Abstract
Background
Obesity is strongly linked to increased blood pressure, which increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. To our knowledge, little literature reported the information about galanin levels in obese individuals with hypertension. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the possible involvement of galanin in the pathogenesis of obese subjects with hypertension.
Methods
We measured body mass index and blood pressure of 38 obese patients with hypertension, 44 obese controls with normal blood pressure and 44 lean controls with normal blood pressure. Blood samples from all cases were collected at 8:00 a.m. after an overnight fast to determine the fasting plasma concentration of galanin, glucose, insulin, triglyceride, total cholesterol, high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Results
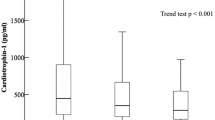
We found that plasma galanin levels were significantly decreased in obese patients with hypertension compared with the obese control group, whereas the galanin levels were significantly increased in obese controls compared with lean controls. Furthermore, in both obese groups the galanin levels were negatively correlative to diastolic blood pressure and positively correlative to insulin and triglyceride levels, but not to heart rate.
Conclusions
Low galanin levels were one of characters of obese patients with high blood pressure, and this levels may be taken as a novel biomarker to predict the development of high blood pressure in obese patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA et al (2006) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 113:898–918
Mi YJ, Zhang B, Wang HJ et al (2015) Prevalence and secular trends in obesity among Chinese adults, 1991–2011. Am J Prev Med 49(5):661–669
De Giorgis T, Marcovecchio ML, Giannini C et al (2016) Blood pressure from childhood to adolescence in obese youths in relation to insulin resistance and asymmetric dimethylarginine. J Endocrinol Invest 39:169–176
Simonds SE, Pryor JT, Ravussin E et al (2014) Leptin mediates the increase in blood pressure associated with obesity. Cell 159:1404–1416
Fang P, Yu M, Shi M et al (2012) Galanin peptide family as a modulating target for contribution to metabolic syndrome. Gen Comp Endocrinol 179:115–120
Lang R, Gundlach AL, Holmes FE et al (2015) Physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of galanin peptides and receptors: three decades of emerging diversity. Pharmacol Rev 67:118–175
Fang P, Yu M, Guo L et al (2012) Galanin and its receptors: a novel strategy for appetite control and obesity therapy. Peptides 36:331–339
Baranowska B, Wasilewska-Dziubińska E, Radzikowska M et al (1997) Neuropeptide Y, galanin, and leptin release in obese women and in women with anorexia nervosa. Metabolism 46:1384–1389
Baranowska B, Radzikowska M, Wasilewska-Dziubinska E et al (2000) Disturbed release of gastrointestinal peptides in anorexia nervosa and in obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab 2:99–103
Díaz-Cabiale Z, Parrado C, Vela C et al (2005) Role of galanin and galanin (1-15) on central cardiovascular control. Neuropeptides 39:185–190
Narváez JA, Diaz Z, Aguirre JA et al (1994) Intracisternally injected galanin-(1-15) modulates the cardiovascular responses of galanin-(1-29) and the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT. Eur J Pharmacol 257:257–265
Degli Uberti EC, Ambrosio MR, Bondanelli M et al (1995) Human galanin reduces plasma norepinephrine levels in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:1894–1898
Zhou BF (2002) Cooperative Meta-Analysis Group of the Working Group on Obesity in C. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults–study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci 15:83–96
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR et al (2003) The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572
Abbott SB, Pilowsky PM (2009) Galanin microinjection into rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat is hypotensive and attenuates sympathetic chemoreflex. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:1019–1026
Narváez JA, Díaz-Cabiale Z, Hedlund PB et al (2000) The galanin receptor antagonist M40 blocks the central cardiovascular actions of the galanin N-terminal fragment (1-15). Eur J Pharmacol 399:197–203
Coelho EF, Ferrari MF, Maximino JR et al (2004) Decreases in the expression of CGRP and galanin mRNA in central and peripheral neurons related to the control of blood pressure following experimental hypertension in rats. Brain Res Bull 64:59–66
Degli Uberti EC, Bondanelli M, Margutti A et al (1996) Acute administration of human galanin in normal subjects reduces the potentiating effect of pyridostigmine-induced cholinergic enhancement on release of norepinephrine and pancreatic polypeptide. Neuroendocrinology 64:398–404
Díaz-Cabiale Z, Narváez JA, Yanaihara N et al (2000) Galanin/alpha2-receptor interactions in central cardiovascular control. Neuropharmacology 39:1377–1385
Leibowitz SF, Dourmashkin JT, Chang GQ et al (2004) Acute high-fat diet paradigms link galanin to triglycerides and their transport and metabolism in muscle. Brain Res 1008:168–178
Plaisier CL, Kyttälä M, Weissglas-Volkov D et al (2009) Galanin preproprotein is associated with elevated plasma triglycerides. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:147–152
Bray GA, York DA (1998) The MONA LISA hypothesis in the time of leptin. Recent Prog Horm Res 53:95–117
Milewicz A, Mikulski E, Bidzinska B (2002) Plasma insulin, cholecystokinin, galanin, neuropeptide Y and leptin levels in obese women with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:152–153
Tang G, Wang Y, Park S et al (2012) Go2 G protein mediates galanin inhibitory effects on insulin release from pancreatic β cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:2636–2641
Anouar Y, Eiden LE (1995) Rapid and long-lasting increase in galanin mRNA levels in rat adrenal medulla following insulin-induced reflex splanchnic nerve stimulation. Neuroendocrinology 62:611–618
Belai A, Calcutt NA, Carrington AL et al (1996) Enteric neuropeptides in streptozotocin-diabetic rats; effects of insulin and aldose reductase inhibition. J Auton Nerv Syst 58:163–169
Wang J, Leibowitz KL (1997) Central insulin inhibits hypothalamic galanin and neuropeptide Y gene expression and peptide release in intact rats. Brain Res 777:231–236
Tang C, Akabayashi A, Manitiu A et al (1997) Hypothalamic galanin gene expression and peptide levels in relation to circulating insulin: possible role in energy balance. Neuroendocrinology 65:265–275
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Program of Taizhou, China (Grant No. TS201512), the National Health and Family Planning Commission of China (Grant No. W201309), the Natural Scientific Fund of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No. 14KJB310012) and the Jiangsu Postgraduate Scientific Research and Innovation Projects (Grant No. KYLX15_1387).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies of human were in accordance with the ethical standards of Ethics Committee of Clinical Medical College, Yangzhou University. This article does not contain any study data with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals recruited in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, P., Yu, M., Gu, X. et al. Low levels of plasma galanin in obese subjects with hypertension. J Endocrinol Invest 40, 63–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0529-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0529-2