Abstract
Background
Today, limited and controversial data are available on predictive markers for diabetic retinopathy. Choroidal thickness (CT) is an unstable parameter affected by many factors. Also, previous studies had conflicting findings on choroidal thickness. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of choroidal vascularity index (CVI), a relatively new marker, in evaluating choroidal vascular status and its relationship with diabetic retinopathy (DR).
Materials and methods
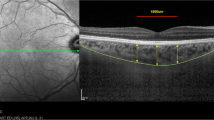
A total of 124 subjects, 84 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and 40 healthy controls, were included in the study. The patients were divided into two groups as follows: those without DR and those with non-proliferative DR (NPDRP). All subjects underwent enhanced-depth imaging optical coherence tomography (EDI-OCT), and CT values were noted. To measure CVI, luminal (LA) and stromal areas of the choroidal images were binarized using Image J program. CVI was defined as the proportion of LA to total choroid area (TCA). Demographic and laboratory data of the patients were collected retrospectively.
Results
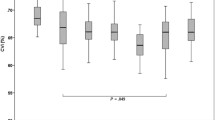
CVI were found to be lower in diabetic patients compared to non-diabetic patients. CVI values in 3 groups were as follows: 67.9% ± 1.8 (healthy controls), 66.1% ± 2.4 (no DR), and 63.2% ± 2.6 (NPDRP) (p < 0.001). All groups were similar in terms of CT values (p = 0.296). The cut-off value for CVI in predicting retinopathy was 64.7%. Hypertension and current smoking were found to be more frequent in diabetic patients with CVI < 64.7% compared to those with CVI > 64.7%.
Conclusions
CVI tends to be lower in diabetic patients with or without DR compared to healthy controls. Moreover, patients with DR have a lower CVI than those without DR. CVI can be considered an early and sensitive biomarker for the onset of DR.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zoungas S, Woodward M, Li Q, Cooper ME, Hamet P, Harrap S et al (2014) Impact of age, age at diagnosis and duration of diabetes on the risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications and death in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 57(12):2465–2474
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J (2001) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414(6865):782–787
Klein BE (2007) Overview of epidemiologic studies of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 14(4):179–183
Venturini M, Fiorina P, Maffi P, Losio C, Vergani A, Secchi A et al (2006) Early increase of retinal arterial and venous blood flow velocities at color Doppler imaging in brittle type 1 diabetes after islet transplant alone. Transplantation 81(9):1274–1277
Lovasik JV, Kergoat H (1993) Electroretinographic results and ocular vascular perfusion in type 1 diabetes. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 34(5):1731–1743
Holopigian K, Greenstein VC, Seiple W, Hood DC, Carr RE (1997) Evidence for photoreceptor changes in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 38(11):2355–2365
Regatieri CV, Branchini L, Carmody J, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS (2012) Choroidal thickness in patients with diabetic retinopathy analyzed by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Retina 32(3):563–568
Esmaeelpour M, Povazay B, Hermann B, Hofer B, Kajic V, Kapoor K et al (2010) Three-dimensional 1060-nm OCT: choroidal thickness maps in normal subjects and improved posterior segment visualization in cataract patients. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(10):5260–5266
Vujosevic S, Martini F, Cavarzeran F, Pilotto E, Midena E (2012) Macular and peripapillary choroidal thickness in diabetic patients. Retina 32(9):1781–1790
Xu J, Xu L, Du KF, Shao L, Chen CX, Zhou JQ et al (2013) Subfoveal choroidal thickness in diabetes and diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 120(10):2023–2028
Iovino C, Pellegrini M, Bernabei F, Borrelli E, Sacconi R, Govetto A et al (2020) Choroidal vascularity index: an in-depth analysis of this novel optical coherence tomography parameter. J Clin Med 9(2)
Goud A, Singh SR, Sahoo NK, Rasheed MA, Vupparaboina KK, Ankireddy S et al (2019) New insights on choroidal vascularity: a comprehensive topographic approach. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 60(10):3563–3569
Hidayat AA, Fine BS (1985) Diabetic choroidopathy. Light and electron microscopic observations of seven cases. Ophthalmology 92(4):512–522
Shiragami C, Shiraga F, Matsuo T, Tsuchida Y, Ohtsuki H (2002) Risk factors for diabetic choroidopathy in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 240(6):436–442
Hamadneh T, Aftab S, Sherali N, Vetrivel Suresh R, Tsouklidis N, An M (2020) Choroidal changes in diabetic patients with different stages of diabetic retinopathy. Cureus 12(10):e10871
Wang H, Tao Y (2019) Choroidal structural changes correlate with severity of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. BMC Ophthalmol 19(1):186
Kim M, Ha MJ, Choi SY, Park YH (2018) Choroidal vascularity index in type-2 diabetes analyzed by swept-source optical coherence tomography. Sci Rep 8(1):70
Tan KA, Laude A, Yip V, Loo E, Wong EP, Agrawal R (2016) Choroidal vascularity index - a novel optical coherence tomography parameter for disease monitoring in diabetes mellitus? Acta Ophthalmol 94(7):e612–e616
Sudhalkar A, Chhablani JK, Venkata A, Raman R, Rao PS, Jonnadula GB (2015) Choroidal thickness in diabetic patients of Indian ethnicity. Indian J Ophthalmol 63(12):912–916
Unsal E, Eltutar K, Zirtiloglu S, Dincer N, OzdoganErkul S, Gungel H (2014) Choroidal thickness in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Clin Ophthalmol 8:637–642
Rewbury R, Want A, Varughese R, Chong V (2016) Subfoveal choroidal thickness in patients with diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema. Eye (London) 30(12):1568–1572
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee by the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Keskin, Ç., Dilekçi, E.N.A., Üçgül, A.Y. et al. Choroidal vascularity index as a predictor for the development of retinopathy in diabetic patients. J Endocrinol Invest 47, 1175–1180 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02236-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02236-8