Abstract
Purpose
The present study is firstly designed to identify the relationship between serum omentin-1 concentration, body fat mass and bone mineral density in healthy Chinese male adults in Changsha city.
Methods
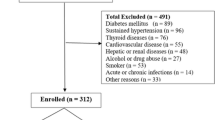
A total of 219 (20–80 years old) healthy subjects were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. Serum omentin-1, adiponectin, leptin, resistin and bone turn over biochemical markers were measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Bone mineral density (BMD) and fat body composition were determined using dual-energy-X-ray absorptiometry.
Results
Serum omentin-1 levels in the overweight subjects were significantly lower than those of the subjects with normal weight (p < 0.05). Omentin-1 was negatively correlated with weight (r = −0.418), body mass index (BMI, r = −0.419), waist circumference (r = −0.402), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR, r = −0.355), fat body mass (FBM, r = −0.430), fat % (r = −0.408), trunk fat (−0.431). However, after controlling for age, BMI and FBM, no significant correlation was noticed between omentin-1 and BMD at different skeletal sites. Pearson’s correlation coefficients and partial correlation coefficients after adjustment showed no significant correlations between omentin-1 and bone turn over biochemical markers, including bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and bone cross-linked N-terminal telopeptides of type I collagen. Multiple line stepwise regression analysis revealed that FBM, WHR, adiponectin were important variables affecting omentin-1. Moreover, lean tissue mass was the most important factor affecting BMD and explained 10.5–14.7 % of the variance. Omentin-1, leptin and resistin were not the predictors of BMD.
Conclusions
Serum omentin-1 was negatively correlated with FBM and BMI in healthy Chinese male adults, It was not significantly correlated with bone turnover biochemical markers. Omentin-1 may exert ambiguous effects on BMD, which maybe caused by the complex interactions among adipokines, hormonal activity, and body composition and bone metabolism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meier U, Gressner AM (2004) Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism: review of pathobiochemical and clinical chemical aspects of leptin, ghrelin, adiponectin, and resistin. Clin Chem 50:1511–1525
Kralisch S, Klein J, Bluher M, Paschke R, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M (2005) Therapeutic perspectives of adipocytokines. Expert Opin Pharmacother 6:863–872
Schaffler A, Neumeier M, Herfarth H, Furst A, Scholmerich J, Buchler C (2005) Genomic structure of human omentin, a new adipocytokine expressed in omental adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta 1732:96–102
Yang RZ, Lee MJ, Hu H, Pray J, Wu HB, Hansen BC, Shuldiner AR, Fried SK, McLenithan JC, Gong DW (2006) Identification of omentin as a novel depot-specific adipokine in human adipose tissue: possible role in modulating insulin action. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E1253–E1261
de Souza Batista CM, Yang RZ, Lee MJ, Glynn NM, Yu DZ, Pray J, Ndubuizu K, Patil S, Schwartz A, Kligman M, Fried SK, Gong DW, Shuldiner AR, Pollin TI, McLenithan JC (2007) Omentin plasma levels and gene expression are decreased in obesity. Diabetes 56:1655–1661
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalan V, Ortega F, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Ricart W, Fruhbeck G, Fernandez-Real JM (2010) Circulating omentin concentration increases after weight loss. Nutr Metab (Lond) 7:27
Tan BK, Pua S, Syed F, Lewandowski KC, O’Hare JP, Randeva HS (2008) Decreased plasma omentin-1 levels in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 25:1254–1255
Tan BK, Adya R, Farhatullah S, Chen J, Lehnert H, Randeva HS (2010) Metformin treatment may increase omentin-1 levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes 59:3023–3031
Duan XY, Xie PL, Ma YL, Tang SY (2011) Omentin inhibits osteoblastic differentiation of calcifying vascular smooth muscle cells through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Amino Acids 41:1223–1231
Yamawaki H, Tsubaki N, Mukohda M, Okada M, Hara Y (2010) Omentin, a novel adipokine, induces vasodilation in rat isolated blood vessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:668–672
Guo LJ, Jiang TJ, Liao L, Liu H, He HB (2013) Relationship between serum omentin-1 level and bone mineral density in girls with anorexia nervosa. J Endocrinol Invest 36:190–194
Xie H, Xie PL, Luo XH, Wu XP, Zhou HD, Tang SY, Liao EY (2012) Omentin-1 exerts bone-sparing effect in ovariectomized mice. Osteoporos Int 23:1425–1436
Xie H, Xie PL, Wu XP, Chen SM, Zhou HD, Yuan LQ, Sheng ZF, Tang SY, Luo XH, Liao EY (2011) Omentin-1 attenuates arterial calcification and bone loss in osteoprotegerin-deficient mice by inhibition of RANKL expression. Cardiovasc Res 92:296–306
Reid IR (2010) Fat and bone. Arch Biochem Biophys 503:20–27
Williams GA, Wang Y, Callon KE, Watson M, Lin JM, Lam JB, Costa JL, Orpe A, Broom N, Naot D, Reid IR, Cornish J (2009) In vitro and in vivo effects of adiponectin on bone. Endocrinology 150:3603–3610
Confavreux CB, Levine RL, Karsenty G (2009) A paradigm of integrative physiology, the crosstalk between bone and energy metabolisms. Mol Cell Endocrinol 310:21–29
Lim S, Joung H, Shin CS, Lee HK, Kim KS, Shin EK, Kim HY, Lim MK, Cho SI (2004) Body composition changes with age have gender-specific impacts on bone mineral density. Bone 35:792–798
Mizuma N, Mizuma M, Yoshinaga M, Iwamoto I, Matsuo T, Douchi T, Osame M (2006) Difference in the relative contribution of lean and fat mass components to bone mineral density with generation. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 32:184–189
Cai RC, Wei L, Di JZ, Yu HY, Bao YQ, Jia WP (2009) Expression of omentin in adipose tissues in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 89:381–384
Tohidi M, Akbarzadeh S, Larijani B, Kalantarhormozi M, Ostovar A, Assadi M, Vahdat K, Farrokhnia M, Sanjdideh Z, Amirinejad R, Nabipour I (2012) Omentin-1, visfatin and adiponectin levels in relation to bone mineral density in Iranian postmenopausal women. Bone 51:876–881
Assadi M, Salimipour H, Akbarzadeh S, Nemati R, Jafari SM, Bargahi A, Samani Z, Seyedabadi M, Sanjdideh Z, Nabipour I (2011) Correlation of circulating omentin-1 with bone mineral density in multiple sclerosis: the crosstalk between bone and adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 6:e24240
Oh KW, Lee WY, Rhee EJ, Baek KH, Yoon KH, Kang MI, Yun EJ, Park CY, Ihm SH, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Park SW (2005) The relationship between serum resistin, leptin, adiponectin, ghrelin levels and bone mineral density in middle-aged men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 63:131–138
Moseley KF, Dobrosielski DA, Stewart KJ, De Beur SM, Sellmeyer DE (2011) Lean mass and fat mass predict bone mineral density in middle-aged individuals with noninsulin-requiring type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 74:565–571
Biver E, Salliot C, Combescure C, Gossec L, Hardouin P, Legroux-Gerot I, Cortet B (2011) Influence of adipokines and ghrelin on bone mineral density and fracture risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:2703–2713
Holecki M, Wiecek A (2010) Relationship between body fat mass and bone metabolism. Pol Arch Med Wewn 120:361–367
Wang QP, Yang L, Li XP, Xie H, Liao EY, Wang M, Luo XH (2012) Effects of 17beta-estradiol on adiponectin regulation of the expression of osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand. Bone 51:515–523
Sheng Z, Xu K, Ou Y, Dai R, Luo X, Liu S, Su X, Wu X, Xie H, Yuan L, Liao E (2011) Relationship of body composition with prevalence of osteoporosis in central south Chinese postmenopausal women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 74:319–324
Kobayashi Y, Udagawa N, Takahashi N (2009) Action of RANKL and OPG for osteoclastogenesis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 19:61–72
Kearns AE, Khosla S, Kostenuik PJ (2008) Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease. Endocr Rev 29:155–192
Morcov C, Vulpoi C, Branisteanu D (2012) Correlation between adiponectin, leptin, insulin growth factor-1 and bone mineral density in pre and postmenopausal women. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 116:785–789
Gregson CL, Paggiosi MA, Crabtree N, Steel SA, McCloskey E, Duncan EL, Fan B, Shepherd JA, Fraser WD, Smith GD, Tobias JH (2013) Analysis of body composition in individuals with high bone mass reveals a marked increase in fat mass in women but not men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:818–828
Richards JB, Valdes AM, Burling K, Perks UC, Spector TD (2007) Serum adiponectin and bone mineral density in women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1517–1523
Kontogianni MD, Dafni UG, Routsias JG, Skopouli FN (2004) Blood leptin and adiponectin as possible mediators of the relation between fat mass and BMD in perimenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 19:546–551
Blain H, Vuillemin A, Guillemin F, Durant R, Hanesse B, de Talance N, Doucet B, Jeandel C (2002) Serum leptin level is a predictor of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:1030–1035
Wosje KS, Binkley TL, Kalkwarf HJ, Specker BL (2004) Relationships between bone mass and circulating leptin concentrations in Hutterites. Bone 34:1017–1022
Juan CC, Au LC, Fang VS, Kang SF, Ko YH, Kuo SF, Hsu YP, Kwok CF, Ho LT (2001) Suppressed gene expression of adipocyte resistin in an insulin-resistant rat model probably by elevated free fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:1328–1333
Schinke T, Haberland M, Jamshidi A, Nollau P, Rueger JM, Amling M (2004) Cloning and functional characterization of resistin-like molecule gamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:356–362
Yang B, Sun H, Wan Y, Wang H, Qin W, Yang L, Zhao H, Yuan J, Yao B (2012) Associations between testosterone, bone mineral density, vitamin D and semen quality in fertile and infertile Chinese men. Int J Androl 35:783–792
Abu EO, Horner A, Kusec V, Triffitt JT, Compston JE (1997) The localization of androgen receptors in human bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:3493–3497
De Oliveira DH, Fighera TM, Bianchet LC, Kulak CA, Kulak J (2012) Androgens and bone. Minerva Endocrinol 37:305–314
Kang D, Liu Z, Wang Y, Zhang H, Feng X, Cao W, Wang P (2014)Relationship of body composition with bone mineral density in northern Chinese men by body mass index levels. J Endocrinol Invest. [Epub ahead of print]
Misra M, Klibanski A (2011) Bone metabolism in adolescents with anorexia nervosa. J Endocrinol Invest 34:324–332
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X.P., Zeng, S., Wang, M. et al. Relationships between serum omentin-1, body fat mass and bone mineral density in healthy Chinese male adults in Changsha area. J Endocrinol Invest 37, 991–1000 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0140-3