Abstract
Objective
The predetermination of the risk for falls in elderly patients, who will have or had a surgery, enables one to carry out the protective/preventive interventions on this matter. The aim of this review was to provide an up-to-date meta-analysis with regard to falls in elderly surgical patients.
Materials and methods
The studies, which were carried out on elderly patients between January 2009 and November 2019 and which investigated the risk factors for falls in elderly surgical patients, were screened on the databases of Google Scholar, Pubmed, Ovid, Cinahl through various combinations of keywords, such as “geriatrics”, “aged”, “surgery”, “accidental falls” in English or Turkish, to determine the risk factors for the falls in elderly surgical patients.
Results
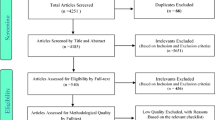
Meeting the study inclusion criteria, 18 studies were analyzed. Of these studies, three were retrospective, seven descriptive, two case–control, four cross-sectional, and two prospective. The kappa value of the general rate of agreement was found as 0.84. No publication bias found in the studies included (Kendall’s tau b = 0.31; p = 0.07) in the meta-analysis based on the values calculated.
Conclusion
In this meta-analysis, it was determined that the falls in elderly surgical patients were quite a prevalent public health problem, that the presence of chronic diseases and previous history of falls constituted an extremely high risk for the falls in elderly patients, and that the age or the presence of a gait-inhibiting condition did not constitute any risk for the falls in elderly patients.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Turkish Statistical Institute (2013) Seniors with statistics. Ankara Number: 16057. Turkish Statistical Institute
Karadakovan A (2017) Elderly and geriatric nursing. In: Karadakovan A, Aslan FE (eds) Care in internal and surgical diseases. Akademisyen Bookstore, Ankara, p 105
T.C. Ministry of Health General Directorate of Primary Health Care Services (2011) Elderly health module: a training guide for educators. Anıl Printing, İstanbul
Karan MA (2018) Evaluation of fall, its importance and risk factors in the elderly. Aegean J Med Sci 4:129–132
NICE clinical guideline 161 (2013) Falls: assessment and prevention of falls in older people. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
Dunne TJ, Gaboury I, Ashe MC (2014) Falls in hospital increase length of stay regardless of degree of harm. J Eval Clin Pract 20:396–400
Wong CA, Recktenwald AJ, Jones ML et al (2011) The cost of serious fall-related injuries at three Midwestern hospitals. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 37:81–87
Barıs VK, Intepeler SS, Yeginboy EY (2016) The cost of serious patient fall-related injuries at hospitals in Turkey: a matched case-control study. Clin Nurs Res 27:162–179. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773816671521
Çeçen D, Özbayır T (2011) Evaluation of practice’s related to falling prevention and determination of falling risk of elderly patients who are treated in surgical clinics. Ege Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Yüksek Okulu Dergisi 27:11–23
Savcı C, Kaya H, Acaroğlu R et al (2009) The determinatıon of patients falling risk and taken preventive measures in neurology and neurosurgery clinics. Maltepe Univ J Nurs Sci 2:19–25
Ackerman DB, Trousdale RT, Bieber P et al (2010) Postoperative patient falls on an orthopedic inpatient unit. J Arthroplasty 25:10–14
Berke D, Aslan FE (2010) Falling risk score in patients undergone to neurosurgery. Turk Klin J Neur 5:147–154
Özden D, Karagözoğlu Ş, Kurukız S (2012) Determining patients fall risk by two scale and this sensitivity of scales in determining falling: pilot operation. Anatolian J Nurs Health Sci 15:1
Jones TS, Dunn CL, Wu DS et al (2013) Relationship between asking an older adult about falls and surgical outcomes. JAMA Surg 148:1132
Tanıl V, Çetinkaya Y, Sayer V et al (2014) Evaluating fall risk. J Health Scholars 1:21–26
Özlü ZK, Yayla A, Özer N et al (2015) Risk of falling in surgical patients. Kafkas J Med Sci 5:94–99. https://doi.org/10.5505/kjms.2015.19870
Çelik GO, Zıngal H (2016) The determination of falling risk of patients and precautions taken in neurosurgery clinic. Izmir Kâtip Çelebi Univ J Health Sci Faculty 1:7–11
Ishikuro M, Ubeda SRG, Obara T et al (2017) Exploring risk factors of patient falls: a retrospective hospital record study in Japan. Tohoku J Exp Med 243:195–203
Kobayashi K, Imagama S, Inagaki Y et al (2017) Incidence and characteristics of accidental falls in hospitalizations. Nagoya J Med Sci 79:291–298. https://doi.org/10.18999/nagjms.79.3.291
Mata LRF, Azevedo C, Policapro AG et al (2017) Factors associated with the risk of fall in adults in the postoperative period: a cross-sectional study. Rev Latino-Am Enfermagem 25:e2904. https://doi.org/10.1590/1518-8345.1775.2904
Victor MAG, Luzia MF, Severo IM et al (2017) Falls ın surgıcal patıents: subsıdıes for safe nursıng care. J Nurs UFPE Online 11:4027–4035. https://doi.org/10.5205/reuol.10712-95194-3-SM.1110sup201704
Yaşar G, Türk G (2018) Determination of risk factors in patients falls. J Nurs Sci 1:15–20
Severo IM, Kuchenbecker RS, Vieira DFVB et al (2018) Risk factors for fall occurrence in hospitalized adult patients: a case-control study. Rev Latino-Am Enfermagem 26:e3016. https://doi.org/10.1590/1518-8345.2460.3016
Najafpour Z, Godarzi Z, Arab M et al (2019) Risk factors for falls in hospital in-patients: a prospective nested case control study. Int J Health Policy Manage 8:300–306. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijhpm.2019.11
Özşaker E, Yapsu F, Yılmaz GD (2019) Determination of falling risks of patients over 65 years old in the surgical clinics. J Harran Univ Med Faculty 16:245–249. https://doi.org/10.35440/hutfd.486797
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting ıtems for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
Polit DF, Beck CT (2009) Literature reviews: finding and reviewing research evidence. In: Polit DF, Tatano BC (eds) Essentails of nursing research: appraising evidence for nursing practice, 7th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 169–193
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ et al (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br Med J 327:557–560
Dinçer S (2014) Applied meta-analysis in educational sciences. Pagem Publishing, Ankara
Pirrie M, Saini G, Angeles R et al (2020) Risk of falls and fear of falling in older adults residing in public housing in Ontario, Canada: findings from a multisite observational study. BMC Geriatr. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1399-1
Ambrose AF, Paul G, Hausdorff JM (2013) Risk factors for falls among older adults: a review of the literature. Maturitas 75:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.02.009
Tinetti ME, Kumar C (2010) The patient who falls “it’s always a trade-off.” JAMA 303:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.2024
Kim T, Choi SD, Xiong S (2020) Epidemiology of fall and its socioeconomic risk factors in community-dwelling Korean elderly. PLoS ONE 15:e0234787. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234787
Fındık YÜ, Yeşilyurt SD, Işıklı GA (2019) Evaluatıng fall rısk ın surgıcal patıents. Namık Kemal Med J 7:90–95
Rashid I, Tiwari P, Singh Lehl S (2019) Prevalence and determinants of fall risk among elderly inpatients at a tertiary care public teaching hospital. J Gerontol Gerıatrıcs 67:96–102
Schwendimann R, Bühler H, Geest SD et al (2008) Characteristics of hospital inpatient falls across clinical departments. Gerontology 54:342–348
Sharif SI, Al-Harbi AB, Al-Shihabi AM et al (2018) Falls in the elderly: assessment of prevalence and risk factors. Pharmacy Practice 16:1206. https://doi.org/10.18549/PharmPract.2018.03.1206
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Ethical approval
This is a meta-analysis study.
İnform consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hacıdursunoğlu Erbaş, D., Çınar, F. & Eti Aslan, F. Elderly patients and falls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res 33, 2953–2966 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-021-01843-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-021-01843-w