Abstract
Aim
To evaluate the relationship between inflammatory and pro inflammatory markers, with obesity and visceral adiposity in male subjects with or without metabolic syndrome (MS).
Subjects and methods
A total of 37 patients with MS and 37 age matched controls were included (mean age 46.35 ± 1.6 years). MS was defined by the criteria of the international diabetes federation 2005. Anthropometric and biochemical profiles, including high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (Hs-CRP), visfatin and interleukin 6 (IL-6), were measured. Data were compared between groups by using t test. Pearson’s correlation was used to evaluate the relationship between variables. P values less than 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
Results
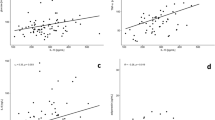
In patients with MS, CRP and IL-6 were significantly correlated with body mass index, waist circumference and waist to hip ratio. Visfatin levels were significantly lower in patients with MS compared to controls (log visfatin: 1.74 ± 0.27 vs. 1.86 ± 0.13 ng/ml, MS vs. control group respectively). We cannot find any significant correlation between visfatin, CRP and IL-6. Also there were no correlation between visfatin levels and any anthropometric parameters in patients with MS or control groups.
Conclusion
Serum visfatin was lower in patients with MS. Therefore it seems that visfatin could not be considered as a pro inflammatory adipocytokine in MS. The positive associations of obesity and visceral adiposity with elevated CRP and IL-6 levels suggest the importance of reducing visceral adiposity to prevent the risk of coronary disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CHD:
-
Coronary heart disease
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular diseases
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EIA:
-
Enzyme immunoassay
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- Hs-CRP:
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- IDF:
-
International diabetes federation
- MS:
-
Metabolic syndrome
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TLGS:
-
Tehran lipid and glucose study
- WHR:
-
Waist to hip ratio
- WC:
-
Waist circumference
References
Lorenzo C, Williams K, Hunt KJ, Haffner SM (2007) The national cholesterol education program-adult treatment panel III, International Diabetes Federation, and World Health Organization definitions of the metabolic syndrome as predictors of incident cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Diabetes Care 30(1):8
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2005) The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet 366(9491):1059
Zimmet P, Magliano D, Matsuzawa Y, Alberti G, Shaw J (2005) The metabolic syndrome: a global public health problem and a new definition. Vascular 7:8
Maury E, Brichard S (2010) Adipokine dysregulation, adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol 314(1):1–16
Lemieux I, Pascot A, Couillard C, Lamarche B, Tchernof A, Alméras N et al (2000) Hypertriglyceridemic waist: a marker of the atherogenic metabolic triad (hyperinsulinemia; hyperapolipoprotein B; small, dense LDL) in men? Circulation 102(2):179–184
Carr DB, Utzschneider KM, Hull RL, Kodama K, Retzlaff BM, Brunzell JD et al (2004) Intra-abdominal fat is a major determinant of the national cholesterol education program adult treatment panel III criteria for the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 53(8):2087–2094
Reaven GM (1988) Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37(12):1595
Koh KK, Han SH, Quon MJ (2005) Inflammatory markers and the metabolic syndrome: insights from therapeutic interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol 46(11):1978–1985
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116(7):1793
Juge-Aubry CE, Henrichot E, Meier CA (2005) Adipose tissue: a regulator of inflammation. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 19(4):547–566
Rifai N, Ridker PM (2001) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: a novel and promising marker of coronary heart disease. Clin Chem 47(3):403
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Rose L, Buring JE, Cook NR (2002) Comparison of C-reactive protein and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in the prediction of first cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med 347(20):1557–1565
Devaraj S, Singh U, Jialal I (2009) Human C-reactive protein and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Lipidol 20(3):182
Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CDA, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW (1999) C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19(4):972–978
Bastard JP, Jardel C, Delattre J, Hainque B, Bruckert E, Oberlin F (1999) Evidence for a link between adipose tissue interleukin-6 content and serum C-reactive protein concentrations in obese subjects. Circulation 99(16):2219–2222
Ognjanovic S, Bao S, Yamamoto S, Garibay-Tupas J, Samal B, Bryant-Greenwood G (2001) Genomic organization of the gene coding for human pre-B-cell colony enhancing factor and expression in human fetal membranes. J Mol Endocrinol 26(2):107–117
Kralisch S, Klein J, Lossner U, Bluher M, Paschke R, Stumvoll M et al (2005) Interleukin-6 is a negative regulator of visfatin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289(4):E586–E590
Kralisch S, Klein J, Lossner U, Bluher M, Paschke R, Stumvoll M et al (2005) Hormonal regulation of the novel adipocytokine visfatin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Endocrinol 185(3):R1
Ahima RS (2006) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Obesity 14:242S–249S
Fukuhara A, Matsuda M, Nishizawa M, Segawa K, Tanaka M, Kishimoto K et al (2005) Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science 307(5708):426
Pagano C, Pilon C, Olivieri M, Mason P, Fabris R, Serra R et al (2006) Reduced plasma visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in obesity is not related to insulin resistance in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(8):3165
Haider DG, Schindler K, Schaller G, Prager G, Wolzt M, Ludvik B (2006) Increased plasma visfatin concentrations in morbidly obese subjects are reduced after gastric banding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(4):1578
Sandeep S, Velmurugan K, Deepa R, Mohan V (2007) Serum visfatin in relation to visceral fat, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. Metabolism 56(4):565–570
Berndt J, Klöting N, Kralisch S, Kovacs P, Fasshauer M, Schön MR et al (2005) Plasma visfatin concentrations and fat depot–specific mRNA expression in humans. Diabetes 54(10):2911
Zahorska-Markiewicz B, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Janowska J, Kocelak P, Semik-Grabarczyk E, Holecki M et al (2007) Serum concentration of visfatin in obese women. Metabolism 56(8):1131–1134
Jin H, Jiang B, Tang J, Lu W, Wang W, Zhou L et al (2008) Serum visfatin concentrations in obese adolescents and its correlation with age and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 79(3):412–418
Davutoglu M, Ozkaya M, Guler E, Garipardic M, Gursoy H, Karabiber H et al (2009) Plasma visfatin concentrations in childhood obesity: relationships with insulin resistance and anthropometric indices. Swiss Med Wkly 139(1–2):22–27
Revollo JR, Körner A, Mills KF, Satoh A, Wang T, Garten A et al (2007) Nampt/PBEF/visfatin regulates insulin secretion in [beta] cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metab 6(5):363–375
Saddi-Rosa P, Oliveira CSV, Giuffrida FMA, Reis AF (2010) Visfatin, glucose metabolism and vascular disease: a review of evidence. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2(1):1–6
Azizi F, Rahmani M, Emami H, Mirmiran P, Hajipour R, Madjid M et al (2002) Cardiovascular risk factors in an Iranian urban population: Tehran lipid and glucose study (phase 1). Soz Praventivmed 47(6):408–426
Azizi F, Ghanbarian A, Momenan AA, Hadaegh F, Mirmiran P, Hedayati M et al (2009) Prevention of non-communicable disease in a population in nutrition transition: Tehran lipid and glucose study phase II. Trials 10(5):19166627
Seo JA, Jang ES, Kim BG, Ryu OH, Kim HY, Lee KW et al (2008) Plasma visfatin levels are positively associated with circulating interleukin-6 in apparently healthy Korean women. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 79(1):108–111
Kim JH, Kim SH, Im JA, Lee DC (2010) The relationship between visfatin and metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women. Maturitas 67(1):67–71
Zhong M, Tan H, Gong H, Wang S, Zhang Y, Zhang W (2008) Increased serum visfatin in patients with metabolic syndrome and carotid atherosclerosis. Clin Endocrinol 69(6):878–884
Filippatos T, Derdemezis C, Gazi I, Lagos K, Kiortsis D, Tselepis A et al (2008) Increased plasma visfatin levels in subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Eur J Clin Invest 38(1):71–72
Lin CC, Lai MM, Li TC, Li CI, Liu CS, Chen CC et al (2009) Relationship between serum retinol-binding protein 4 and visfatin and the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 85(1):24–29
Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Kocełak P, Janowska J, Skorupa A, Nylec M, Zahorska-Markiewicz B (2011) Plasma visfatin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a) levels in metabolic syndrome. Kardiol Polska 69(8):802
Chen CC, Li TC, Li CI, Liu CS, Lin WY, Wu MT et al (2007) The relationship between visfatin levels and anthropometric and metabolic parameters: association with cholesterol levels in women. Metabolism 56(9):1216–1220
Wen Y, Wang H, Wu J, Lu H, Hu XF, Cianflone K (2006) Effects of fatty acid regulation on visfatin gene expression in adipocytes. Chin Med J (Engl) 119(20):1701
MacLaren R, Cui W, Cianflone K (2007) Visfatin expression is hormonally regulated by metabolic and sex hormones in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes and adipocytes. Diabetes Obes Metab 9(4):490–497
Nüsken KD, Niisken E, Petrasch M, Rauh M, Dötsch J (2007) Preanalytical influences on the measurement of visfatin by enzyme immuno assay. Clin Chim Acta 382(1–2):154–156
Körner A, Garten A, Blüher M, Tauscher R, Kratzsch J, Kiess W (2007) Molecular characteristics of serum visfatin and differential detection by immunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(12):4783–4791
Mohamed-Ali V, Pinkney J, Coppack S (1998) Adipose tissue as an endocrine and paracrine organ. Int J Obes 22:1145–1158
Pickup J, Mattock M, Chusney G, Burt D (1997) NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X. Diabetologia 40(11):1286–1292
Yudkin JS, Kumari M, Humphries SE, Mohamed-Ali V (2000) Inflammation, obesity, stress and coronary heart disease: is interleukin-6 the link? Atherosclerosis 148(2):209–214
Florez H, Castillo-Florez S, Mendez A, Casanova-Romero P, Larreal-Urdaneta C, Lee D et al (2006) C-reactive protein is elevated in obese patients with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 71(1):92–100
Lyon CJ, Law RE, Hsueh WA (2003) Minireview: adiposity, inflammation, and atherogenesis. Endocrinology 144(6):2195–2200
Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Nakamura T (1999) Molecular mechanism of metabolic syndrome x: contribution of adipocytokines· adipocyte-derived bioactive substances. Ann N Y Acad Sci 892(1):146–154
Clement K, Viguerie N, Poitou C, Carette C, Pelloux V, Curat CA et al (2004) Weight loss regulates inflammation-related genes in white adipose tissue of obese subjects. FASEB J 18(14):1657–1669
Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A (2004) Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol 25(1):4–7
Fernández-Real JM, Ricart W (2003) Insulin resistance and chronic cardiovascular inflammatory syndrome. Endocr Rev 24(3):278–301
Arnaud C, Burger F, Steffens S, Veillard NR, Nguyen TH, Trono D et al (2005) Statins reduce interleukin-6-induced C-reactive protein in human hepatocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(6):1231–1236
Acknowledgments
We thank all persons who participated in this study. We also thank Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences for this collaboration within the framework of the Tehran lipid and glucose study (TLGS). This piece of research was granted by Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (grant number: 6068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J., Golpaie, A., Foroughi, M. et al. The relationship between visfatin and serum concentrations of C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 917–922 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0457-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0457-1