Abstract
Background
An impact of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis (CLT) on papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) outcome has long been advocated but it is still controversial.
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of CLT in a retrospective cohort of PTC patients and to characterize the lymphocytic subpopulations and infiltrate (LI).
Materials and methods
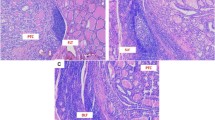
We assessed 375 PTC patients, aged 45.2 ± 16.4 years, and treated with thyroidectomy and radioiodine remnant ablation, with a mean follow-up of 6.28 ± 3.86 years. In a subgroup of patients (n = 81) tissue sections were reviewed for the presence of CLT or lymphocytes associated with tumor in absence of background thyroiditis (TAL); cytotoxic CD8+/regulatory Foxp3+ T lymphocyte (CD8+/Foxp3+) ratio was characterized by immunohistochemistry: a low ratio is suggestive of a less effective anti tumor immune response.
Results
Seventy-five/375 patients (20%) had a histological diagnosis of CLT and showed at the last follow-up a significantly better outcome compared to those with no CLT (cure rate: 91.8 versus 76.3%, p = 0.003). LI was characterized in 81 PTC patients (24 with CLT and 57 with TAL): the peri-tumoral CD8+/Foxp3+ ratio was lower in patients not cured at the final evaluation.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that concurrent CLT has a protective effect on PTC outcome and that the imbalance between cytotoxic and regulatory T lymphocytes in the peri-tumoral TAL may affect the tumor-specific immune response favoring a more aggressive behavior of cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Houghton AN, Guevara-Patiño JA (2004) Immune recognition of self in immunity against cancer. J Clin Investig 114:468–471. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI22685
Zou W (2006) Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 6:295–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1806
Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B, Zhang Z, Yang H, Zhang H, Zhou C, Yao J, Jin L, Wang H, Yang Y, Fu YX, Wang FS (2007) Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology 132:2328–2339. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.102
Leffers N, Gooden MJ, de Jong RA, Hoogeboom BN, ten Hoor KA, Hollema H, Boezen HM, van der Zee AG, Daemen T, Nijman HW (2009) Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes in primary and metastatic lesions of advanced stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0583-5
Gooden MJ, de Bock GH, Leffers N, Daemen T, Nijman HW (2011) The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 105:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.189
Singh B, Shaha AR, Trivedi H, Carew JF, Poluri A, Shah JP (1999) Coexistent Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with papillary thyroid carcinoma: impact on presentation, management, and outcome. Surgery 126:1070–1076
Souza SL, Montalli Da Assumpção LV, Ward LS (2003) Impact of previous thyroid autoimmune diseases on prognosis of patients with well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 13:491–495. https://doi.org/10.1089/105072503322021160
Kim EY, Kim WG, Kim WB, Kim TY, Kim JM, Ryu JS, Hong SJ, Gong G, Shong YK (2009) Coexistence of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with lower recurrence rates in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Clin Endocrinol 71:581–586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03537.x
Kebebew E, Treseler PA, Ituarte PH, Clark OH (2001) Coexisting chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and papillary thyroid cancer revisited. World J Surg 25:632–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002680020165
Schäffler A, Palitzsch KD, Seiffarth C, Höhne HM, Riedhammer FJ, Hofstädter F, Schölmerich J, Rüschoff J (1998) Coexistent thyroiditis is associated with lower tumour stage in thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Clin Invest 28:838–844
Loh KC, Greenspan FS, Dong F, Miller TR, Yeo PP (1999) Influence of lymphocytic thyroiditis on the prognostic outcome of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:458–462. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.2.5443
Cunha LL, Marcello MA, Ward LS (2014) The role of the inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis. Endocr Relat Cancer 21:R85–R103. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-13-0431 (PubMed PMID: 24302667)
Kim SK, Song KH, Lim SD, Lim YC, Yoo YB, Kim JS, Hwang TS (2009) Clinical and pathological features and the BRAF(V600E) mutation in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma with and without concurrent Hashimoto thyroiditis. Thyroid 19:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2008.0144
French JD, Weber ZJ, Fretwell DL, Said S, Klopper JP, Haugen BR (2010) Tumor-associated lymphocytes and increased FoxP3 + regulatory T cell frequency correlate with more aggressive papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:2325–2333. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-2564
French JD, Kotnis GR, Said S, Raeburn CD, McIntyre RC Jr, Klopper JP, Haugen BR (2012) Programmed death-1 + T cells and regulatory T cells are enriched in tumor-involved lymph nodes and associated with aggressive features in papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E934–E943. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-3428
Gogali F, Paterakis G, Rassidakis GZ, Kaltsas G, Liakou CI, Gousis P, Neonakis E, Manoussakis MN, Liapi C (2012) Phenotypical analysis of lymphocytes with suppressive and regulatory properties (Tregs) and NK cells in the papillary carcinoma of thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:1474–1482. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-1838
Cunha LL, Morari EC, Guihen AC, Razolli D, Gerhard R, Nonogaki S, Soares FA, Vassallo J, Ward LS (2012) Infiltration of a mixture of immune cells may be related to good prognosis in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Clin Endocrinol 77:918–925. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2012.04482
Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Pacini F, Schlumberger M, Sherman SI, Steward DL, Tuttle R (2009) Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelinesfor patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 19:1167–1214. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2009.0110 (Erratum. In: Thyroid. 2010Jun;20(6):674-5. Thyroid. 2010 Aug; 20(8):942. Hauger, Bryan R [corrected to Haugen, Bryan R])
Rotondi M, Coperchini F, Pignatti P, Sideri R, Groppelli G, Leporati P, La Manna L, Magri F, Mariotti S, Chiovato L (2013) Interferon-γ and tumor necrosisfactor-α sustain secretion of specific CXC chemokines in human thyrocytes: afirst step toward a differentiation between autoimmune and tumor-relatedinflammation? J Clin Endocrinology and Metabolism 98:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-2555
Marazuela M, García-López MA, Figueroa-Vega N, De La Fuente H, Alvarado-Sánchez B, Monsiváis-Urenda A, Sánchez-Madrid F, González-Amaro R (2006) Regulatory T cells in human autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3639–3646. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-2337
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Italian Ministry of Health- RF-2011-02350673.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilli, T., Toti, P., Occhini, R. et al. Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis (CLT) has a positive prognostic value in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) patients: the potential key role of Foxp3+ T lymphocytes. J Endocrinol Invest 41, 703–709 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0794-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0794-8