Abstract
Purpose
Musculoskeletal disorders are among the most disabling comorbidities in patients with acromegaly. This study examined muscle and bone quality in patients with acromegaly.
Methods
Thirty-three patients with acromegaly and nineteen age- and body mass index-matched healthy controls were included in the study. Body composition was determined using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. The participants underwent abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for cross-sectional evaluation of muscle area and vertebral MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF). Muscular strength was measured using hand grip strength (HGS). Skeletal muscle quality (SMQ) was classified as weak, low, or normal, according to HGS/ASM (appendicular skeletal muscle mass) ratio.
Results
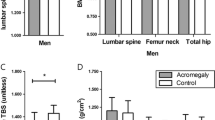
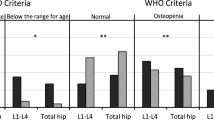
Groups had similar lean tissues, total body fat ratios, and total abdominal muscle areas. Acromegalic patients had lower pelvic BMD (p = 0.012) and higher vertebral MRI-PDFF (p = 0.014), while total and spine bone mineral densities (BMD) were similar between the groups. The SMQ score rate was normal only 57.5% in the acromegaly group, and 94.7% of the controls had a normal SMQ score (p = 0.01). Subgroup analysis showed that patients with active acromegaly (AA) had higher lean tissue and lower body fat ratios than controlled acromegaly (CA) and control groups. Vertebral MRI-PDFF was higher in the CA group than that in the AA and control groups (p = 0.022 and p = 0.001, respectively). The proportion of participants with normal SMQ was lower in the AA and CA groups than that in the control group (p = 0.012 and p = 0.013, respectively).
Conclusion
Acromegalic patients had reduced SMQ and pelvic BMD, but greater vertebral MRI-PDFF. Although lean tissue increases in AA, this does not affect SMQ. Therefore, increased vertebral MRI-PDFF in controlled acromegalic patients may be due to ectopic adiposity.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Rolla M, Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska A, Halupczok-Żyła J, Kałużny M, Konopka BM, Błoniecka I et al (2021) Complications and Comorbidities of Acromegaly-Retrospective Study in Polish Center. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:642131
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA (2019) Sarcopenia. Lancet 393(10191):2636–2646
Park J, Gil JR, Shin Y, Won SE, Huh J, You MW et al (2019) Reliable and robust method for abdominal muscle mass quantification using CT/MRI: an explorative study in healthy subjects. PLoS ONE 14(9):e0222042
He J, Fang H, Li X (2019) Vertebral bone marrow fat content in normal adults with varying bone densities at 3T magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Radiol 60(4):509–515
McNab TL, Khandwala HM (2005) Acromegaly as an endocrine form of myopathy: case report and review of literature. Endocr Pract 11(1):18–22
Padova G, Borzì G, Incorvaia L, Siciliano G, Migliorino V, Vetri M et al (2011) Prevalence of osteoporosis and vertebral fractures in acromegalic patients. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 8(3):37–43
Studenski SA, Peters KW, Alley DE, Cawthon PM, McLean RR, Harris TB et al (2014) The FNIH sarcopenia project: rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 69(5):547–558
Baumgartner RN, Koehler KM, Gallagher D, Romero L, Heymsfield SB, Ross RR et al (1998) Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am J Epidemiol 147(8):755–763
Khan AI, Reiter DA, Sekhar A, Sharma P, Safdar NM, Patil DH et al (2019) MRI quantitation of abdominal skeletal muscle correlates with CT-based analysis: implications for sarcopenia measurement. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 44(8):814–819
Prado CM, Lieffers JR, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, Sawyer MB, Martin L et al (2008) Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 9(7):629–635
Silva TLD, Mulder AP (2021) Sarcopenia and poor muscle quality associated with severe obesity in young adults and middle-aged adults. Clin Nutr ESPEN 45:299–305
Colao A, Ferone D, Marzullo P, Lombardi G (2004) Systemic complications of acromegaly: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr Rev 25(1):102–152
Biermasz NR, Pereira AM, Smit JW, Romijn JA, Roelfsema F (2005) Morbidity after long-term remission for acromegaly: persisting joint-related complaints cause reduced quality of life. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(5):2731–2739
Tütüncü NB, Erbaş T (2004) Factors associated with bone metabolism in acromegalic patients: hypogonadism and female gender. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 112(6):328–332
Ozer FF, Dagdelen S, Erbas T (2018) Relation of RANKL and OPG Levels with Bone Resorption in Patients with Acromegaly and Prolactinoma. Horm Metab Res 50(7):562–567
Claessen KM, Mazziotti G, Biermasz NR, Giustina A (2016) Bone and Joint Disorders in Acromegaly. Neuroendocrinology 103(1):86–95
Ueland T, Ebbesen EN, Thomsen JS, Mosekilde L, Brixen K, Flyvbjerg A et al (2002) Decreased trabecular bone biomechanical competence, apparent density, IGF-II and IGFBP-5 content in acromegaly. Eur J Clin Invest 32(2):122–128
Mazziotti G, Biagioli E, Maffezzoni F, Spinello M, Serra V, Maroldi R et al (2015) Bone turnover, bone mineral density, and fracture risk in acromegaly: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(2):384–394
Mazziotti G, Bianchi A, Bonadonna S, Cimino V, Patelli I, Fusco A et al (2008) Prevalence of vertebral fractures in men with acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(12):4649–4655
Claessen KM, Kroon HM, Pereira AM, Appelman-Dijkstra NM, Verstegen MJ, Kloppenburg M et al (2013) Progression of vertebral fractures despite long-term biochemical control of acromegaly: a prospective follow-up study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(12):4808–4815
Pelsma ICM, Biermasz NR, Pereira AM, van Furth WR, Appelman-Dijkstra NM, Kloppenburg M et al (2020) Progression of vertebral fractures in long-term controlled acromegaly: a 9-year follow-up study. Eur J Endocrinol 183(4):427–437
Kužma M, Vaňuga P, Ságová I, Pávai D, Jackuliak P, Killinger Z et al (2021) Vertebral fractures occur despite control of acromegaly and are predicted by cortical volumetric bone mineral density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 106(12):e5088–e5096
Godang K, Olarescu NC, Bollerslev J, Heck A (2016) Treatment of acromegaly increases BMD but reduces trabecular bone score: a longitudinal study. Eur J Endocrinol 175(2):155–164
Diamond T, Nery L, Posen S (1989) Spinal and peripheral bone mineral densities in acromegaly: the effects of excess growth hormone and hypogonadism. Ann Intern Med 111(7):567–573
Rajan R, Cherian KE, Kapoor N, Paul TV (2020) Trabecular bone score-an emerging tool in the management of osteoporosis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 24(3):237–243
Idilman IS, Yildiz AE, Karaosmanoglu AD, Ozmen MN, Akata D, Karcaaltincaba M (2022) Proton density fat fraction: magnetic resonance imaging applications beyond the liver. Diagn Interv Radiol 28(1):83–91
Schwartz AV, Sigurdsson S, Hue TF, Lang TF, Harris TB, Rosen CJ et al (2013) Vertebral bone marrow fat associated with lower trabecular BMD and prevalent vertebral fracture in older adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(6):2294–2300
Brummer RJ, Lönn L, Kvist H, Grangård U, Bengtsson BA, Sjöström L (1993) Adipose tissue and muscle volume determination by computed tomography in acromegaly, before and 1 year after adenomectomy. Eur J Clin Invest 23(4):199–205
Freda PU, Shen W, Reyes-Vidal CM, Geer EB, Arias-Mendoza F, Gallagher D et al (2009) Skeletal muscle mass in acromegaly assessed by magnetic resonance imaging and dual-photon x-ray absorptiometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(8):2880–2886
Füchtbauer L, Olsson DS, Bengtsson B, Norrman LL, Sunnerhagen KS, Johannsson G (2017) Muscle strength in patients with acromegaly at diagnosis and during long-term follow-up. Eur J Endocrinol 177(2):217–226
Guedes da Silva DP, Guimarães FS, Dias CM, Guimarães Sde A, Kasuki L, Gadelha MR et al (2013) On the functional capacity and quality of life of patients with acromegaly: are they candidates for rehabilitation programs? J Phys Ther Sci 25(11):1497–1501
Funding
This research was supported by the Hacettepe University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (Project number TTU-2021-19463).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
İmdat Eroğlu, Burçin Gönül İremli, Aysegul Erkoç, Ilkay S. Idilman, Deniz Yuce, Ebru Calik-Kutukcu, Deniz Akata, and Tomris Erbas declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hacettepe University (Project Number: GO 21/166, Decision Number:2021/05-38). The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all of the subjects.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eroğlu, İ., İremli, B.G., Erkoç, A. et al. Osteosarcopenia in acromegaly: reduced muscle quality and increased vertebral fat deposition. J Endocrinol Invest 46, 2573–2582 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02114-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02114-3