for confounding factors (p = 0.002).
Conclusions
USEMA is independently associated with CKD in both diabetic and non diabetic hypertensive patients. Further studies may help clarify the mechanisms underlying this association and possibly the pathogenic changes leading to the development of CKD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vadasz Z, Toubi E (2013) Semaphorins: their dual role in regulating immune-mediated diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. doi:10.1007/s12016-013-8360-4
Roth L, Koncina E, Satkauskas S, Crémel G, Aunis D, Bagnard D (2009) The many faces of semaphorins: from development to pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:649–666
Vadasz Z, Haj T, Halasz K et al (2012) Semaphorin 3A is a marker for disease activity and a potential immunoregulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R146
Vadasz Z, Toubi E (2012) Semaphorin 3A––a marker for disease activity and a potential putative disease-modifying treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 21:1266–1270
Reidy KJ, Villegas G, Teichman J et al (2009) Semaphorin3a regulates endothelial cell number and podocyte differentiation during glomerular development. Development 136:3979–3989
Tufro A, Teichman J, Woda C, Villegas G (2008) Semaphorin3a inhibits ureteric bud branching morphogenesis. Mech Dev 125:558–568
Reidy K, Tufro A (2011) Semaphorins in kidney development and disease: modulators of ureteric bud branching, vascular morphogenesis, and podocyte–endothelial crosstalk. Pediatr Nephrol 26:1407–1412
Villegas G, Tufro A (2002) Ontogeny of semaphorins 3A and 3F and their receptors neuropilins 1 and 2 in the kidney. Gene Expr Patterns 2:151–155
Tapia R, Guan F, Gershin I, Teichman J, Villegas G, Tufro A (2008) Semaphorin3a disrupts podocyte foot processes causing acute proteinuria. Kidney Int 73:733–740
Jayakumar C, Ranganathan P, Devarajan P, Krawczeski CD, Looney S, Ramesh G (2013) Semaphorin 3A is a new early diagnostic biomarker of experimental and pediatric acute kidney injury. PLoS One 8:e58446. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058446
Veron D, Bertuccio CA, Marlier A et al (2011) Podocyte vascular endothelial growth factor (Vegf164) overexpression causes severe nodular glomerulosclerosis in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 54:1227–1241
Leoncini G, Viazzi F, Agabiti Rosei E et al (2010) Chronic kidney disease in hypertension under specialist care: the I-DEMAND study. J Hypertens 28:156–162
Leoncini G, Viazzi F, Agabiti Rosei E et al (2012) Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in high-risk Italian hypertensive patients: the I-DEMAND study. J Nephrol 25:63–74
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) et al (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612
Sciarretta S, Valenti V, Tocci G et al (2010) Association of renal damage with cardiovascular diseases is independent of individual cardiovascular risk profile in hypertension: data from the Italy-Developing Education and awareness on MicroAlbuminuria in patients with hypertensive Disease study. J Hypertens 28:251–258
Acevedo LM, Barillas S, Weis SM, Göthert JR, Cheresh DA (2008) Semaphorin 3A suppresses VEGF-mediated angiogenesis yet acts as a vascular permeability factor. Blood 111:2674–2680
Gansevoort RT, Nauta FL, Bakker SJ (2010) Albuminuria: all you need to predict outcomes in chronic kidney disease? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19:513–518
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an R01 Grant (1R01DK083379-01A3) to Ganesan Ramesh from NIH-NIDDK.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Ganesan Ramesh filed a provisional patent for the discovery of semaphorin 3A as a biomarker of injury and disease. All other authors declared no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viazzi, F., Ramesh, G., Jayakumar, C. et al. Increased urine semaphorin-3A is associated with renal damage in hypertensive patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested case–control study. J Nephrol 28, 315–320 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-014-0097-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-014-0097-5