Abstract
Background
Previous studies have shown that exercise could improve β-cell function in humans or animal models of type 2 diabetes. However, whether it can prevent the progression of pre-diabetes to diabetes remains unclear.
Aim
To study the effects of exercise on glycolipid metabolism, β-cell function, and insulin resistance in the non-diabetic young offsprings of diabetic patients.
Methods
One hundred and eighty-two normal glucose tolerance young offsprings of type 2 diabetic parents were enrolled. Individuals with fasting insulin ≥12.0 mU/L were assigned to hyperinsulinemia group (n = 72) and those with fasting insulin <12.0 mU/L were assigned to normal group (n = 110). The subjects in hyperinsulinemia group received 12-week exercise intervention. A 75-g oral glucose tolerance test and insulin release test were conducted before and after intervention. The area under curve of glucose (AUCglu), area under curve of insulin (AUCINS), HOMA insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR), HOMA β-cell function (HOMA-β), and early insulin secretion index (ΔI 30/ΔG 30) were calculated. Body composition was measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Results
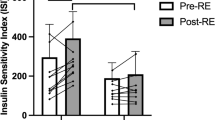
At baseline, AUCINS and HOMA-β in hyperinsulinemia group were significantly higher compared with the normal group (P < 0.05). After the 12-week exercise intervention, no significant changes in blood pressure, body mass index, blood glucose, serum lipids, and percentage of body fat were found in hyperinsulinemia group; however, AUCINS, HOMA-β, HOMA-IR (P < 0.05) and ΔI 30/ΔG 30 (P < 0.01) were significantly decreased.
Conclusions
Exercise is effective for preventing pre-diabetic insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction in non-diabetic young offsprings of diabetic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUCglu :
-
Area under curve of glucose
- AUCINS :
-
Area under curve of insulin
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- FINS:
-
Fasting insulin
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- HOMA:
-
Homeostatic model assessment
- HOMA-IR:
-
HOMA insulin resistance index
- HOMA-β:
-
HOMA β-cell function
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
References
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Ge J, Lin L, Chen L, Guo X et al (2010) Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 362(12):1090–1101
Buchanan TA, Xiang AH, Peters RK, Kjos SL, Marroquin A, Goico J, Ochoa C, Tan S, Berkowitz K, Hodis HN, Azen SP (2002) Preservation of pancreatic beta-cell function and prevention of type 2 diabetes by pharmacological treatment of insulin resistance in high-risk Hispanic women. Diabetes 51(9):2796–2803
Slentz CA, Tanner CJ, Bateman LA, Durheim MT, Huffman KM, Houmard JA, Kraus WE (2009) Effects of exercise training intensity on pancreatic beta-cell function. Diabetes Care 32(10):1807–1811
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444(7121):840–846
Rodnick KJ, Haskell WL, Swislocki AL, Foley JE, Reaven GM (1987) Improved insulin action in muscle, liver, and adipose tissue in physically trained human subjects. Am J Physiol 253(5 Pt 1):E489–E495
Weyer C, Bogardus C, Mott DM, Pratley RE (1999) The natural history of insulin secretory dysfunction and insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 104(6):787–794
Martin BC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Bergman RN, Soeldner JS, Kahn CR (1992) Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet 340(8825):925–929
DeFronzo RA, Abdul-Ghani M (2011) Type 2 diabetes can be prevented with early pharmacological intervention. Diabetes Care 34(Suppl 2):S202–S209
Holloszy JO (2005) Exercise-induced increase in muscle insulin sensitivity. J Appl Physiol 99(1):338–343
Short KR, Vittone JL, Bigelow ML, Proctor DN, Rizza RA, Coenen-Schimke JM, Nair KS (2003) Impact of aerobic exercise training on age-related changes in insulin sensitivity and muscle oxidative capacity. Diabetes 52(8):1888–1896
Cox JH, Cortright RN, Dohm GL, Houmard JA (1999) Effect of aging on response to exercise training in humans: skeletal muscle GLUT-4 and insulin sensitivity. J Appl Physiol 86(6):2019–2025
Bloem CJ, Chang AM (2008) Short-term exercise improves beta-cell function and insulin resistance in older people with impaired glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(2):387–392
Kahn SE, Larson VG, Beard JC, Cain KC, Fellingham GW, Schwartz RS, Veith RC, Stratton JR, Cerqueira MD, Abrass IB (1990) Effect of exercise on insulin action, glucose tolerance, and insulin secretion in aging. Am J Physiol 258(6 Pt 1):E937–E943
Kirwan JP, Kohrt WM, Wojta DM, Bourey RE, Holloszy JO (1993) Endurance exercise training reduces glucose-stimulated insulin levels in 60- to 70-year-old men and women. J Gerontol 48(3):M84–M90
Bergman RN, Ader M, Huecking K, Van Citters G (2002) Accurate assessment of beta-cell function: the hyperbolic correction. Diabetes 51(Suppl 1):S212–S220
Kahn SE, Prigeon RL, McCulloch DK, Boyko EJ, Bergman RN, Schwartz MW, Neifing JL, Ward WK, Beard JC, Palmer JP et al (1993) Quantification of the relationship between insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in human subjects. Evidence for a hyperbolic function. Diabetes 42(11):1663–1672
Park S, Hong SM, Sung SR (2008) Exendin-4 and exercise promotes beta-cell function and mass through IRS2 induction in islets of diabetic rats. Life Sci 82(9–10):503–511
Phillips D, Clark P, Hales C, Osmond C (2009) Understanding oral glucose tolerance: comparison of glucose or insulin measurements during the oral glucose tolerance test with specific measurements of insulin resistance and insulin secretion. Diabet Med 11(3):286–292
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27(5):1047–1053
Zhu H, Zhang X, Li MZ, Xie J, Yang XL (2013) Prevalence of Type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes among overweight or obese children in Tianjin. China. Diabetic Med 30(12):1457–1465
Chiasson JL, Josse RG, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Karasik A, Laakso M (2002) Acarbose for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the STOP-NIDDM randomised trial. Lancet 359(9323):2072–2077
Gerstein HC, Yusuf S, Bosch J, Pogue J, Sheridan P, Dinccag N, Hanefeld M, Hoogwerf B, Laakso M, Mohan V, Shaw J, Zinman B, Holman RR (2006) Effect of rosiglitazone on the frequency of diabetes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 368(9541):1096–1105
Kawamori R, Tajima N, Iwamoto Y, Kashiwagi A, Shimamoto K, Kaku K (2009) Voglibose for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomised, double-blind trial in Japanese individuals with impaired glucose tolerance. Lancet 373(9675):1607–1614
Bergman RN (2007) Orchestration of glucose homeostasis: from a small acorn to the California oak. Diabetes 56(6):1489–1501
Ferrannini E, Gastaldelli A, Miyazaki Y, Matsuda M, Pettiti M, Natali A, Mari A, DeFronzo RA (2003) Predominant role of reduced beta-cell sensitivity to glucose over insulin resistance in impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 46(9):1211–1219
Richter EA, Mikines KJ, Galbo H, Kiens B (1989) Effect of exercise on insulin action in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 66(2):876–885
Solomon TP, Haus JM, Kelly KR, Rocco M, Kashyap SR, Kirwan JP (2010) Improved pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetic patients after lifestyle-induced weight loss is related to glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. Diabetes Care 33(7):1561–1566
Chang AM, Smith MJ, Bloem CJ, Galecki AT, Halter JB, Supiano MA (2006) Limitation of the homeostasis model assessment to predict insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction in older people. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(2):629–634
Perseghin G, Price TB, Petersen KF, Roden M, Cline GW, Gerow K, Rothman DL, Shulman GI (1996) Increased glucose transport-phosphorylation and muscle glycogen synthesis after exercise training in insulin-resistant subjects. N Engl J Med 335(18):1357–1362
St-Onge MP, Janssen I, Heymsfield SB (2004) Metabolic syndrome in normal-weight Americans: new definition of the metabolically obese, normal-weight individual. Diabetes Care 27(9):2222–2228
Stadler M, Pacini G, Petrie J, Luger A, Anderwald C (2009) Beta cell (dys)function in non-diabetic offspring of diabetic patients. Diabetologia 52(11):2435–2444
Conflict of interest
The authors Xuemei Yu, Peihong Chen, Hongtao Wang, Hua Jin, Weina Jia, and Lingyan Wang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Chen, P., Wang, H. et al. Clinical study of exercise on improvement of β-cell function and insulin resistance in non-diabetic young offsprings of diabetic patients. J Endocrinol Invest 37, 353–358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-013-0033-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-013-0033-x