Abstract
Introduction
Cushing’s disease (CD) results from uncontrolled hypercortisolism induced by ACTH-secreting corticotroph adenomas; accordingly, patients diagnosed with CD usually present several comorbidities and an increased risk of mortality. Hypothesis-driven screenings have led to identification of rare alterations in a low number of patients, although the genetic basis underlying CD has remained unclear until recently. Using whole-exome sequencing, recurrent mutations have been reported in the gene coding for the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 (USP8), a protein with deubiquitinase (DUB) activity that modulates the lysosomal turnover of the EGF receptor (EGFR) and other membrane proteins.
Methods
In this review, we summarize the recent genetic findings and discuss the clinical and pathological implications of USP8 deregulation in corticotroph adenomas.
Conclusions
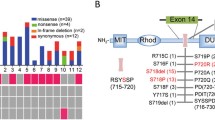
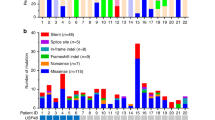
Mutations in USP8 have been identified in 35–62 % of functional sporadic corticotroph adenomas causing Cushing’s disease, but not in any other type of pituitary tumor. These mutations are found mostly in adult female patients and lead to an aberrant DUB activation by impairing the regulation of USP8 by members of the 14-3-3 family of proteins. The consequence of this hyperactivation is a longer retention of EGFR at the plasma membrane which promotes an enhanced production of ACTH.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Cushing’s disease
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- POMC:
-
Pro-opiomelacortin
- USP8:
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 8
- DUB:
-
Deubiquitinase
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
References
Lacroix A, Feelders RA, Stratakis CA, Nieman LK (2015) Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet 6736:1–15
Sharma ST, Nieman LK, Feelders RA (2015) Comorbidities in Cushing’s disease. Pituitary 18:188–194
Ezzat S, Asa SL, Couldwell WT et al (2004) The prevalence of pituitary adenomas: a systematic review. Cancer 101:613–619
Libuit LG, Karageorgiadis AS, Sinaii N et al (2015) A gender-dependent analysis of Cushing’s disease in childhood: pre-and postoperative follow-up. Clin Endocrinol 83:72–77
Storr HL, Isidori AM, Monson JP et al (2004) Prepubertal Cushing’s disease is more common in males, but there is no increase in severity at diagnosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3818–3820
Storr HL, Alexandraki KI, Martin L et al (2011) Comparisons in the epidemiology, diagnostic features and cure rate by transsphenoidal surgery between paediatric and adult-onset Cushing’s disease. Eur J Endocrinol 164:667–674
Lonser RR, Wind JJ, Nieman LK et al (2013) Outcome of surgical treatment of 200 children with Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:892–901
Gicquel C, Le Bouc Y, Luton JP et al (1992) Monoclonality of corticotroph macroadenomas in Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75:472–475
Biller BM, Alexander JM, Zervas NT et al (1992) Clonal origins of adrenocorticotropin-secreting pituitary tissue in Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75:1303–1309
Schulte HM, Oldfield EH, Allolio B et al (1991) Clonal composition of pituitary adenomas in patients with Cushing’s disease: determination by X-chromosome inactivation analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 73:1302–1308
Stratakis CA, Tichomirowa MA, Boikos S et al (2010) The role of germline AIP, MEN1, PRKAR1A, CDKN1B and CDKN2C mutations in causing pituitary adenomas in a large cohort of children, adolescents, and patients with genetic syndromes. Clin Genet 78:457–463
Georgitsi M, Raitila A, Karhu A et al (2007) Brief report: germline CDKN1B/p27Kip1 mutation in multiple endocrine neoplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:3321–3325
Korbonits M, Storr HL, Kumar AV (2012) Familial pituitary adenomas—who should be tested for AIP mutations? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 77:351–356
Cazabat L, Bouligand J, Salenave S et al (2012) Germline AIP mutations in apparently sporadic pituitary adenomas: prevalence in a prospective single-center cohort of 443 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:663–670
Preda V, Korbonits M, Cudlip S et al (2014) Low rate of germline AIP mutations in patients with apparently sporadic pituitary adenomas before the age of 40: a single-centre adult cohort. Eur J Endocrinol 171:659–666
Williamson EA, Ince PG, Harrison D et al (1995) G-protein mutations in human pituitary adrenocorticotrophic hormone-secreting adenomas. Eur J Clin Invest 25:128–131
Xekouki P, Stratakis CA (2012) Succinate dehydrogenase (SDHx) mutations in pituitary tumors: could this be a new role for mitochondrial complex II and/or Krebs cycle defects? Endocr Relat Cancer 19:33–40
De Menis E, Roncaroli F, Calvari V et al (2005) Corticotroph adenoma of the pituitary in a patient with X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita due to a novel mutation of the DAX-1 gene. Eur J Endocrinol 153:211–215
De Kock L, Sabbaghian N, Plourde F et al (2014) Pituitary blastoma: a pathognomonic feature of germ-line DICER1 mutations. Acta Neuropathol 128:111–122
Pinto EM, Siqueira SA, Cukier P et al (2011) Possible role of a radiation-induced p53 mutation in a Nelson’s syndrome patient with a fatal outcome. Pituitary 14:400–404
Karl M, Lamberts SW, Koper JW et al (1996) Cushing’s disease preceded by generalized glucocorticoid resistance: clinical consequences of a novel, dominant-negative glucocorticoid receptor mutation. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 108:296–307
Beuschlein F, Boulkroun S, Osswald A et al (2013) Somatic mutations in ATP1A1 and ATP2B3 lead to aldosterone-producing adenomas and secondary hypertension. Nat Genet 45:440–444
Beuschlein F, Fassnacht M, Assié G et al (2014) Constitutive activation of PKA catalytic subunit in adrenal Cushing’s syndrome. N Engl J Med 370:1019–1028
Reincke M, Sbiera S, Hayakawa A et al (2014) Mutations in the deubiquitinase gene USP8 cause Cushing’s disease. Nat Genet 47:31–38
Pérez-Rivas LG, Theodoropoulou M, Ferraù F et al (2015) The gene of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 is frequently mutated in adenomas causing Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E997–E1004
Ma ZY, Song ZJ, Chen JH et al (2015) Recurrent gain-of-function USP8 mutations in Cushing’s disease. Cell Res 25:306–317
Mizuno E, Kitamura N, Komada M (2007) 14-3-3-dependent inhibition of the deubiquitinating activity of UBPY and its cancellation in the M phase. Exp Cell Res 313:3624–3634
Naviglio S (1998) UBPY: a growth-regulated human ubiquitin isopeptidase. EMBO J 17:3241–3250
Niendorf S, Oksche A, Kisser A et al (2007) Essential role of ubiquitin-specific protease 8 for receptor tyrosine kinase stability and endocytic trafficking in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 27:5029–5039
Cao Z, Wu X, Yen L et al (2007) Neuregulin-induced ErbB3 downregulation is mediated by a protein stability cascade involving the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1. Mol Cell Biol 27:2180–2188
Byun S, Lee SYY, Lee J et al (2013) USP8 is a novel target for overcoming gefitinib resistance in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:3894–3904
Meijer IMJ, van Leeuwen JEM (2011) ERBB2 is a target for USP8-mediated deubiquitination. Cell Signal 23:458–467
Goh LK, Sorkin A (2013) Endocytosis of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a017459
Avraham R, Yarden Y (2011) Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:104–117
Mizuno E, Iura T, Mukai A et al (2005) Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulation by UBPY-mediated deubiquitination at endosomes. Mol Biol Cell 16:5163–5174
Kontogeorgos G, Stefaneanu L, Kovacs K, Cheng Z (1996) Localization of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) in human pituitary adenomas and nontumorous pituitaries: an immunocytochemical study. Endocr Pathol 7:63–70
Theodoropoulou M, Arzberger T, Gruebler Y et al (2004) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in neoplastic pituitary cells: evidence for a role in corticotropinoma cells. J Endocrinol 183:385–394
Onguru O, Scheithauer BW, Kovacs K et al (2004) Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor and activated epidermal growth factor receptor expression in pituitary adenomas and carcinomas. Mod Pathol 17:772–780
Honda J, Oomizu S, Kiuchi Y et al (2000) Identification of epidermal growth factor mRNA-expressing cells in the mouse anterior pituitary. Neuroendocrinology 71:155–162
Fukuoka H, Cooper O, Ben-Shlomo A et al (2011) EGFR as a therapeutic target for human, canine, and mouse ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas. J Clin Invest 121:4712–4721
Acknowledgments
M.R. is supported by the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung (Grant # 2012_A103) and the German Research Foundation (DFG, Grant # RE 752/20-1). L.G.P.R. is supported by funds from the People Programme (Marie Curie Actions) of the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) under REA Grant Agreement No. 608765.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez-Rivas, L.G., Reincke, M. Genetics of Cushing’s disease: an update. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 29–35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0353-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0353-0