Abstract
Purpose
The incidence of thyroid cancer (TC) is increasing. Cytology by itself cannot distinguish TC from some benign nodules especially in certain subtypes of TC. Our immediate goal is to identify DNA methylation markers for early detection of TC and to molecularly differentiate TC subtypes from benign nodules.
Methods
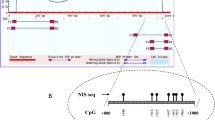
Promoter methylation status of 21 candidate genes was examined on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue (FFPE) utilizing quantitative methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (QMSP) in a retrospective cohort of 329 patients (56% white, 29% African American, 61% female) comprising 71 normal thyroid, 83 benign nodules [follicular adenomas (FA)], 90 follicular TC (FTC) and 85 papillary TC (PTC). All genes were analyzed individually (Kruskal–Wallis and Wilcoxon rank sum tests) and in combination (logistic regression models) to identify genes whose methylation levels might best separate groups.
Results
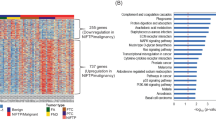
Combination gene panels TPO and UCHL1 (ROC = 0.607, sensitivity 78%) discriminated FTC from FA, and RASSF1 and TPO (ROC = 0.881, sensitivity 78%) discriminated FTC from normal. Methylation of TSHR distinguished PTC from FTC (ROC = 0.701, sensitivity 84%) and PTC from FA (ROC = 0.685, sensitivity 70%). The six gene panel of TIMP3, RARB2, SERPINB5, RASSF1, TPO and TSHR, which differentiates PTC from normal thyroid, had the best combination sensitivity (91%) and specificity (81%) of the panels addressing discrimination of cancer tissue.
Conclusions
Aberrant gene methylation used in combination panels may be useful clinically in differentiating FTC and PTC from benign nodules. If confirmed in additional studies, these findings could help reduce the over diagnosis of thyroid cancer and surgeries related to over diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simard EP, Ward EM, Siegel R, Jemal A (2012) Cancers with increasing incidence trends in the United States: 1999 through 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. doi:10.3322/caac.20141
Boufraqech M, Patel D, Xiong Y, Kebebew E (2013) Diagnosis of thyroid cancer: state of art. Expert Opin Med Diagn 7(4):331–342. doi:10.1517/17530059.2013.800481
McGee VF (ed) (2009) QuickFACTS thyroid cancer. American Cancer Society, Atlanta, pp 1–131
Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP (2008) Thyroid and parathyroid cancers. In: Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (eds) Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach, 11th edn. Cmp United Business Media, New York
Hermanek P, Sobin L (2002) Thyroid gland (ICD-OC73). TNM classification of malignant tumors, 6th edn. Springer, New York
Trovato M (2007) New research communication on thyroid tumor markers. In: Sinise G (ed) Tumor markers research perspectives. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, pp 191–202
Segev DL, Clark DP, Zeiger MA, Umbricht C (2003) Beyond the suspicious thyroid fine needle aspirate. A review. Acta Cytol 47(5):709–722
Gharib H, Goellner JR (1993) Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid: an appraisal. Ann Intern Med 118(4):282–289
Ulazzi L, Sabbioni S, Miotto E, Veronese A, Angusti A, Gafa R, Manfredini S, Farinati F, Sasaki T, Lanza G, Negrini M (2007) Nidogen 1 and 2 gene promoters are aberrantly methylated in human gastrointestinal cancer. Mol Cancer 6:17. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-6-17
Hellebrekers DM, Lentjes MH, van den Bosch SM, Melotte V, Wouters KA, Daenen KL, Smits KM, Akiyama Y, Yuasa Y, Sanduleanu S, Khalid-de Bakker CA, Jonkers D, Weijenberg MP, Louwagie J, van Criekinge W, Carvalho B, Meijer GA, Baylin SB, Herman JG, de Bruine AP, van Engeland M (2009) GATA4 and GATA5 are potential tumor suppressors and biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(12):3990–3997. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0055
Pattani KM, Zhang Z, Demokan S, Glazer C, Loyo M, Goodman S, Sidransky D, Bermudez F, Jean-Charles G, McCaffrey T, Padhya T, Phelan J, Spivakovsky S, Bowne HY, Goldberg JD, Rolnitzky L, Robbins M, Kerr AR, Sirois D, Califano JA (2010) Endothelin receptor type B gene promoter hypermethylation in salivary rinses is independently associated with risk of oral cavity cancer and premalignancy. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3(9):1093–1103. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0115
Arantes LM, de Carvalho AC, Melendez ME, Carvalho AL, Goloni-Bertollo EM (2014) Methylation as a biomarker for head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 50(6):587–592. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.02.015
Chen K, Sawhney R, Khan M, Benninger MS, Hou Z, Sethi S, Stephen JK, Worsham MJ (2007) Methylation of multiple genes as diagnostic and therapeutic markers in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133(11):1131–1138
Stephen JK, Chen KM, Merritt J, Chitale D, Divine G, Worsham MJ (2015) Methylation markers for early detection and differentiation of follicular thyroid cancer subtypes. Cancer Clin Oncol 4(2):1–12
Carvalho AL, Henrique R, Jeronimo C, Nayak CS, Reddy AN, Hoque MO, Chang S, Brait M, Jiang WW, Kim MM, Claybourne Q, Goldenberg D, Khan Z, Khan T, Westra WH, Sidransky D, Koch W, Califano JA (2011) Detection of promoter hypermethylation in salivary rinses as a biomarker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma surveillance. Clin Cancer Res 17(14):4782–4789. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0324
Youden WJ (1950) Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 3(1):32–35
Eberhardt N (2003) Biomarkers in thyroid neoplasia. In: American Thyroid Association 75th Annual Meeting, Palm Beach, FL, September 16–21
Elisei R, Cosci B, Romei C, Bottici V, Renzini G, Molinaro E, Agate L, Vivaldi A, Faviana P, Basolo F, Miccoli P, Berti P, Pacini F, Pinchera A (2008) Prognostic significance of somatic RET oncogene mutations in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer: a 10-year follow-up study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(3):682–687
Patel HH, Goyal N, Goldenberg D (2014) Imaging, genetic testing, and biomarker assessment of follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer. Ann Med 46(6):409–416. doi:10.3109/07853890.2014.923739
Spambalg D, Sharifi N, Elisei R, Gross JL, Medeiros-Neto G, Fagin JA (1996) Structural studies of the thyrotropin receptor and Gs alpha in human thyroid cancers: low prevalence of mutations predicts infrequent involvement in malignant transformation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(11):3898–3901. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.11.8923835
Xing M (2007) Gene methylation in thyroid tumorigenesis. Endocrinology 148(3):948–953
Xing M, Westra WH, Tufano RP, Cohen Y, Rosenbaum E, Rhoden KJ, Carson KA, Vasko V, Larin A, Tallini G, Tolaney S, Holt EH, Hui P, Umbricht CB, Basaria S, Ewertz M, Tufaro AP, Califano JA, Ringel MD, Zeiger MA, Sidransky D, Ladenson PW (2005) BRAF mutation predicts a poorer clinical prognosis for papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(12):6373–6379. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-0987
Costello JF, Fruhwald MC, Smiraglia DJ, Rush LJ, Robertson GP, Gao X, Wright FA, Feramisco JD, Peltomaki P, Lang JC, Schuller DE, Yu L, Bloomfield CD, Caligiuri MA, Yates A, Nishikawa R, Su Huang H, Petrelli NJ, Zhang X, O’Dorisio MS, Held WA, Cavenee WK, Plass C (2000) Aberrant CpG-island methylation has non-random and tumour-type-specific patterns. Nat Genet 24(2):132–138. doi:10.1038/72785
Lin SY, Yeh KT, Chen WT, Chen HC, Chen ST, Chang JG (2004) Promoter CpG methylation of caveolin-1 in sporadic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 24(3a):1645–1650
Smith JA, Fan CY, Zou C, Bodenner D, Kokoska MS (2007) Methylation status of genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133(10):1006–1011
Hu S, Liu D, Tufano RP, Carson KA, Rosenbaum E, Cohen Y, Holt EH, Kiseljak-Vassiliades K, Rhoden KJ, Tolaney S, Condouris S, Tallini G, Westra WH, Umbricht CB, Zeiger MA, Califano JA, Vasko V, Xing M (2006) Association of aberrant methylation of tumor suppressor genes with tumor aggressiveness and BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Cancer 119(10):2322–2329. doi:10.1002/ijc.22110
Xing M, Cohen Y, Mambo E, Tallini G, Udelsman R, Ladenson PW, Sidransky D (2004) Early occurrence of RASSF1A hypermethylation and its mutual exclusion with BRAF mutation in thyroid tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 64(5):1664–1668
Carvalho AL, Jeronimo C, Kim MM, Henrique R, Zhang Z, Hoque MO, Chang S, Brait M, Nayak CS, Jiang WW, Claybourne Q, Tokumaru Y, Lee J, Goldenberg D, Garrett-Mayer E, Goodman S, Moon CS, Koch W, Westra WH, Sidransky D, Califano JA (2008) Evaluation of promoter hypermethylation detection in body fluids as a screening/diagnosis tool for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14(1):97–107. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0722
Donninger H, Vos MD, Clark GJ (2007) The RASSF1A tumor suppressor. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 18):3163–3172. doi:10.1242/jcs.010389
Ruf J, Carayon P (2006) Structural and functional aspects of thyroid peroxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys 445(2):269–277. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2005.06.023
Korah R, Healy JM, Kunstman JW, Fonseca AL, Ameri AH, Prasad ML, Carling T (2013) Epigenetic silencing of RASSF1A deregulates cytoskeleton and promotes malignant behavior of adrenocortical carcinoma. Mol Cancer 12:87. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-87
Schagdarsurengin U, Gimm O, Hoang-Vu C, Dralle H, Pfeifer GP, Dammann R (2002) Frequent epigenetic silencing of the CpG island promoter of RASSF1A in thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res 62(13):3698–3701
Hoque MO, Rosenbaum E, Westra WH, Xing M, Ladenson P, Zeiger MA, Sidransky D, Umbricht CB (2005) Quantitative assessment of promoter methylation profiles in thyroid neoplasms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(7):4011–4018. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-0313
Brown TC, Juhlin CC, Healy JM, Prasad ML, Korah R, Carling T (2014) Frequent silencing of RASSF1A via promoter methylation in follicular thyroid hyperplasia: a potential early epigenetic susceptibility event in thyroid carcinogenesis. JAMA Surg 149(11):1146–1152. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2014.1694
Ruggeri RM, Campenni A, Baldari S, Trimarchi F, Trovato M (2008) What is new on thyroid cancer biomarkers. Biomark Insights 3:237–252
Hou P, Bojdani E, Xing M (2010) Induction of thyroid gene expression and radioiodine uptake in thyroid cancer cells by targeting major signaling pathways. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(2):820–828
Venkataraman GM, Yatin M, Marcinek R, Ain KB (1999) Restoration of iodide uptake in dedifferentiated thyroid carcinoma: relationship to human Na+/I-symporter gene methylation status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(7):2449–2457
Kim WG, Zhu X, Kim DW, Zhang L, Kebebew E, Cheng SY (2013) Reactivation of the silenced thyroid hormone receptor beta gene expression delays thyroid tumor progression. Endocrinology 154(1):25–35. doi:10.1210/en.2012-1728
Nikiforov YE, Seethala RR, Tallini G, Baloch ZW, Basolo F, Thompson LD, Barletta JA, Wenig BM, Al Ghuzlan A, Kakudo K, Giordano TJ, Alves VA, Khanafshar E, Asa SL, El-Naggar AK, Gooding WE, Hodak SP, Lloyd RV, Maytal G, Mete O, Nikiforova MN, Nose V, Papotti M, Poller DN, Sadow PM, Tischler AS, Tuttle RM, Wall KB, LiVolsi VA, Randolph GW, Ghossein RA (2016) Nomenclature revision for encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a paradigm shift to reduce overtreatment of indolent tumors. JAMA Oncol 2(8):1023–1029. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0386
Acknowledgements
Dr. Stephen had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Supported by NIH R03 CA159426 (Dr. Josena K. Stephen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this retrospective study, formal consent is not required. The current IRB is authorized for chart review and collection of discarded thyroid tissue. The latter obviates the need for informed consent.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephen, J.K., Chen, K.M., Merritt, J. et al. Methylation markers differentiate thyroid cancer from benign nodules. J Endocrinol Invest 41, 163–170 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0702-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0702-2