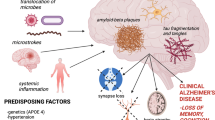
Abstract
Purpose of Review
This paper studies the different mechanisms that link oral dysbiosis and various inflammatory diseases.
Recent Findings
Oral bacteria have been found in atherosclerotic plaques. Experiments in mouse models have shown that after inoculation with Porphyromonas gingivalis, there is a higher brain barrier permeability. Fusobacterium nucleatum is present in higher amounts in patients with colorectal cancer than in healthy subjects. Porphyromonas gingivalis, along with other oral bacteria, has a strong capacity for peptide citrullination, which increases the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
Summary
Different epidemiological and experimental studies have indicated a positive correlation between a dysbiotic oral microbiome and a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, colorectal cancer, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, experimental studies of patients with inflammatory diseases have demonstrated that after periodontal treatment, their inflammatory conditions improved. These findings show that there is a strong link between the oral microbiome and the development of inflammatory diseases but that periodontal interventions could be beneficial in the treatment and management of the progression of these diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Dominguez-Bello MG, Godoy-Vitorino F, Knight R, Blaser MJ. Role of the microbiome in human development. Gut. 2019;68:1108–14.
(2019) The integrative human microbiome project. Nature. 2019;569(7758):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1238-8.
Giordano-Kelhoffer B, Lorca C, March Llanes J, Rábano A, del Ser T, Serra A, Gallart-Palau X. Oral microbiota, its equilibrium and implications in the pathophysiology of human diseases: a systematic review. Biomedicines. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOMEDICINES10081803.
Weyrich LS. (2021) The evolutionary history of the human oral microbiota and its implications for modern health. Periodontol. 2000;85:90–100.
Shang Q, Gao Y, Qin T, Wang S, Shi Y, Chen T. Interaction of oral and toothbrush microbiota affects oral cavity health. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCIMB.2020.00017.
Radaic A, Kapila YL. The oralome and its dysbiosis: new insights into oral microbiome-host interactions. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:1335–60.
Benn AML, Heng NCK, Broadbent JM, Thomson WM. Studying the human oral microbiome: challenges and the evolution of solutions. Aust Dent J. 2018;63:14–24.
Proctor LM, Creasy HH, Fettweis JM, et al. The integrative human microbiome project. Nature. 2019;569:641–8.
• Peng X, Cheng L, You Y, Tang C, Ren B, Li Y, Xu X, Zhou X. Oral microbiota in human systematic diseases. Int J Oral Sci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41368-022-00163-7. This review enhances the interest to oral microbes improving clinician’s understanding of their role in systemic diseases.
Abranches J, Zeng L, Kajfasz JK, Palmer SR, Chakraborty B, Wen ZT, Richards VP, Brady LJ, Lemos JA. Biology of oral streptococci. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1128/MICROBIOLSPEC.GPP3-0042-2018.
Yamazaki K. Oral-gut axis as a novel biological mechanism linking periodontal disease and systemic diseases: A review. Japanese Dental Sci Rev. 2023;59:273–80.
• Sedghi L, DiMassa V, Harrington A, Lynch S V, Kapila YL. The oral microbiome: role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontol 2000. 2021;87:107–131. This article reviews the current knowledge and understanding regarding oral microbial communities and their challenges to contribute to states of health or disease.
Kitamoto S, Nagao-Kitamoto H, Hein R, Schmidt TM, Kamada N. The bacterial connection between the oral cavity and the gut diseases. J Dent Res. 2020;99:1021–9.
Belibasakis GN, Bostanci N, Marsh PD, Zaura E. Applications of the oral microbiome in personalized dentistry. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;104:7–12.
• Bacali C, Vulturar R, Buduru S, Cozma A, Fodor A, Chiș A, Lucaciu O, Damian L, Moldovan ML. Oral microbiome: getting to know and befriend neighbors, a biological approach. Biomedicines. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030671. The present review reports the current knowledge regarding the oral microbiome and its relationship to modulator factors, oral and systemic health.
Joseph S. Curtis MA (2021) Microbial transitions from health to disease. Periodontol. 2000;86:201–9.
Bertolini M, Costa RC, Barão VAR, Cunha Villar C, Retamal-Valdes B, Feres M, Silva Souza JG. Oral microorganisms and biofilms: new insights to defeat the main etiologic factor of oral diseases. Microorganisms. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122413.
Valen H, Scheie AA. Biofilms and their properties. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018;126:13–8.
Santacroce L, Passarelli PC, Azzolino D, Bottalico L, Charitos IA, Cazzolla AP, Colella M, Topi S, Godoy FG, D’Addona A. Oral microbiota in human health and disease: a perspective. Exp Biol Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/15353702231187645.
Kumar PS. From focal sepsis to periodontal medicine: a century of exploring the role of the oral microbiome in systemic disease. J Physiol. 2017;595:465–76.
Simón-Soro A, Tomás I, Cabrera-Rubio R, Catalan MD, Nyvad B, Mira A. Microbial geography of the oral cavity. J Dent Res. 2013;92:616–21.
Lamont RJ, Koo H, Hajishengallis G. The oral microbiota: dynamic communities and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018;16:745–59.
Ningsih DS, Idroes R, Bachtiar BM, Khairan K, Tallei TE, Kemala P, Maulydia NB, Idroes GM, Helwani Z. Clinical and oral microbiome pattern of halitosis patients with periodontitis and gingivitis. Narra J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.52225/NARRA.V3I2.163.
Simon-Soro A, Sherriff A, Sadique S, Ramage G, MacPherson L, Mira A, Culshaw S, Malcolm J. Combined analysis of the salivary microbiome and host defence peptides predicts dental disease. Sci Rep. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20085-x.
Mira A. Oral microbiome studies: potential diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Adv Dent Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034517737024.
Rosier BT, Palazón C, García-Esteban S, Artacho A, Galiana A, Mira A. A single dose of nitrate increases resilience against acidification derived from sugar fermentation by the oral microbiome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:692883.
Pang L, Zhi Q, Jian W, Liu Z, Lin H. The oral microbiome impacts the link between sugar consumption and caries: a preliminary study. Nutrients. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU14183693.
Zhang JS, Chu C-H, Yu OY. Oral microbiome and dental caries development. Dent J (Basel). 2022;10:184.
Rosier BT, Takahashi N, Zaura E, Krom BP, MartÍnez-Espinosa RM, van Breda SGJ, Marsh PD, Mira A. The importance of nitrate reduction for oral health. J Dent Res. 2022;101:887–97.
Rosier BT, Moya-Gonzalvez EM, Corell-Escuin P, Mira A. Isolation and characterization of nitrate-reducing bacteria as potential probiotics for oral and systemic health. Front Microbiol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.555465.
Mato EG, Montaño-Barrientos BJ, Rivas-Mundiña B, Aneiros IV, López LS, Posse JL, Lamas LM. Anti-caries Streptococcus spp.: a potential preventive tool for special needs patients. Spec Care Dent. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/SCD.12920.
Llena C, Almarche A, Mira A, López MA. Antimicrobial efficacy of the supernatant of streptococcus dentisani against microorganisms implicated in root canal infections. J Oral Sci. 2019;61:184–94.
Ferrer MD, Pérez S, Lopez AL, Sanz JL, Melo M, Llena C, Mira A. Evaluation of clinical, biochemical and microbiological markers related to dental caries. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18116049.
Maki KA, Ganesan SM, Meeks B, Farmer N, Kazmi N, Barb JJ, Joseph PV, Wallen GR. The role of the oral microbiome in smoking-related cardiovascular risk: a review of the literature exploring mechanisms and pathways. J Transl Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12967-022-03785-X.
Sedghi LM, Bacino M, Kapila YL. Periodontal disease: the good, the bad, and the unknown. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.766944.
Pussinen PJ, Kopra E, Pietiäinen M, Lehto M, Zaric S, Paju S, Salminen A. Periodontitis and cardiometabolic disorders: the role of lipopolysaccharide and endotoxemia. Periodontol 2000. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12433.
Oppermann RV, Weidlich P, Musskopf ML. Periodontal disease and systemic complications. Braz Oral Res. 2012;26(Suppl 1):39–47.
Pietiäinen M, Liljestrand JM, Kopra E, Pussinen PJ. Mediators between oral dysbiosis and cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018;126:26–36.
Li Y, Zhu M, Liu Y, Luo B, Cui J, Huang L, Chen K, Liu Y. The oral microbiota and cardiometabolic health: a comprehensive review and emerging insights. Front Immunol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/FIMMU.2022.1010368.
Alfaddagh A, Martin SS, Leucker TM, Michos ED, Blaha MJ, Lowenstein CJ, Jones SR, Toth PP. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2020;4:100130.
Tonelli A, Lumngwena EN, Ntusi NAB. The oral microbiome in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41569-022-00825-3.
Shin JH. Dementia epidemiology fact sheet 2022. Ann Rehabil Med. 2022;46:53–9.
Yanakiev M, Soper O, Berg DA, Kang E. Modelling Alzheimer’s disease using human brain organoids: current progress and challenges. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1017/ERM.2022.40.
Baechle JJ, Chen N, Makhijani P, Winer S, Furman D, Winer DA. Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol Metab. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLMET.2023.101755.
Cecoro G, Annunziata M, Iuorio MT, Nastri L, Guida L. Periodontitis, low-grade inflammation and systemic health: a scoping review. Medicina (B Aires). 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/MEDICINA56060272.
Martínez-García M, Hernández-Lemus E. Periodontal inflammation and systemic diseases: an overview. Front Physiol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.709438.
Kamer AR, Dasanayake AP, Craig RG, Glodzik-Sobanska L, Bry M, De Leon MJ. Alzheimer’s disease and peripheral infections: the possible contribution from periodontal infections, model and hypothesis. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2008-13408.
Larvin H, Gao C, Kang J, Aggarwal VR, Pavitt S, Wu J. The impact of study factors in the association of periodontal disease and cognitive disorders: systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/AGEING/AFAD015.
Cirstea MS, Kliger D, Maclellan AD, et al. The oral and fecal microbiota in a Canadian cohort of alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;87:247–58.
Beydoun MA, Beydoun HA, Hossain S, El-Hajj ZW, Weiss J, Zonderman AB. Clinical and bacterial markers of periodontitis and their association with incident all-cause and Alzheimer’s disease dementia in a large national survey. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;75:157–72.
Nascimento PC, Castro MML, Magno MB, Almeida APCPSC, Fagundes NCF, Maia LC, Lima RR. Association between periodontitis and cognitive impairment in adults: a systematic review. Front Neurol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNEUR.2019.00323.
Ilievski V, Zuchowska PK, Green SJ, Toth PT, Ragozzino ME, Le K, Aljewari HW, O’Brien-Simpson NM, Reynolds EC, Watanabe K. Chronic oral application of a periodontal pathogen results in brain inflammation, neurodegeneration and amyloid beta production in wild type mice. PLoS ONE. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0204941.
Borsa L, Dubois M, Sacco G, Lupi L. Analysis the link between periodontal diseases and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH18179312.
Guo H, Li B, Yao H, Liu D, Chen R, Zhou S, Ji Y, Zeng L, Du M. Profiling the oral microbiomes in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Oral Dis. 2023;29:1341–55.
Dominy SS, Lynch C, Ermini F, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci Adv. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIADV.AAU3333.
Kanagasingam S, Von Ruhland C, Welbury R, Chukkapalli SS, Singhrao SK. Porphyromonas gingivalis conditioned medium induces amyloidogenic processing of the amyloid-β protein precursor upon in vitro infection of SH-SY5Y cells. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2022;6:577–87.
Lei S, Li J, Yu J, Li F, Pan Y, Chen X, Ma C, Zhao W, Tang X. Porphyromonas gingivalis bacteremia increases the permeability of the blood-brain barrier via the Mfsd2a/Caveolin-1 mediated transcytosis pathway. Int J Oral Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41368-022-00215-Y.
Cheng X, Chi L, Lin T, Liang F, Pei Z, Sun J, Teng W. Exogenous monocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cells ameliorate immune imbalance, neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in 5xFAD mice infected with Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12974-023-02743-8.
D’Aiuto F, Parkar M, Andreou G, Suvan J, Brett PM, Ready D, Tonetti MS. Periodontitis and systemic inflammation: control of the local infection is associated with a reduction in serum inflammatory markers. J Dent Res. 2004;83:156–60.
Lyra P, Machado V, Proença L, Domingos J, Godinho C, Mendes JJ, Botelho J. Parkinson’s disease, periodontitis and patient-related outcomes: a cross-sectional study. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56:1–11.
Hu S, Li S, Ning W, et al. Identifying crosstalk genetic biomarkers linking a neurodegenerative disease, Parkinson’s disease, and periodontitis using integrated bioinformatics analyses. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNAGI.2022.1032401.
Lyra P, Botelho J, Machado V, Rota S, Walker R, Staunton J, Proença L, Chaudhuri KR, Mendes JJ. Self-reported periodontitis and C-reactive protein in Parkinson’s disease: a cross-sectional study of two American cohorts. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41531-022-00302-1.
Botelho J, Lyra P, Proença L, Godinho C, Mendes JJ, Machado V. Relationship between blood and standard biochemistry levels with periodontitis in Parkinson’s disease patients: data from the NHANES 2011–2012. J Pers Med. 2020;10:1–11.
Giannopoulou N, Constantinou C. Recent developments in diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer: a narrative review. Oncology. 2023;101:675–84.
Laredo V, García-Mateo S, Martínez-Domínguez SJ, López de la Cruz J, Gargallo-Puyuelo CJ, Gomollón F. Risk of cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and keys for patient management. Cancers (Basel). 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS15030871.
Byrd KM, Gulati AS. The “gum–gut” axis in inflammatory bowel diseases: a hypothesis-driven review of associations and advances. Front Immunol. 2021;12:1.
Molinero N, Taladrid D, Zorraquín-Peña I, de Celis M, Belda I, Mira A, Bartolomé B, Moreno-Arribas MV. Ulcerative colitis seems to imply oral microbiome dysbiosis. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022;44:1513–27.
Tanwar H, Gnanasekaran JM, Allison D, et al. Unraveling the link between periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease: challenges and outlook. ArXiv. 2023.
Lam GA, Albarrak H, McColl CJ, Pizarro A, Sanaka H, Gomez-Nguyen A, Cominelli F, Batista P, da Silva A. The oral-gut axis: periodontal diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/IBD/IZAC241.
Kitamoto S, Nagao-Kitamoto H, Jiao Y, et al. The intermucosal connection between the mouth and gut in commensal pathobiont-driven colitis. Cell. 2020;182:447-462.e14.
Abed J, Maalouf N, Manson AL, et al. Colon cancer-associated Fusobacterium nucleatum may originate from the oral cavity and reach colon tumors via the circulatory system. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:556050.
Wang N, Fang J-Y. Fusobacterium nucleatum, a key pathogenic factor and microbial biomarker for colorectal cancer. Trends Microbiol. 2023;31:159–72.
Alon-Maimon T, Mandelboim O, Bachrach G. Fusobacterium nucleatum and cancer. Periodontol. 2022;2000(89):166–80.
Nasiri K, Amiri Moghaddam M, Etajuri EA, Badkoobeh A, Tavakol O, Rafinejad M, Forutan Mirhosseini A, Fathi A. Periodontitis and progression of gastrointestinal cancer: current knowledge and future perspective. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023;25:2801–11.
Pani G (2023) Fusobacterium & Co. at the stem of cancer: microbe–cancer stem cell interactions in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel) 15:2583.
McCallum G, Tropini C. The gut microbiota and its biogeography. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-023-00969-0.
Liu H, Hong XL, Sun TT, Huang XW, Wang JL, Xiong H. Fusobacterium nucleatum exacerbates colitis by damaging epithelial barriers and inducing aberrant inflammation. J Dig Dis. 2020;21:385–98.
Ou S, Wang H, Tao Y, Luo K, Ye J, Ran S, Guan Z, Wang Y, Hu H, Huang R. Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: from phenomenon to mechanism. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.1020583.
Kageyama S, Takeshita T, Takeuchi K, et al. Characteristics of the salivary microbiota in patients with various digestive tract cancers. Front Microbiol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2019.01780.
Zekeridou A, Gilbert B, Finckh A, Giannopoulou C. Periodontitis in first degree-relatives of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis: a short narrative review. Front Oral Health. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/FROH.2022.895753.
Kondo N, Kuroda T, Kobayashi D. Cytokine networks in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:10922.
Karami J, Aslani S, Jamshidi A, Garshasbi M, Mahmoudi M. Genetic implications in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis; an updated review. Gene. 2019;702:8–16.
Holers VM, Demoruelle MK, Kuhn KA, Buckner JH, Robinson WH, Okamoto Y, Norris JM, Deane KD. Rheumatoid arthritis and the mucosal origins hypothesis: protection turns to destruction. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14:542–57.
González-Febles J. Sanz M (2021) Periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned about their connection and their treatment? Periodontol. 2000;87:181–203.
Manoil D, Bostanci N, Mumcu G, Inanc N, Can M, Direskeneli H, Belibasakis GN. Novel and known periodontal pathogens residing in gingival crevicular fluid are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J Periodontol. 2021;92:359–70.
Moentadj R, Wang Y, Bowerman K, et al. Streptococcus species enriched in the oral cavity of patients with RA are a source of peptidoglycan-polysaccharide polymers that can induce arthritis in mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:573–81.
de Molon RS, Rossa C, Thurlings RM, Cirelli JA, Koenders MI. Linkage of periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis: current evidence and potential biological interactions. Int J Mol Sci 2019. 2019; 20:4541.
Rodríguez-Lozano B, González-Febles J, Garnier-Rodríguez JL, Dadlani S, Bustabad-Reyes S, Sanz M, Sánchez-Alonso F, Sánchez-Piedra C, González-Dávila E, Díaz-González F. Association between severity of periodontitis and clinical activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a case-control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21:1–12.
Looh SC, Soo ZMP, Wong JJ, Yam HC, Chow SK, Hwang JS. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans as the aetiological cause of rheumatoid arthritis: what are the unsolved puzzles? Toxins (Basel). 2022;14:50.
Olsen I, Singhrao SK, Potempa J. Citrullination as a plausible link to periodontitis, rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. J Oral Microbiol. 2018;10:1487742.
Sapart E, Faria M, Dierckx S, Durez P, Fonseca JE. Editorial: Risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis and pre-rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.1052618.
Onuora S. P. gingivalis exacerbates arthritis via gut barrier dysfunction. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(9):512–512.
Perricone C, Ceccarelli F, Matteo S, Di Carlo G, Bogdanos DP, Lucchetti R, Pilloni A, Valesini G, Polimeni A, Conti F. Porphyromonas gingivalis and rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31:517–24.
Kobayashi T, Bartold PM. Periodontitis and periodontopathic bacteria as risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the last 10 years. Japanese Dental Sci Rev. 2023;59:263–72.
Li C, Yu R, Ding Y. Association between Porphyromonas Gingivalis and systemic diseases: focus on T cells-mediated adaptive immunity. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.1026457.
Cheng Z, Do T, Mankia K, Meade J, Hunt L, Clerehugh V, Speirs A, Tugnait A, Emery P, Devine D. Dysbiosis in the oral microbiomes of anti-CCP positive individuals at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:162–8.
Lopez-Oliva I, Paropkari AD, Saraswat S, et al. Dysbiotic subgingival microbial communities in periodontally healthy patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70:1008–13.
Tong Y, Xu S, Huang L, Chen C. Obesity and insulin resistance: pathophysiology and treatment. Drug Discov Today. 2022;27:822–30.
Wondmkun YT. <p>Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: associations and therapeutic implications</p>. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:3611–6.
Qin H, Li G, Xu X, Zhang C, Zhong W, Xu S, Yin Y, Song J. The role of oral microbiome in periodontitis under diabetes mellitus. J Oral Microbiol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/20002297.2022.2078031.
Ojo KO, Odukoya OO, Ayanbadejo PO, Akinlawon D. Prevalence of periodontitis and oral hygiene practices among diabetic and non-diabetic patients in a tertiary hospital in Lagos: a cross-sectional study. Pan African Med J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2023.45.131.37904.
Păunică I, Giurgiu M, Dumitriu AS, Păunică S, Pantea Stoian AM, Martu MA, Serafinceanu C. The bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus—a review. Diagnostics 2023. 2023;13:681.
Xiao E, Mattos M, Vieira GHA, Chen S, Corrêa JD, Wu Y, Albiero ML, Bittinger K, Graves DT. Diabetes enhances IL-17 expression and alters the oral microbiome to increase its pathogenicity. Cell Host Microbe. 2017;22:120-128.e4.
Hajishengallis G, Chavakis T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:426–40.
Sakanaka A, Kuboniwa M, Katakami N, et al. Saliva and plasma reflect metabolism altered by diabetes and periodontitis. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMOLB.2021.742002.
Singh M, Bains V, Jhingran R, Srivastava R, Madan R, Maurya S, Rizvi I. Prevalence of periodontal disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study. Contemp Clin Dent. 2019;10:349.
Wu CZ, Yuan YH, Liu HH, et al. Epidemiologic relationship between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20:1–15.
Courbon G, Rinaudo-Gaujous M, Blasco-Baque V, Auger I, Caire R, Mijola L, Vico L, Paul S, Marotte H. Porphyromonas gingivalis experimentally induces periodontis and an anti-CCP2-associated arthritis in the rat. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:594–9.
Blasco-Baque V, Garidou L, Pomié C, et al. Periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis drives periodontal microbiota dysbiosis and insulin resistance via an impaired adaptive immune response. Gut. 2017;66:872–85.
Shi B, Lux R, Klokkevold P, Chang M, Barnard E, Haake S, Li H. The subgingival microbiome associated with periodontitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. ISME J. 2020;14:519–30.
Su Y, Ye L, Hu C, Zhang Y, Liu J, Shao L. Periodontitis as a promoting factor of T2D: current evidence and mechanisms. Int J Oral Sci. 2023;15:25.
Thouvenot K, Turpin T, Taïlé J, Clément K, Meilhac O, Gonthier M-P. Links between insulin resistance and periodontal bacteria: insights on molecular players and therapeutic potential of polyphenols. Biomolecules. 2022;12:378.
Vergnes JN, Canceill T, Vinel A, et al. The effects of periodontal treatment on diabetic patients: The DIAPERIO randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45:1150–63.
Minty M, Canceil T, Serino M, Burcelin R, Tercé F, Blasco-Baque V. Oral microbiota-induced periodontitis: a new risk factor of metabolic diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019;20:449–59.
Montenegro MM, Ribeiro IWJ, Kampits C, Saffi MAL, Furtado MV, Polanczyk CA, Haas AN, Rösing CK. Randomized controlled trial of the effect of periodontal treatment on cardiovascular risk biomarkers in patients with stable coronary artery disease: Preliminary findings of 3 months. J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46:321–31.
Roca-Millan E, Gonzalez-Navarro B, Sabater-Recolons M, Mari-Roig A, Jane-Salas E, Lopez-Lopez J. Periodontal treatment on patients with cardiovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018;0–0.
Santos-Paul MA, Neves RS, Gowdak LHW, de Paula FJ, David-Neto E, Bortolotto LA, Ramires JAF, De Lima JJG. Cardiovascular risk reduction with periodontal treatment in patients on the waiting list for renal transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.13658.
Zhou Q-B, Xia W-H, Ren J, et al. Effect of intensive periodontal therapy on blood pressure and endothelial microparticles in patients with prehypertension and periodontitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Periodontol. 2017;88:711–22.
Mauri-Obradors E, Merlos A, Estrugo-Devesa A, Jané-Salas E, López-López J, Viñas M. Benefits of non-surgical periodontal treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45:345–53.
Ahuja CR, Kolte AP, Kolte RA, Gupta M, Chari S. Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on gingival crevicular fluid and serum leptin levels in periodontally healthy chronic periodontitis and chronic periodontitis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/JICD.12420.
Goyal L, Gupta S, Samujh T. Does nonsurgical periodontal therapy improve glycemic control? Evid Based Dent. 2023;24:21–2.
Di Domenico GL, Minoli M, Discepoli N, Ambrosi A, de Sanctis M. Effectiveness of periodontal treatment to improve glycemic control: an umbrella review. Acta Diabetol. 2022;60:101–13.
Thilagar S, Theyagarajan R, Mugri MH, Bahammam HA, Bahammam SA, Bahammam MA, Yadalam PK, Raj AT, Bhandi S, Patil S. Periodontal treatment for chronic periodontitis with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Dent J. 2022;72:832–8.
Cosgarea R, Tristiu R, Dumitru RB, Arweiler NB, Rednic S, Sirbu CI, Lascu L, Sculean A, Eick S. Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on periodontal laboratory and clinical data as well as on disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Oral Investig. 2019;23:141–51.
Zhao X, Liu Z, Shu D, Xiong Y, He M, Xu S, Si S, Guo B. Association of periodontitis with rheumatoid arthritis and the effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:5802–10.
Nguyen V, Nguyen T, Huynh N, Nguyen K, Le T, Hoang H. Effects of non-surgical periodontal treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomized clinical trial. Dent Med Probl. 2021;58:97–105.
Schwahn C, Frenzel S, Holtfreter B, et al. Effect of periodontal treatment on preclinical Alzheimer’s disease-results of a trial emulation approach. Alzheimers Dement. 2022;18:127–41.
Cakmak O, Alkan BA, Saatci E, Tasdemir Z. The effect of nonsurgical periodontal treatment on gingival crevicular fluid stress hormone levels: a prospective study. Oral Dis. 2019;25:250–7.
Yoshihara T, Kioi M, Baba J, et al. A prospective interventional trial on the effect of periodontal treatment on Fusobacterium nucleatum abundance in patients with colorectal tumours. Sci Rep. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-021-03083-4.
Khan NS, Craven R, Rafiq A, Rafiq A. Treatment of periodontal disease in pregnancy for the prevention of adverse pregnancy outcomes: a systematic review of systematic reviews. J Pak Med Assoc. 2023;73:611–20.
Govindasamy R, Periyasamy S, Narayanan M, Balaji V, Dhanasekaran M, Karthikeyan B. The influence of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on the occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes: a systematic review of the current evidence. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2020;24:7–14.
Rosier BT, Marsh PD, Mira A. Resilience of the oral microbiota in health: mechanisms that prevent dysbiosis. J Dent Res. 2018;97:371–80.
Ren Z, Xue Y, Zhang H, Zhang T, Wang M, Guo T, Xie J. Association between probiotic consumption and periodontitis: evidence from <scp>NHANES</scp> 2009–2014. J Clin Periodontol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13865.
Featherstone JDB, Chaffee BW. The evidence for caries management by risk assessment (CAMBRA®). Adv Dent Res. 2018;29:9–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors wrote and reviewed the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of Interest
Sofía Jiménez de Nunzio declares that she has no conflict of interest. Sergio Portal-Núñez declares that he has no conflict of interest. Caridad M. Arias Macías declares that she has no conflict of interest. Marta Bruna Del Cojo declares that she has no conflict of interest. Carlos Adell-Pérez declares that he has no conflict of interest. María Latorre Molina declares that she has no conflict of interest. Manuel Macías-González declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ana Adell-Pérez declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez De Nunzio, S., Portal-Núñez, S., Arias Macías, C.M. et al. Does a Dysbiotic Oral Microbiome Trigger the Risk of Chronic Inflammatory Disease?. Curr Treat Options Allergy 10, 364–383 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40521-023-00355-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40521-023-00355-4