Abstract
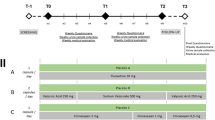
Buprenorphine is an important medication for treating opioid use disorder, but medication adherence and treatment retention are key issues that can limit its impact, especially when patients have concurrent stimulant use. Contingency management is efficacious in promoting medication adherence and drug abstinence. Delivering contingency management via smartphones addresses practical barriers to its adoption and improves patient access. A single-group (n = 20) nonexperimental study was conducted to evaluate the feasibility of smartphone-based contingency management to promote adherence to buprenorphine treatment in people with opioid use disorder. Participants were recruited from outpatient treatment clinics. Over 12 weeks participants had access to a smartphone app that provided contingency management supported with peer recovery coaching. Adherence was confirmed daily either by GPS monitoring of clinic medication visits or self-recorded video, and salivary toxicology was conducted weekly. The overall rate of confirmed buprenorphine adherence was 76%, and visual inspection of individual participant outcomes shows consistent medication use for a large majority of participants. All participants were able to successfully use all app features and spend earnings. Participants rated the app and intervention highly on measures of likability, ease of use, and helpfulness. All participants (100%) were retained in buprenorphine treatment throughout the study period. Direct methods for confirming adherence appear superior to confirmation via salivary toxicology. This study shows that smartphone-based contingency management is a feasible means of promoting buprenorphine adherence. The potential efficacy of smartphone-based contingency management as a means of promoting buprenorphine adherence warrants evaluation in a randomized controlled trial.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassuk, E. L., Hanson, J., Greene, R. N., Richard, M., & Laudet, A. (2016). Peer-delivered recovery support services for addictions in the United States: A systematic review. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 63, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2016.01.003
Byrne, K. A., Roth, P. J., Merchant, K., Baginski, B., Robinson, K., Dumas, K., Collie, J., Ramsey, B., Cull, J., Cooper, L., Churitch, M., Rennert, L., Heo, M., & Jones, R. (2020). Inpatient link to peer recovery coaching: Results from a pilot randomized control trial. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 215, 108234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108234
Dallery, J., Raiff, B. R., Grabinski, M. J., & Marsch, L. A. (2019). Technology-based contingency management in the treatment of substance-use disorders. Perspectives on Behavior Science, 42(3), 445–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-019-00214-1
Davis, D. R., Kurti, A. N., Skelly, J. M., Redner, R., White, T. J., & Higgins, S. T. (2016). A review of the literature on contingency management in the treatment of substance use disorders, 2009–2014. Preventive Medicine, 92, 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.08.008
DeFulio, A. (2022). Dissemination of contingency management for the treatment of opioid use disorder. Perspectives on Behavior Science. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-022-00328-z
DeFulio, A., & Silverman, K. (2012). The use of incentives to reinforce medication adherence. [Special issue]. Preventive Medicine, 55, S86–S94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2012.04.017
DeFulio, A., Everly, J. J., Leoutsakos, J. M. S., Umbricht, A., Fingerhood, M., Bigelow, G. E., & Silverman, K. (2012). Employment-based reinforcement of adherence to an FDA approved extended release formulation of naltrexone in opioid-dependent adults: A randomized controlled trial. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 120(1–3), 48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.06.023
DeFulio, A., Devoto, A., Traxler, H., Cosottile, D., Fingerhood, M., Nuzzo, P., & Dallery, J. (2021a). Smartphone-based incentives for promoting adherence to antiretroviral therapy: A randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine Reports, 21, 101318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2021.101318
DeFulio, A., Furgeson, J., Brown, H. D., & Ryan, S. (2021b). A smartphone–smartcard platform for implementing contingency management in buprenorphine maintenance patients with concurrent stimulant use disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, Article 778992. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.778992
DeFulio, A., Rzeszutek, M. J., Furgeson, J., Ryan, S., & Rezania, S. (2021c). A smartphone-smartcard platform for contingency management in an inner-city substance use disorder outpatient program. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 120, 108188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2020.108188
Dennis, M. L., Scott, C. K., Funk, R., & Foss, M. A. (2005). The duration and correlates of addiction and treatment careers. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 28(2), S51–S62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2004.10.013
Dunn, K. E., Defulio, A., Everly, J. J., Donlin, W. D., Aklin, W. M., Nuzzo, P. A., Leoutsakos, J. M. S., Umbricht, A., Fingerhood, M., Bigelow, G. E., & Silverman, K. (2013). Employment-based reinforcement of adherence to oral naltrexone treatment in unemployed injection drug users. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 21(1), 74–83. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030743
Dutra, L., Stathopoulou, G., Basden, S. L., Leyro, T. M., Powers, M. B., & Otto, M. W. (2008). A meta-analytic review of psychosocial interventions for substance use disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 165(2), 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06111851
Gagne, C. A., Finch, W. L., Myrick, K. J., & Davis, L. M. (2018). Peer workers in the behavioral and integrated health workforce: Opportunities and future directions. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 54(6), S258–S266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2018.03.010
Gerra, G., Saenz, E., Busse, A., Maremmani, I., Ciccocioppo, R., Zaimovic, A., Gerra, M., Amore, M., Manfredini, M., Donnini, C., & Somaini, L. (2011). Supervised daily consumption, contingent take-home incentive and non-contingent take-home in methadone maintenance. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 35(2), 483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.12.002
Hart, J. E., Jeon, C. Y., Ivers, L. C., Behforouz, H. L., Caldas, A., Drobac, P. C., & Shin, S. S. (2010). Effect of directly observed therapy for highly active antiretroviral therapy on virologic, immunologic, and adherence outcomes: A meta-analysis and systematic review. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 54(2), 167–179. https://doi.org/10.1097/qai.0b013e3181d9a330
Holtyn, A. F., Toegel, F., Novak, M. D., Leoutsakos, J. M., Fingerhood, M., & Silverman, K. (2021). Remotely delivered incentives to promote buprenorphine treatment engagement in out-of-treatment adults with opioid use disorder. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 225, 108786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108786
Hser, Y. I., Saxon, A. J., Huang, D., Hasson, A., Thomas, C., Hillhouse, M., Jacobs, P., Teruya, C., McLaughlin, P., Wiest, K., Cohen, A., & Ling, W. (2013). Treatment retention among patients randomized to buprenorphine/naloxone compared to methadone in a multi-site trial. Addiction, 109(1), 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12333
Jarvis, B. P., Holtyn, A. F., DeFulio, A., Koffarnus, M. N., Leoutsakos, J. M. S., Umbricht, A., Fingerhood, M., Bigelow, G. E., & Silverman, K. (2019). The effects of extended-release injectable naltrexone and incentives for opiate abstinence in heroin-dependent adults in a model therapeutic workplace: A randomized trial. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 197, 220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.12.026
Kampman, K. M. (2010). What’s new in the treatment of cocaine addiction? Current Psychiatry Reports, 12(5), 441–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-010-0143-5
Karumbi, J., & Garner, P. (2015). Directly observed therapy for treating tuberculosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2015(5), Article CD003343. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003343.pub4
Koob, G., and Le Moal, M. (2001). Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology, 24(2), 97–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0893-133x(00)00195-0
Kurti, A. N., Davis, D., Redner, R., Jarvis, B., Zvorsky, I., Keith, D. R., Bolivar, H., White, T. J., Rippberger, P., Markeish, C., Atwood, G., & Higgins, S. T. (2016). A review of the literature on remote monitoring technology in incentive-based interventions for health-related behavior change. Translational Issues in Psychological Science, 2(2), 128–152. https://doi.org/10.1037/tps0000067
Lussier, J. P., Heil, S. H., Mongeon, J. A., Badger, G. J., & Higgins, S. T. (2006). A meta-analysis of voucher-based reinforcement therapy for substance use disorders. Addiction, 101(2), 192–203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01311.x
Maricich, Y. A., Bickel, W. K., Marsch, L. A., Gatchalian, K., Botbyl, J., & Luderer, H. F. (2021). Safety and efficacy of a prescription digital therapeutic as an adjunct to buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 37(2), 167–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/03007995.2020.1846022
Mattick, R. P., Breen, C., Kimber, J., & Davoli, M. (2014). Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2, CD002207. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
McLellan, A. T., Cacciola, J. S., & Zanis, D. (1997). The Addiction Severity Index–“Lite” (ASI–“Lite”). Center for the Studies of Addiction, University of Pennsylvania/Philadelphia VA Medical Center.
Petry, N. M., Alessi, S. M., Olmstead, T. A., Rash, C. J., & Zajac, K. (2017). Contingency management treatment for substance use disorders: How far has it come, and where does it need to go? Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 31(8), 897–906. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000287
Prendergast, M., Podus, D., Finney, J., Greenwell, L., & Roll, J. (2006). Contingency management for treatment of substance use disorders: a meta-analysis. Addiction, 101(11), 1546–1560. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01581.x
Preston, K. L., Silverman, K., Umbricht, A., DeJesus, A., Montoya, I. D., & Schuster, C. R. (1999). Improvement in naltrexone treatment compliance with contingency management. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 54(2), 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0376-8716(98)00152-5
Stitzer, M., Bigelow, G., Lawrence, C., Cohen, J., D’Lugoff, B., & Hawthorne, J. (1977). Medication take-home as a reinforcer in a methadone maintenance program. Addictive Behaviors, 2(1), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(77)90003-x
Timko, C., Schultz, N. R., Cucciare, M. A., Vittorio, L., & Garrison-Diehn, C. (2015). Retention in medication-assisted treatment for opiate dependence: A systematic review. Journal of Addictive Diseases, 35(1), 22–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/10550887.2016.1100960
Tsui, J. I., Leroux, B. G., Radick, A. C., Schramm, Z. A., Blalock, K., Labelle, C., Heerema, M., Klein, J. W., Merrill, J. O., Saxon, A. J., Samet, J. H., & Kim, T. W. (2021). Video directly observed therapy for patients receiving office-based buprenorphine: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Drug & Alcohol Dependence, 227, 108917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108917
Washington State Institute for Public Policy. (2019, December). Benefit-cost results: Substance use disorders. Retrieved March 3, 2022 from http://www.wsipp.wa.gov/BenefitCost?topicId=7
White, W. L. (2010). Nonclinical addiction recovery support services: History, rationale, models, potentials, and pitfalls. Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly, 28(3), 256–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/07347324.2010.488527
Acknowledgments
We thank Zoey Golston and Sarah Morrissey for their assistance with data management and processing.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (R41DA049390, PI – DeFulio). The funding source had no role in the study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anthony DeFulio: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing (original draft, review, and editing), visualization, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition.
Hayley Brown: Formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing (review and editing), visualization.
Rosemarie Davidson: Formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing (review and editing).
Sean Regnier: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing (review and editing).
Navdeep Kang: Methodology, resources, writing (review and editing).
Melissa Ehart: Methodology, resources, writing (review and editing).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The first author has served as a research consultant for DynamiCare Health, Inc. The remaining authors declare no conflicts.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Western Michigan University Human Subjects Institutional Review Board. All participants provided informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DeFulio, A., Brown, H.D., Davidson, R.M. et al. Feasibility, Acceptability, and Preliminary Efficacy of a Smartphone-Based Contingency Management Intervention for Buprenorphine Adherence. Behav Analysis Practice 16, 450–458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40617-022-00730-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40617-022-00730-8