Abstract
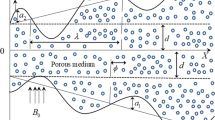
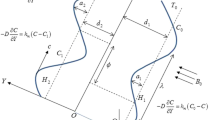
The present investigation is based on the two-phase flow of a non-Newtonian fluid through a uniform channel with heat transfer. Stress tensor of third-grade fluid is taken into account to treat as non-Newtonian fluid. Two different types of viscous suspensions are formed with the tiny size Hafnium and crystal particles, respectively. Owing to the high magnetic susceptibility of the Hafnium metallic particles magnetic effects are applied, as well. Each magnetohydrodynamics bi-phase flow is caused, due to gravitational force. An asymptotic solution is obtained with the help of the “Regular perturbation method,” for the set nonlinear and coupled differential equations. A detailed parametric study is carried out to analyze the effective contribution of significant parameters and quantities. It is inferred that the strong magnetic effects and dominant viscous dissipation introduce additional thermal energy to the multiphase flow. Moreover, highly viscous multiphase suspensions are suitable in chemical industries to manufacture such paints and emulsions which contain small polymer particles.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({\hat{\mathbf{T}}}\) :
-
Stress tensor of a 3rd grade fluid
- \({\hat{\mathbf{V}}}_{{\text{f}}}\) :
-
The velocity profile of fluid phase
- \({\hat{\mathbf{L}}}\) :
-
Velocity gradient
- \({\hat{\mathbf{J}}}\) :
-
Current vector
- \({\mathbf{S}}\) :
-
Drag force
- M :
-
Hartmann number
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Inclination of plates
- \({\Lambda }_{1}\) :
-
Third-grade parameter
- \({\hat{\text{u}}}_{{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Fluid’s velocity
- \(\rho_{{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Fluid’s density
- \(\hat{P}\) :
-
Pressure
- \({\hat{\text{T}}}_{l}\) :
-
The temperature of the suspension at \({\Psi } = - {\text{L}}\)
- \(\beta_{1} , \;\beta_{2} \& \beta_{3}\) :
-
Material constants
- \(t\) :
-
Time
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Electrical conductivity
- \({\hat{\text{T}}}\) :
-
The temperature of the suspension
- \({\hat{\mathbf{V}}}_{{\text{p}}}\) :
-
The velocity profile of particle phase
- \({\text{L}}\) :
-
Separation between plates
- \({\hat{\mathbf{B}}}\) :
-
Magnetic force
- \({\hat{\mathbf{E}}}\) :
-
Electric force
- Fr:
-
Froude number
- \(C\) :
-
Density number
- \({\Lambda }_{2}\) :
-
Brinkman number
- \({\hat{\text{u}}}_{{\text{p}}}\) :
-
Particle’s velocity
- \(\rho_{{\text{p}}}\) :
-
Particle’s density
- \(\overline{P}\) :
-
Modified pressure
- \({\hat{\text{T}}}_{u}\) :
-
The temperature of the suspension at \({\Psi } = {\text{L}}\)
- \(\alpha_{1} \& \alpha_{2}\) :
-
Material constants
- g :
-
Gravitational force
- \(\frac{{\text{D}}}{{{\text{D}}t}}\) :
-
Material time derivative
- p :
-
Particle
- f :
-
Fluid
References
Zubair M, Waqas M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Ayub M (2018) Stagnation point flow of third-grade liquid due to variable thickness: a useful application to non-Fourier heat flux approach. Results Phys 8:1010–1016
Anjum N, Khan WA, Hobiny A, Azam M, Waqas M, Irfan M (2022) Numerical analysis for thermal performance of modified Eyring Powell nanofluid flow subject to activation energy and bioconvection dynamic. Case Stud ThermEng 39:102427
Thohura S, Molla M, Sarker MMA (2021) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of MHD Non-Newtonian power-law nanofluid in a rectangular enclosure using GPU computing. AIP Conf Proc 2324:040010
Ellahi R, Hussain F, Ishtiaq F, Hussain A (2019) Peristaltic transport of Jeffrey fluid in a rectangular duct through a porous medium under the effect of partial slip: an application to upgrade industrial sieves/filters. Pramana 93(3):34
Pasha AA, Irshad K, Algarni S, Alqahtani T, Waqas M (2023) Analysis of tangent-hyperbolic rheological model considering nonlinear mixed convection, Joule heating and Soret-Dufour aspects from a stretchable convective stratified surface. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 140:106519
Anjum N, Khan WA, Azam M, Ali M, Waqas M, Hussain I (2023) Significance of bioconvection analysis for thermally stratified 3D Cross nanofluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms and activation energy aspects. Therm Sci Eng Prog 38:101596
Al-Zubaidi A, Nazeer M, Khalid K, Yaseen S, Saleem S, Hussain F (2021) Thermal analysis of blood flow of Newtonian, pseudo-plastic, and dilatant fluids through an inclined wavy channel due to metachronal wave of Cilia. Adv Mech Eng 13(9):1–12
Nazeer M, Ali N, Ahmad F, Ali W, Saleem A, Ali Z, Sarfraz A (2020) Effects of radiative heat flux and joule heating on electro-osmotically flow of non-Newtonian fluid: analytical approach. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 117:104744–104755
Hayat T, Saleem N, Ali N (2010) Effect of induced magnetic field on peristaltic transport of a Carreau fluid. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15(9):2407–2423
Sajid M, Abbas Z, Ali N, Javed T (2017) Note on effect of joule heating and MHD in the presence of convective boundary condition for upper-convected Maxwell fluid through wall jet. J Mol Liq 230:235–236
Nazeer M, Hussain F, Hameed MK, Khan MI, Ahmad F, Malik MY, Shi Q (2021) Development of mathematical modeling of multi-phase flow of Casson rheological fluid: theoretical approach. Chaos Solitons Fractals 150:111198
Siddiqa S, Molla MM, Naqvi SB (2021) Carreau ferrofluid flow with inclined magnetic field in an enclosure having heated cylinder. Phys Scr 96:105007
Thohura S, Molla M, Sarker MMA (2020) Bingham fluid flow simulation in a lid-driven skewed cavity using finite volume method. Int J Comput Math 97(6):1212–1233
Thohura S, Molla M, Sarker MMA (2019) Numerical simulation of Non-Newtonian power-law fluid flow in a lid-driven skewed cavity, mathematics and computers in simulation. Int J Appl Comput Math 5(14):1–29
Nazeer M, Ali N, Ahmad F, Latif M (2020) Numerical and perturbation solutions of third-grade fluid in a porous channel: boundary and thermal slip effects. Pramana J Phys 94:44
Ellahi R, Hayat T, Mahomed FM, Asghar S (2010) Effects of slip on the non-linear flows of a third grade fluid. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11(1):139–146
Aksoy Y, Pakdemirli M (2010) Approximate analytical solutions for flow of a third-grade fluid through a parallel-plate channel filled with a porous medium. Transp Porous Med 83(3):375–395
Ogunmola BY, Akinshilo AT, Sobamowo MG (2016) Perturbation solutions for Hagen-Poiseuille flow and heat transfer of third-grade fluid with temperature-dependent viscosities and internal heat generation. Hindawi Publ Corp 12(2):8915745
Akinshilo AT, Sobamowo GM (2017) Perturbation solutions for the study of MHD blood as a third grade nanofluid transporting gold nanoparticles through a porous channel. J Appl Comput Mech 3(2):103–113
Hayat T, Shahzad F, Ayub M (2007) Analytical solution for the steady flow of the third grade fluid in a porous half space. Appl Math Model 31(2):2424–2432
Nazeer M, Hussain F, Shahzad Q, Khan MI, Kadry S, Chu Y (2021) Perturbation solution of the multiphase flows of third grade dispersions suspended with Hafnium and crystal particles. Surf Interfaces 22:100803
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hussain F, Abbas T (2019) Two-phase Couette flow of couple stress fluid with temperature dependent viscosity thermally affected by magnetized moving surface. Symmetry 11(5):11050647
Ramya D, Chamkha AJ, Raju RS, Rao JA (2016) Effects of velocity and thermal wall slip on magneto-hydrodynamics (MHD) boundary layer viscous flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a non-linearly-stretching sheet: a numerical study. Propuls Power Res 7(2):182–195
Chu YM, Nazeer M, Khan MI, Hussain F, Rafi H, Qayyum S, Abdelmalek Z (2021) Combined impacts of heat source/sink, radiative heat flux, temperature dependent thermal conductivity on forced convective Rabinowitsch fluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 120:105011
Alamri SZ, Ellahi R, Shehzad N, Zeeshan A (2019) Convective radiative plane Poiseuille flow of nanofluid through porous medium with slip: an application of Stefan blowing. J Mol Liq 273(1):292–304
Hassan M, Ellahi R, Bhatti MM, Zeeshan A (2019) A comparative study of magnetic and non-magnetic particles in nanofluid propagating over a wedge. Can J Phys 97(1):277–285
Hassan M, Marin M, Alsharif A, Ellahi R (2018) Convective heat transfer flow of nanofluid in a porous medium over wavy surface. Phys Lett 382(1):2749–2753
Nazeer M, Hussain F, Iftikhar S, Khan MI, Ramesh K, Shehzad N, Baig A, Kadry S, Chu Y (2021) Mathematical modeling of bio-magnetic fluid bounded within ciliated walls of wavy channel. Numer Methods Partial Differ Eq. https://doi.org/10.1002/num.22763
Nazeer M, Saleem S, Hussain F, Iftikhar S, Al-Qahtani A (2021) Mathematical modeling of bio-magnetic fluid bounded by ciliated walls of wavy channel incorporated with viscous dissipation: discarding mucus from lungs and blood streams. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 124:105274
Nemati M, Sefid M (2022) Magnetohydrodynamics combined convection modeling via LBM for shear thinning nanofluids within an inclined enclosure: appraisement of heat transfer and entropy under the impact of various parameters. Comput Part Mech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-022-00544-z
Nemati M, Farahani SD (2022) Using lattice Boltzmann method to control entropy generation during conjugate heat transfer of power-law liquids with magnetic field and heat absorption/production. Comput Part Mech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-022-00497-3
Zeeshan A, Ali Z, Gorji MR, Hussain F, Nadeem S (2020) Flow analysis of biconvective heat and mass transfer of two-dimensional couple stress fluid over a paraboloid of revolution. Int J Mod Phys B 34(11):2050110
Chu YM, Ahmad F, Khan MI, Nazeer M, Hussain F, Khan NB, Kadry S, Mei L (2021) Numerical and scale analysis of non-Newtonian fluid (Eyring-Powell) through pseudo-spectral collocation method (PSCM) towards a magnetized stretchable Riga surface. Alex Eng J 60:2127–2137
Ramesh K, Kumar D, Nazeer M, Waqfi D, Hussain F (2020) Mathematical modeling of MHD Jeffrey nanofluid in a microchannel incorporated with lubrication effects: a Graetz problem. Phys Scr 96(2):025225
Firdous H, Husnine SM, Hussain F, Nazeer M (2020) Velocity and thermal slip effects on two-phase flow of MHD Jeffrey fluid with the suspension of tiny metallic particles. Phys Scr 96(1):025803
Hussain F, Subia GS, Nazeer M, Ghafar MM, Ali Z, Hussain A (2021) Simultaneous effects of Brownian motion and thermophoretic force on Eyring-Powell fluid through porous geometry. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 76(7):569–580
Nazeer M (2021) Numerical and perturbation solutions of cross flow of an Eyring-Powell fluid. SN Appl Sci 3:213
Ge-JiLe H, Nazeer M, Hussain F, Khan MI, Saleem A, Siddique I (2021) Two-phase flow of MHD Jeffrey fluid with the suspension of tiny metallic particles incorporated with viscous dissipation and Porous Medium. Adv Mech Eng 13(3):1–15
Nazeer M, Hussain F, Shahzad Q, Ali Z, Kadry S, Chu YM (2020) Computational study of solid-liquid supercritical flow of 4th-grade fluid through magnetized surface. Phys Scr 96(1):015201
Ellahi R, Hussain F, Abbas A, Sarafraz M, Goodarzi M, Shadloo M (2020) Study of two-phase Newtonian nanofluid flow hybrid with hafnium particles under the effects of slip. Inventions 5(1):6
Nazeer M, Khan MI, Chu Y, Kadry S, Eid MR (2022) Mathematical modeling of multiphase flows of third-grade fluid with lubrication effects through an inclined channel: analytical treatment. J Dispers Sci Technol 43(10):1555–1567. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2021.1877557
Hussain F, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Vafai K (2018) Modelling study on heated couple stress fluid peristaltically conveying gold nanoparticles through coaxial tubes: a remedy for gland tumors and arthritis. J Mol Liq 268:149–155
Nazeer M, Ahmad F, Saleem A, Saeed M, Naveed S, Shaheen M, Al Aidarous E (2019) Effects of constant and space-dependent viscosity on Eyring-powell fluid in a pipe: comparison of the perturbation and explicit finite difference methods. Z Naturforsch 74:961–969
Khan MI, Nazeer M, Shehzad N, Saleem A, Ahmad F (2020) Scrutiny of entropy optimized tangent hyperbolic fluid (non-Newtonian) through perturbation and numerical methods between heated plates. Adv Mech Eng 12(12):1–12
Nazeer M, Khan MI, Saleem A, Chu Y, Kadry S, Rasheed MT (2021) Perturbation based analytical solutions of non-Newtonian differential equation with heat and mass transportation between horizontal permeable channel. Numer Methods Part Differ Eq. https://doi.org/10.1002/num.22765
Mekheimer KS, El Shehawey EF, Elaw AM (1998) Peristaltic motion of a particle-fluid suspension in a planar channel. Int J Theor Phys 37:2895–2920
Zeeshan A, Ellahi R, Mabood F, Hussain F (2019) Numerical study on bi-phase coupled stress fluid in the presence of Hafnium and metallic nanoparticles over an inclined plane. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow 29(8):2854–2869
Acknowledgment
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through research groups program under Grant No. R.G.P1/276/43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
\({A}_{1}=\frac{ M }{\sqrt{\left(1-C\right)}}\),\( {A}_{2}={m}_{1}+{m}_{3}\), \({A}_{3}={m}_{1}{m}_{3}\), \({A}_{4}=\frac{{m}_{1}+{m}_{3}}{{m}_{1}{m}_{3}}\), \({B}_{1}=-\frac{\mathrm{sech}\left({A}_{1}\eta \right)\left(\frac{{A}_{4}g\mathrm{sin}\alpha }{\left(1-C\right){\left(\mathrm{Fr}\right)}^{2}}-\frac{P}{\left(1-C\right)}\right)}{2{{A}_{1}}^{2}}\),
\({B}_{2}=-\frac{\mathrm{sech}\left({A}_{1}\eta \right)\left(\frac{{A}_{4}g\mathrm{sin}\alpha }{\left(1-C\right){\left(\mathrm{Fr}\right)}^{2}}-\frac{P}{\left(1-C\right)}\right)}{2{{A}_{1}}^{2}}\),
\({B}_{3}=-\mathrm{csch}\left({2A}_{1}\right){B}_{6}-{B}_{7}-\mathrm{coth}\left({2A}_{1}\right){B}_{8}+{B}_{9}-2\mathrm{cosh}\left({2A}_{1}\right){B}_{10}\),
\({B}_{4}=-{B}_{5}+\mathrm{coth}\left({2A}_{1}\right){B}_{6}+\mathrm{csch}\left({2A}_{1}\right){B}_{8}-2\mathrm{cosh}\left({2A}_{1}\right){B}_{9}+{B}_{10}\).
\({B}_{5}=-\frac{3}{2}{B}_{1}{B}_{2}^{2}\left({{A}_{1}}^{2}\right)\), \({B}_{6}=-3{B}_{1}{B}_{2}^{2}{{A}_{1}}^{6}\), \({B}_{7}=-\frac{3}{2}{B}_{1}^{2}{B}_{2}\left({{A}_{1}}^{2}\right)\), \({B}_{8}=3{B}_{1}^{2}{B}_{2}{{A}_{1}}^{6}\),
\({B}_{9}=-\frac{3}{4}{B}_{2}^{3}\left({{A}_{1}}^{2}\right)\), \({B}_{10}=-\frac{3}{4}{B}_{1}^{3}\left({{A}_{1}}^{2}\right)\), \({D}_{1}=\frac{1}{4}\mathrm{cosh}\left(2{A}_{1}\right){B}_{1}^{2}{\Lambda }_{2}+\frac{1}{4}\mathrm{cosh}\left(2{A}_{1}\right){B}_{2}^{2}{\Lambda }_{2}-{4B}_{1}{B}_{2}{A}_{1}^{2}{\Lambda }_{2}\), \({D}_{2}=\frac{1}{4}\mathrm{sinh}\left(2{A}_{1}\right){B}_{1}^{2}{\Lambda }_{2}-\mathrm{sinh}\left(2{A}_{1}\right){B}_{2}^{2}{\Lambda }_{2}\),
\({D}_{3}=\left.\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{8}\overline{\lambda }(4Sinh\left(2{A}_{1}\right)(-{B}_{2}{B}_{6}+{B}_{1}{B}_{8})\\ +8{A}_{1}(6{A}_{1}^{3}{B}_{1}^{2}{B}_{2}^{2}+{B}_{1}{B}_{6}-{A}_{1}({B}_{1}\left({B}_{4}+{B}_{5}\right)\\ +{B}_{2}({B}_{3}+{B}_{7}))-{B}_{2}{B}_{8})-4Cosh\left(2{A}_{1}\right)\\ \left(\begin{array}{c}4{A}_{1}^{2}{B}_{1}{B}_{2}\left({B}_{1}^{2}+{B}_{2}^{2}\right)-{B}_{1}\left({B}_{3}+{B}_{7}-3{B}_{9}\right)\\ -{B}_{2}\left({B}_{4}+{B}_{5}-3{B}_{10}\right)\end{array}\right)\\ Cosh\left(2{A}_{1}\right)({A}_{1}^{2}({B}_{1}^{4}+{B}_{2}^{4})\\ +3({B}_{2}{B}_{9}+{B}_{1}{B}_{10}))){\Lambda }_{2}\end{array}\right\},\)
\({D}_{4}=\left.\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{24}\overline{\lambda }(12Cosh\left(2{A}_{1}\right)\left({B}_{2}{B}_{6}+{B}_{1}{B}_{8}\right)\\ -8{A}_{1}^{2}\left({B}_{1}{B}_{6}+{B}_{2}{B}_{8}\right)\\ +3Sinh\left(4{A}_{1}\right)\left({A}_{1}^{2}\left({B}_{1}^{4}-{B}_{2}^{4}\right)\right.\\ \left.-3{B}_{2}{B}_{9}+3{B}_{1}{B}_{10}\right)-12Sinh\left(2{A}_{1}\right)\\ (4{A}_{1}^{2}{B}_{1}{B}_{2}({B}_{1}^{2}-{B}_{2}^{2})\\ -{B}_{1}({B}_{3}+{B}_{7}+3{B}_{9})+{B}_{2}\\ ({B}_{4}+{B}_{5}+3{B}_{10}))){\Lambda }_{2}\end{array}\right\}\).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nazeer, M., Alqarni, M.Z., Hussain, F. et al. Computational analysis of multiphase flow of non-Newtonian fluid through inclined channel: heat transfer analysis with perturbation method. Comp. Part. Mech. 10, 1371–1381 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-023-00569-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-023-00569-y