Abstract
Introduction
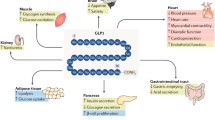
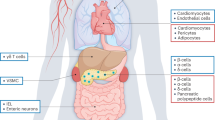
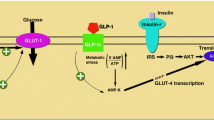
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is an intestinal hormone secreted after the ingestion of various nutrients. The main role of GLP-1 is to stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. However, the expression of GLP-1 receptor was found to be expressed in a variety of tissues beyond pancreas such as lung, stomach, intestine, kidney, heart and brain. Beyond pancreas, a beneficial effect of GLP-1 on body weight reduction has been shown, suggesting its role for the treatment of obesity. In addition, GLP-1 has been demonstrated to reduce cardiovascular risk factors and to have a direct cardioprotective effect, fostering heart recovery after ischemic injury. Further, data from both experimental animal models and human studies have shown beneficial effect of GLP-1 on bone metabolism, either directly or indirectly on bone cells.
Materials and methods
We review here the recent findings of the extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 focusing on both basic and clinical studies, thus opening future perspectives to the use of GLP-1 analogs for the treatment of disease beyond type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
Finally, the GLP-1 has been demonstrated to have a beneficial effect on both vascular, degenerative diseases of central nervous system and psoriasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holst JJ (2007) The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev 87:1409–1439. doi:10.1152/physrev.00034.2006
Lamont BJ, Li Y, Kwan E et al (2012) Pancreatic GLP-1 receptor activation is sufficient for incretin control of glucose metabolism in mice. J Clin Invest 122:388–402
D’Alessio DA, Kahn SE, Leusner CR, Ensinck JW (1994) Glucagon-like peptide 1 enhances glucose tolerance both by stimulation of insulin release and by increasing insulin-independent glucose disposal. J Clin Invest 93:2263–2266. doi:10.1172/JCI117225
Chai W, Zhang X, Barrett EJ, Liu Z (2014) Glucagon-like peptide 1 recruits muscle microvasculature and improves insulin’s metabolic action in the presence of insulin resistance. Diabetes
Hare KJ, Knop FK, Asmar M et al (2009) Preserved inhibitory potency of GLP-1 on glucagon secretion in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4679–4687
Creutzfeldt WO, Kleine N, Willms B et al (1996) Glucagonostatic actions and reduction of fasting hyperglycemia by exogenous glucagon-like peptide I(7-36) amide in type I diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 19:580–586
Nauck MA, Niedereichholz U, Ettler R et al (1997) Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibition of gastric emptying outweighs its insulinotropic effects in healthy humans. Am J Physiol 273:981–988
Blundell JE, Naslund E (1999) Glucagon-like peptide-1, satiety and appetite control. Br J Nutr 81:259–260
Pyke C, Heller RS, Kirk RK et al (2014) GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology 155:1280–1290
Mikhail N (2014) Effects of incretin-based therapy in patients with heart failure and myocardial infarction. Endocrine. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0175-4
Barrera JG, Sandoval DA, D’Alessio DA, Seeley RJ (2011) GLP-1 and energy balance: an integrated model of short-term and long-term control. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:507–516. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2011.77
Hsieh J, Longuet C, Baker CL et al (2010) The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor is essential for postprandial lipoprotein synthesis and secretion in hamsters and mice. Diabetologia 53:552–561
Imeryuz N, Yegen BC, Bozkurt A et al (1997) Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits gastric emptying via vagal afferent-mediated central mechanisms. Am J Physiol 273:920–927
Yamada C, Yamada Y, Tsukiyama K et al (2008) The murine glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is essential for control of bone resorption. Endocrinology 149:574–579
Seufert J, Gallwitz B (2013) The extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: a focus on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems. Diabetes Obes Metab
Seino Y, Fukushima M, Yabe D (2010) GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: similarities and differences. J Diabetes Investig 1:8–23. doi:10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x
Turton MD, O’Shea D, Gunn I et al (1996) A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 379:69–72. doi:10.1038/379069a0
Alhadeff AL, Rupprecht LE, Hayes MR (2012) GLP-1 neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract project directly to the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens to control for food intake. Endocrinology 153:647–658
Dossat AM, Lilly N, Kay K, Williams DL (2011) Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors in nucleus accumbens affect food intake. J Neurosci 31:14453–14457
Bullock BP, Heller RS, Habener JF (1996) Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Endocrinology 137:2968–2978
Arakawa M, Mita T, Azuma K et al (2010) Inhibition of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4. Diabetes 59:1030–1037. doi:10.2337/db09-1694
Martin B, Dotson CD, Shin Y-K et al (2009) Modulation of taste sensitivity by GLP-1 signaling in taste buds. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1170:98–101. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.03920.x
Lankat-Buttgereit B, Goke R, Fehmann HC et al (1994) Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding for the GLP-1 receptor expressed in rat lung. Exp Clin Endocrinol 102:341–347
Liberman A, Esser M, Marx N, Burgmaier M (2013) Glucagon-like peptide-1(9-36) inhibits chemokine-induced migration of human CD4-positive lymphocytes. PLoS One 8:e58445. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058445
Ussher JR, Drucker DJ (2014) Cardiovascular actions of incretin-based therapies. Circ Res 114:1788–1803. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.301958
Nuche-Berenguer B, Portal-Nunez S, Moreno P et al (2010) Presence of a functional receptor for GLP-1 in osteoblastic cells, independent of the cAMP-linked GLP-1 receptor. J Cell Physiol 225:585–592
Seufert J, Gallwitz B (2014) A focus on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(8):673–688. doi:10.1111/dom.12251
Vilsboll T, Christensen M, Junker AE et al (2012) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ (Clinical Res ed) 344:d7771. doi:10.1136/bmj.d7771
Van Bloemendaal L, Ten Kulve JS, la Fleur SE et al (2014) Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on appetite and body weight: focus on the CNS. J Endocrinol 221:T1–T16. doi:10.1530/JOE-13-0414
Vahl TP, Tauchi M, Durler TS et al (2007) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors expressed on nerve terminals in the portal vein mediate the effects of endogenous GLP-1 on glucose tolerance in rats. Endocrinology 148:4965–4973
Abbott CR, Monteiro M, Small CJ et al (2005) The inhibitory effects of peripheral administration of peptide YY(3-36) and glucagon-like peptide-1 on food intake are attenuated by ablation of the vagal-brainstem-hypothalamic pathway. Brain Res 1044:127–131. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.03.011
Fujiwara K, Gotoh K, Chiba S et al (2012) Intraportal administration of DPP-IV inhibitor regulates insulin secretion and food intake mediated by the hepatic vagal afferent nerve in rats. J Neurochem 121:66–76
Hayes MR, Kanoski SE, De Jonghe BC et al (2011) The common hepatic branch of the vagus is not required to mediate the glycemic and food intake suppressive effects of glucagon-like-peptide-1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:1479–1485
Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V, Pan W (2002) Interactions of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) with the blood–brain barrier. J Mol Neurosci 18:7–14
Hölscher C (2012) Potential role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in neuroprotection. CNS Drugs 26:871–882. doi:10.2165/11635890-000000000-00000
McClean PL, Parthsarathy V, Faivre E, Holscher C (2011) The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 31:6587–6594
McClean PL, Gault VA, Harriott P, Hölscher C (2010) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues enhance synaptic plasticity in the brain: a link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 630:158–162. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.12.023
Xiong H, Zheng C, Wang J et al (2013) The neuroprotection of liraglutide on Alzheimer-like learning and memory impairment by modulating the hyperphosphorylation of tau and neurofilament proteins and insulin signaling pathways in mice. J Alzheimers Dis 37:623–635
Yang Y, Zhang J, Ma D et al (2013) Subcutaneous administration of liraglutide ameliorates Alzheimer-associated tau hyperphosphorylation in rats with type 2 diabetes. J Alzheimers Dis 37:637–648
Bertilsson G, Patrone C, Zachrisson O et al (2008) Peptide hormone exendin-4 stimulates subventricular zone neurogenesis in the adult rodent brain and induces recovery in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 86:326–338
Li Y, Perry T, Kindy MS et al (2009) GLP-1 receptor stimulation preserves primary cortical and dopaminergic neurons in cellular and rodent models of stroke and Parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1285–1290. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806720106
Harkavyi A, Abuirmeileh A, Lever R et al (2008) Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation reverses key deficits in distinct rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 5:19
Aviles-Olmos I, Dickson J, Kefalopoulou Z et al (2013) Exenatide and the treatment of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Invest 123:2730–2736
Li Y, Chigurupati S, Holloway HW et al (2012) Exendin-4 ameliorates motor neuron degeneration in cellular and animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 7(2):e32008. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032008
Knippenberg S, Thau N, Dengler R et al (2012) Intracerebroventricular injection of encapsulated human mesenchymal cells producing glucagon-like peptide 1 prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALS. PLoS One 7
Sun H, Knippenberg S, Thau N et al (2013) Therapeutic potential of N-acetyl-glucagon-like peptide-1 in primary motor neuron cultures derived from non-transgenic and SOD1-G93A ALS mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:347–357
Lee CH, Yan B, Yoo K-Y et al (2011) Ischemia-induced changes in glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and neuroprotective effect of its agonist, exendin-4, in experimental transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res 89:1103–1113
Teramoto S, Miyamoto N, Yatomi K et al (2011) Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, provides neuroprotection in mice transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1696–1705
Wang M-D, Huang Y, Zhang G-P et al (2012) Exendin-4 improved rat cortical neuron survival under oxygen/glucose deprivation through PKA pathway. Neuroscience 226:388–396
Monami M, Marchionni N, Mannucci E (2009) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Eur J Endocrinol 160:909–917. doi:10.1530/EJE-09-0101
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Marchionni N et al (2012) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight: a meta-analysis. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:672658. doi:10.1155/2012/672658
Jendle J, Nauck MA, Matthews DR et al (2009) Weight loss with liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue for type 2 diabetes treatment as monotherapy or added to metformin, is primarily as a result of a reduction in fat tissue. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:1163–1172. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01158.x
Jensterle Sever M, Kocjan T, Pfeifer M et al (2014) Short-term combined treatment with liraglutide and metformin leads to significant weight loss in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and previous poor response to metformin. Eur J Endocrinol 170:451–459. doi:10.1530/EJE-13-0797
Li C, Li J, Zhang Q et al (2012) Efficacy and safety comparison between liraglutide as add-on therapy to insulin and insulin dose-increase in Chinese subjects with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and abdominal obesity. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:142. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-11-142
Inoue K, Maeda N, Kashine S et al (2011) Short-term effects of liraglutide on visceral fat adiposity, appetite, and food preference: a pilot study of obese Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:109. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-10-109
Dushay J, Gao C, Gopalakrishnan GS et al (2012) Short-term exenatide treatment leads to significant weight loss in a subset of obese women without diabetes. Diabetes Care 35:4–11. doi:10.2337/dc11-0931
Osaka T, Endo M, Yamakawa M, Inoue S (2005) Energy expenditure by intravenous administration of glucagon-like peptide-1 mediated by the lower brainstem and sympathoadrenal system. Peptides 26:1623–1631. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2005.02.016
Lockie SH, Heppner KM, Chaudhary N et al (2012) Direct control of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis by central nervous system glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling. Diabetes 61:2753–2762. doi:10.2337/db11-1556
Horowitz M, Flint A, Jones KL et al (2012) Effect of the once-daily human GLP-1 analogue liraglutide on appetite, energy intake, energy expenditure and gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 97:258–266. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.02.016
Harder H, Nielsen L, Thi TDT, Astrup A (2004) The effect of liraglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 derivative, on glycemic control, body composition, and 24-h energy expenditure in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27:1915–1921. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.8.1915
Bradley DP, Kulstad R, Racine N et al (2012) Alterations in energy balance following exenatide administration. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37:893–899. doi:10.1139/h2012-068
Göke R, Larsen PJ, Mikkelsen JD, Sheikh SP (1995) Distribution of GLP-1 binding sites in the rat brain: evidence that exendin-4 is a ligand of brain GLP-1 binding sites. Eur J Neurosci 7:2294–2300
Flint A, Raben A, Astrup A, Holst JJ (1998) Glucagon-like peptide 1 promotes satiety and suppresses energy intake in humans. J Clin Invest 101:515–520
Giorgino F, Leonardini A, Natalicchio A, Laviola L (2011) Multifactorial intervention in type 2 diabetes: the promise of incretin-based therapies. J Endocrinol Invest 34:69–77. doi:10.3275/7444
Raun K, von Voss P, Knudsen LB (2007) Liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, minimizes food intake in severely obese minipigs. Obes (Silver Spring) 15:1710–1716
Raun K, von Voss P, Gotfredsen CF et al (2007) Liraglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, reduces body weight and food intake in obese candy-fed rats, whereas a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor, vildagliptin, does not. Diabetes 56:8–15
Kinzig KP, D’Alessio DA, Seeley RJ (2002) The diverse roles of specific GLP-1 receptors in the control of food intake and the response to visceral illness. J Neurosci 22:10470–10476
Tang-Christensen M, Larsen PJ, Göke R et al (1996) Central administration of GLP-1-(7-36) amide inhibits food and water intake in rats. Am J Physiol 271:R848–R856
Toft-Nielsen MB, Madsbad S, Holst JJ (1999) Continuous subcutaneous infusion of glucagon-like peptide 1 lowers plasma glucose and reduces appetite in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 22:1137–1143
Gutzwiller JP, Drewe J, Goke B et al (1999) Glucagon-like peptide-1 promotes satiety and reduces food intake in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Am J Physiol 276:1541–1544
Verdich C, Flint A, Gutzwiller JP et al (2001) A meta-analysis of the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide on ad libitum energy intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4382–4389. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.9.7877
Edwards CM, Stanley SA, Davis R et al (2001) Exendin-4 reduces fasting and postprandial glucose and decreases energy intake in healthy volunteers. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281:E155–E161
Rüttimann EB, Arnold M, Hillebrand JJ et al (2009) Intrameal hepatic portal and intraperitoneal infusions of glucagon-like peptide-1 reduce spontaneous meal size in the rat via different mechanisms. Endocrinology 150:1174–1181. doi:10.1210/en.2008-1221
Schirra J, Göke B (2005) The physiological role of GLP-1 in human: incretin, ileal brake or more? Regul Pept 128:109–115. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2004.06.018
Andrews CN, Bharucha AE, Camilleri M et al (2007) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and sympathetic stimulation on gastric accommodation in humans. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:716–723. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2007.00923.x
Schirra J (2002) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36) amide on motility and sensation of the proximal stomach in humans. Gut 50:341–348. doi:10.1136/gut.50.3.341
Young AA, Gedulin BR, Rink TJ (1996) Dose-responses for the slowing of gastric emptying in a rodent model by glucagon-like peptide (7-36) NH2, amylin, cholecystokinin, and other possible regulators of nutrient uptake. Metabolism 45:1–3
Umapathysivam MM, Lee MY, Jones KL et al (2014) Comparative effects of prolonged and intermittent stimulation of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor on gastric emptying and glycemia. Diabetes 63:785–790. doi:10.2337/db13-0893
Rotondo A, Janssen P, Mulè F, Tack J (2013) Effect of the GLP-1 analog liraglutide on satiation and gastric sensorimotor function during nutrient-drink ingestion. Int J Obes (Lond) 37:693–698. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.101
Madsbad S (2009) Exenatide and liraglutide: different approaches to develop GLP-1 receptor agonists (incretin mimetics)–preclinical and clinical results. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 23:463–477. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2009.03.008
Van Can J, Sloth B, Jensen CB et al (2013) Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite and energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Int J Obes (Lond). doi:10.1038/ijo.2013.162
Janssen P, Vanden Berghe P, Verschueren S et al (2011) Review article: the role of gastric motility in the control of food intake. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33:880–894. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04609.x
YK, Shin, Martin B, Golden E, Dotson CD, Maudsley S, Kim W, Jang HJ, Mattson MP, Drucker DJ, Egan JM MS, Shin Y-K, Martin B et al (2008) Modulation of taste sensitivity by GLP-1 signaling. J Neurochem 106:455–63. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05397.x
Merida E, Delgado E, Molina LM et al (1993) Presence of glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide receptors in solubilized membranes of human adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77:1654–1657
Le Kim Chung T, Hosaka T, Yoshida M et al (2009) Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, directly induces adiponectin expression through protein kinase A pathway and prevents inflammatory adipokine expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:613–618. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.015
Perea A, Vinambres C, Clemente F et al (1997) GLP-1 (7-36) amide: effects on glucose transport and metabolism in rat adipose tissue. Horm Metab Res 29:417–421. doi:10.1055/s-2007-979068
Ruiz-Grande C, Alarcon C, Merida E, Valverde I (1992) Lipolytic action of glucagon-like peptides in isolated rat adipocytes. Peptides 13:13–16
Sancho V, Trigo MV, Gonzalez N et al (2005) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and exendins on kinase activity, glucose transport and lipid metabolism in adipocytes from normal and type-2 diabetic rats. J Mol Endocrinol 35:27–38. doi:10.1677/jme.1.01747
Vendrell J, El Bekay R, Peral B et al (2011) Study of the potential association of adipose tissue GLP-1 receptor with obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology 152:4072–4079. doi:10.1210/en.2011-1070
Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML, Marquez L, Gonzalez N et al (2001) Effect of GLP-1 on lipid metabolism in human adipocytes. Horm Metab Res 33:73–77
Zhao TC (2013) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and protective effects in cardiovascular disease: a new therapeutic approach for myocardial protection. Cardiovasc Diabetol 12:90. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-12-90
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Nardini C et al (2014) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 16:38–47. doi:10.1111/dom.12175
Wei Y, Mojsov S (1995) Tissue-specific expression of the human receptor for glucagon-like peptide-I: brain, heart and pancreatic forms have the same deduced amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett 358:219–224
Vila Petroff MG, Egan JM, Wang X, Sollott SJ (2001) Glucagon-like peptide-1 increases cAMP but fails to augment contraction in adult rat cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 89:445–452
Barragan JM, Rodriguez RE, Eng J, Blazquez E (1996) Interactions of exendin-(9-39) with the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide and of exendin-4 on arterial blood pressure and heart rate in rats. Regul Pept 67:63–68
Yamamoto H, Lee CE, Marcus JN et al (2002) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor stimulation increases blood pressure and heart rate and activates autonomic regulatory neurons. J Clin Invest 110:43–52
Nikolaidis LA, Elahi D, Shen Y-T, Shannon RP (2005) Active metabolite of GLP-1 mediates myocardial glucose uptake and improves left ventricular performance in conscious dogs with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:2401–2408
Zhao T, Parikh P, Bhashyam S et al (2006) Direct effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on myocardial contractility and glucose uptake in normal and postischemic isolated rat hearts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:1106–1113
Laviola L, Leonardini A, Melchiorre M et al (2012) Glucagon-like peptide-1 counteracts oxidative stress-dependent apoptosis of human cardiac progenitor cells by inhibiting the activation of the c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway. Endocrinology 153:5770–5781. doi:10.1210/en.2012-1461
Yu M, Moreno C, Hoagland KM et al (2003) Antihypertensive effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Hypertens 21:1125–1135
Pacheco BP, Crajoinas RO, Couto GK et al (2011) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition attenuates blood pressure rising in young spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 29:520–528
Gaspari T, Liu H, Welungoda I et al (2011) A GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits endothelial cell dysfunction and vascular adhesion molecule expression in an ApoE−/− mouse model. Diab Vasc Dis Res 8:117–124. doi:10.1177/1479164111404257
Han L, Yu Y, Sun X, Wang B (2012) Exendin-4 directly improves endothelial dysfunction in isolated aortas from obese rats through the cAMP or AMPK-eNOS pathways. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 97:453–460. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.04.001
Tashiro Y, Sato K, Watanabe T et al (2014) A glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide suppresses macrophage foam cell formation and atherosclerosis. Peptides 54C:19–26
Sokos GG, Nikolaidis LA, Mankad S et al (2006) Glucagon-like peptide-1 infusion improves left ventricular ejection fraction and functional status in patients with chronic heart failure. J Card Fail 12:694–699
Sokos GG, Bolukoglu H, German J et al (2007) Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) on glycemic control and left ventricular function in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Am J Cardiol 100:824–829. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.05.022
Read PA, Hoole SP, White PA et al (2011) A pilot study to assess whether glucagon-like peptide-1 protects the heart from ischemic dysfunction and attenuates stunning after coronary balloon occlusion in humans. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 4:266–272. doi:10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.110.960476
Read PA, Khan FZ, Dutka DP (2012) Cardioprotection against ischaemia induced by dobutamine stress using glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart 98:408–413. doi:10.1136/hrt.2010.219345
Gejl M, Lerche S, Mengel A et al (2014) Influence of GLP-1 on myocardial glucose metabolism in healthy men during normo- or hypoglycemia. PLoS One 9(1):e83758. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083758
Fonseca VDJH, Bain SC (2011) Liraglutide improves the profile of lipid and cardiovascular risk biomarkers from baseline. In: IDF 2011 21th World Congress Abstract Book Poster vol 135, pp 442–443
Lonborg J, Vejlstrup N, Kelbæk H et al (2012) Exenatide reduces reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 33:1491–1499
Kelly AS, Bergenstal RM, Gonzalez-Campoy JM et al (2012) Effects of exenatide vs. metformin on endothelial function in obese patients with pre-diabetes: a randomized trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:64
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Mannucci E (2014) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 24(7):689–697. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2014.01.017
Wu S, Hopper I, Skiba M, Krum H (2014) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes: meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials with 55,141 participants. Cardiovasc Ther 32(4):147–158. doi:10.1111/1755-5922.12075
Clowes JA, Hannon RA, Yap TS et al (2002) Effect of feeding on bone turnover markers and its impact on biological variability of measurements. Bone 30:886–890
Schlemmer A, Hassager C (1999) Acute fasting diminishes the circadian rhythm of biochemical markers of bone resorption. Eur J Endocrinol 140:332–337
Nuche-Berenguer B, Moreno P, Esbrit P et al (2009) Effect of GLP-1 treatment on bone turnover in normal, type 2 diabetic, and insulin-resistant states. Calcif Tissue Int 84:453–461
Mabilleau G, Mieczkowska A, Irwin N et al (2013) Optimal bone mechanical and material properties require a functional glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J Endocrinol 219:59–68
Davidovici BB, Sattar N, Prinz JC et al (2010) Psoriasis and systemic inflammatory diseases: potential mechanistic links between skin disease and co-morbid conditions. J Invest Dermatol 130:1785–1796. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.103
Buysschaert M, Tennstedt D, Preumont V (2012) Improvement of psoriasis during exenatide treatment in a patient with diabetes. Diabetes Metab 38:86–88
Faurschou A, Knop FK, Thyssen JP et al (2014) Improvement in psoriasis after treatment with the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide. Acta Diabetol 51:147–150. doi:10.1007/s00592-011-0359-9
Ahern T, Tobin A-M, Corrigan M et al (2013) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue therapy for psoriasis patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27(11):1440–1443. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04609.x
Faurschou A, Pedersen J, Gyldenløve M et al (2013) Increased expression of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors in psoriasis plaques. Exp Dermatol 22:150–152. doi:10.1111/exd.12081
Buysschaert M, Baeck M, Preumont V et al (2014) Improvement of psoriasis during GLP-1 analogue therapy in type 2 diabetes is associated with decreasing dermal γδ T cells number: a prospective case series study. Br J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/bjd.12886
Acknowledgments
This review was conceived in the context of the activity of Engioi Club (Italian Society of Endocrinology-SIE). The Authors wish to thank Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE), Prof Alessandro Peri and Prof Luigi Bartalena for supporting the initiative.
Conflict of interest
All authors have no potential conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muscogiuri, G., Cignarelli, A., Giorgino, F. et al. GLP-1: benefits beyond pancreas. J Endocrinol Invest 37, 1143–1153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0137-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-014-0137-y