Abstract
Background
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is one of the most common subtypes of thyroid carcinoma. Exosomal miR-181a plays an important role in the development of PTC. This study examined the regulatory mechanism of miR-181a under conditions of hypoxia and its impact on angiogenesis.
Methods
A ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation (RIP) experiment was conducted to verify the interaction between HOTAIR and RELA. The relationship between RELA and the miR-181a promoter was detected by ChIP-qPCR. Short hairpin (sh) RNA was designed to knock down HOTAIR in TPC cells. The underlying mechanism of miR-181a was verified by use of dual-luciferase assays and rescue experiments. The regulatory effect of GATA6 on angiogenesis was studied using CCK8, EdU, Transwell, and western blot assays.
Results
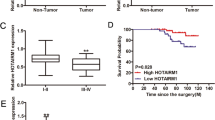
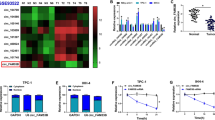
A RIP assay showed that HOTAIR could bind to RELA under hypoxic conditions. ChIP-qPCR and dual luciferase assays showed RELA could interact with the miR181a promoter and upregulate miR-181a. Knockdown of HOTAIR downregulated miR-181a in TPC-1 cells, and the downregulation could be rescued by RELA overexpression. MiR-181a downregulated GATA6 in HUVEC cells. Overexpression of GATA6 inhibited HUVEC proliferation, migration, tube formation, and EGFR expression. Exosomal miR-181a promoted angiogenesis by downregulating GATA6 expression.
Conclusion
HOTAIR activated RELA to upregulate miR-181a during hypoxia. Exosomal miR-181a promotes tumor angiogenesis by downregulating GATA6.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sherman SI (2003) Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet 361(9356):501–511
Siegel RL et al (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71(1):7–33
Xing M (2013) Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 13(3):184–199
Miro C et al (2021) Thyroid hormone enhances angiogenesis and the Warburg effect in squamous cell carcinomas. Cancers 13(11):2743
Park JE et al (2010) Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics 9(6):1085–1099
Wu F et al (2019) Exosomes increased angiogenesis in papillary thyroid cancer microenvironment. Endocr Relat Cancer 26(5):525–538
Zhu H et al (2016) Onco-lncRNA HOTAIR and its functional genetic variants in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Sci Rep 6:31969
Bhan A et al (2017) Histone methylase MLL1 coordinates with HIF and regulate lncRNA HOTAIR expression under hypoxia. Gene 629:16–28
Colombo M, Raposo G, Théry C (2014) Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30:255–289
Umezu T et al (2014) Exosomal miR-135b shed from hypoxic multiple myeloma cells enhances angiogenesis by targeting factor-inhibiting HIF-1. Blood 124(25):3748–3757
Huang X et al (2009) Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell 35(6):856–867
Moriondo G et al (2023) Intermittent hypoxia mediates cancer development and progression through HIF-1 and miRNA regulation. Arch Bronconeumol 59(10):629–637
Ghosh G et al (2010) Hypoxia-induced microRNA-424 expression in human endothelial cells regulates HIF-α isoforms and promotes angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 120(11):4141–4154
Bao L et al (2018) Metastasis-associated miR-23a from nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived exosomes mediates angiogenesis by repressing a novel target gene TSGA10. Oncogene 37(21):2873–2889
Yu J et al (2018) MicroRNA-181a promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer by targeting RASSF1A. Oncol Rep 40(4):1959–1970
Sun W et al (2018) MicroRNA-181a promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting SRCIN1 to promote the SRC/VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 9(4):438
Sun CX et al (2022) MiR-181a promotes cell proliferation and migration through targeting KLF15 in papillary thyroid cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 24(1):66–75
Hu M et al (2020) LncRNA HOTAIR knockdown inhibits glycolysis by regulating miR-130a-3p/HIF1A in hepatocellular carcinoma under hypoxia. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109703
Zhao X, Zhang W, Ji W (2018) miR-181a targets GATA6 to inhibit the progression of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Future Oncol 14(17):1741–1753
Sun X et al (2014) Systemic delivery of microRNA-181b inhibits nuclear factor-κb activation, vascular inflammation, and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E–deficient mice. Circ Res 114(1):32–40
Larsen AK et al (2011) Targeting EGFR and VEGF (R) pathway cross-talk in tumor survival and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Ther 131(1):80–90
Wang Y et al (2021) miR-181a, delivered by hypoxic PTC-secreted exosomes, inhibits DACT2 by downregulating MLL3, leading to YAP-VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 24:610–621
Xue X et al (2016) LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 35(21):2746–2755
Ding J et al (2018) Estrogen receptor β promotes renal cell carcinoma progression via regulating LncRNA HOTAIR-miR-138/200c/204/217 associated CeRNA network. Oncogene 37(37):5037–5053
Chang YT et al (2018) HOTAIR is a REST-regulated lncRNA that promotes neuroendocrine differentiation in castration resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Lett 433:43–52
Taniue K et al (2016) ASBEL-TCF3 complex is required for the tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(45):12739–12744
Özeş AR et al (2016) NF-κB-HOTAIR axis links DNA damage response, chemoresistance and cellular senescence in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 35(41):5350–5361
Li X et al (2014) Modulation of gene expression regulated by the transcription factor NF-κB/RelA. J Biol Chem 289(17):11927–11944
Kim GC et al (2018) Upregulation of Ets1 expression by NFATc2 and NFKB1/RELA promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness. Oncogenesis 7(11):91
Khare V et al (2019) RNA helicase p68 deploys β-catenin in regulating RelA/p65 gene expression: implications in colon cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):330
Chandrasekaran KS, Sathyanarayanan A, Karunagaran D (2017) miR-214 activates TP53 but suppresses the expression of RELA, CTNNB1, and STAT3 in human cervical and colorectal cancer cells. Cell Biochem Funct 35(7):464–471
Zhang Y et al (2014) Immunohistochemical evaluation of midkine and nuclear factor-kappa B as diagnostic biomarkers for papillary thyroid cancer and synchronous metastasis. Life Sci 118(1):39–45
Xu RX et al (2015) DNA damage-induced NF-κB activation in human glioblastoma cells promotes miR-181b expression and cell proliferation. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(3):913–925
Sun Y, Xiong X, Wang X (2019) RELA promotes hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells via LINC01693/miR-302d/CXCL12 axis. J Cell Biochem 120(8):12549–12558
Nam SY et al (2011) A hypoxia-dependent upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by nuclear factor-κB promotes gastric tumour growth and angiogenesis. Br J Cancer 104(1):166–174
Wu Q et al (2019) Exosome-mediated communication in the tumor microenvironment contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):53
Liu H et al (2022) Correction to: GATA6 suppresses migration and metastasis by regulating the miR-520b/CREB1 axis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis 13(3):243
Zhong Y et al (2011) GATA6 activates Wnt signaling in pancreatic cancer by negatively regulating the Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1. PLoS One 6(7):e22129
Song Y et al (2015) GATA6 is overexpressed in breast cancer and promotes breast cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by upregulating slug expression. Exp Mol Pathol 99(3):617–627
Peng T et al (2019) The interaction of LOXL2 with GATA6 induces VEGFA expression and angiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Oncol 55(3):657–670
Froese N et al (2011) GATA6 promotes angiogenic function and survival in endothelial cells by suppression of autocrine transforming growth factor beta/activin receptor-like kinase 5 signaling. J Biol Chem 286(7):5680–5690
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou (No. 202102010081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yingxue Wang conceived and designed the experiments. Jieying Lu, Xinyi Liu performed the experiments. Aiying Cen and Yuanjia Hong analyzed the data. Yingxue Wang wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Animal and human experiments are not involved in this manuscript.
Informed consent
For this type of study, no informed consent is required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Liu, X., Cen, A. et al. HYPOXIA induces lncRNA HOTAIR for recruiting RELA in papillary thyroid cancer cells to upregulate miR-181a and promote angiogenesis. J Endocrinol Invest (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-024-02388-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-024-02388-1