Abstract
Introduction
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a serious psychiatric disorder that is difficult to treat and often follows a protracted course. A number of theoretical models have been proposed for the etiology and maintenance of AN. Two domains that have received substantial attention in the literature on AN are affect and reward/punishment processes. However, despite an overlap in the nature and implications of these processes, studies of AN addressing these constructs have typically investigated them independently.
Purpose
The purpose of this narrative review is to integrate the literature on the role of affect, reward, and punishment in AN.
Method
We provide a focused narrative overview of the literature relating to the affect, reward, and punishment in AN via a synthesis of recent reviews and meta-analyses.
Results
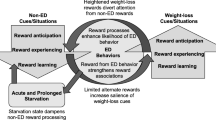
We first describe several prominent affect and reward/punishment-based conceptualizations of AN, followed by a brief overview of the existing empirical literature in these domains.
Conclusion
We provide a critical discussion of the disparate nature of these literatures in AN, including associated limitations. We then conclude with an extensive discussion of directions for future research that integrate the study of affect and reward/punishment processes in AN.
Level of evidence
Level V, narrative review.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. Washington
Katzman DK (2005) Medical complications in adolescents with anorexia nervosa: a review of the literature. Int J Eat Disord 37(S1):S52–S59. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20118
Kaye WH, Bulik CM, Thornton L, Barbarich N, Masters K (2004) Comorbidity of anxiety disorders with anorexia and bulimia nervosa. Am J Psychiatry 161:2215–2221. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.12.2215
Papadopoulos FC, Ekbom A, Brandt L, Ekselius L (2009) Excess mortality, causes of death and prognostic factors in anorexia nervosa. Br J Psychiatry 194(1):10–17. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.108.054742
Sullivan PF (1995) Mortality in anorexia nervosa. Am J Psychiatry 152(7):1073–1074. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.152.7.1073
Bulik CM, Berkman KA, Brownley KA, Sedway JA, Lohr KN (2007) Anorexia nervosa treatment: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int J Eat Disord 40(4):310–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20367
Culber KM, Racine SE, Klump KL (2015) Research review: What we have learned about the causes of eating disorders—a synthesis of sociocultural, psychological, and biological research. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 56(11):1141–1164. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12441
Lavender JM, Wonderlich SA, Engel SG, Gordon KH, Kaye WH, Mitchell JE (2015) Dimensions of emotion dysregulation in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: a conceptual review of the empirical literature. Clin Psychol Rev 40:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2015.05.010
Oldershaw A, Lavender T, Sallis H, Stahl D, Schmidt U (2015) Emotion generation and regulation in anorexia nervosa: a systematic review and meta-analysis of self-report data. Clin Psychol Rev 39:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2015.04.005
Harrison A, O’Brien N, Lopez C, Treasure J (2010) Sensitivity to reward and punishment in eating disorders. Psychiatry Res 177(1–2):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2009.06.010
Keating C, Tilbrook AJ, Rossell SL, Enticott PG, Fitzgerald PB (2012) Reward processing in anorexia nervosa. Neuropsychologia 50(5):567–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.01.036
O’Hara CB, Campbell IC, Schmidt U (2015) A reward-centred model of anorexia nervosa: a focussed narrative review of the neurological and psychophysiological literature. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 52:131–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.02.012
Forbes EE, Dahl RE (2005) Neural systems of positive affect: Relevance to understanding child and adolescent depression? Dev Psychopathol 17(3):827–850. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095457940505039X
Watson D (2000) Mood and temperament. Guilford Press, New York
Berridge KC, Robinson TE (2003) Parsing reward. Trends Neurosci 26(9):507–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(03)00233-9
Berridge KC, Kringelbach ML (2008) Affective neuroscience of pleasure: reward in humans and animals. Psychopharmacology 199(3):457–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1099-6
Gray J (1970) The psychophysiological basis of introversion-extraversion. Behav Res Ther 8(3):249–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-7967(70)90069-0
Watson D, Wiese D, Vaidya J, Tellegen A (1999) The two general activation systems of affect: structural findings, evolutionary considerations, and psychobiological evidence. J Pers Soc Psychol 76(5):820–838. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.76.5.820
Rolls E (2000) On the brain and emotion. Behav Brain Sci 23(02):219–228. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X00512424
Heatherton TF, Baumeister RF (1991) Binge eating as escape from self-awareness. Psychol Bull 110(1):86–108. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.110.1.86
Wildes JE, Ringham RM, Marcus MD (2010) Emotion avoidance in patients with anorexia nervosa: initial test of a functional model. Int J Eat Disord 43(5):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.20730
Fruzzetti AE, Shenk C, Hoffman PD (2005) Family interaction and the development of borderline personality disorder: a transactional model. Dev Psychopathol 17(4):1007–1030. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579405050479
Linehan MM (1993) Dialectical behavior therapy for treatment of borderline personality disorder: Implications for the treatment of substance abuse. In: Onken LS, Blane JD, Boren JJ (eds) National Institute on Drug Abuse research monograph: behavioral treatments for drug abuse and dependence. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, pp 201–216
Haynos AF, Fruzzetti AE (2011) Anorexia nervosa as a disorder of emotion dysregulation: Evidence and treatment implications. Clin Psychol Sci Pract 18(3):183–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2850.2011.01250.x
Corstorphine E (2006) Cognitive–emotional–behavioural therapy for the eating disorders: working with beliefs about emotions. Eur Eat Disord Rev 14(6):448–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.747
Selby EA, Wonderlich SA, Crosby RD, Engel SG, Panza E, Mitchell JE et al (2014) Nothing tastes as good as thin feels low positive emotion differentiation and weight-loss activities in anorexia nervosa. Clin Psychol Sci 39:870–911. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702613512794
Schmidt U, Treasure J (2006) Anorexia nervosa: valued and visible. A cognitive-interpersonal maintenance model and its implications for research and practice. Br J Clin Psychol 45(3):343–366. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466505x53902
Fairburn CG, Cooper Z, Shafran R (2003 May) Cognitive behaviour therapy for eating disorders: a “transdiagnostic” theory and treatment. Behav Res Ther 41(5):509–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(02)00088-8
Bergh C, Södersten P (1996) Anorexia nervosa, self–starvation and the reward of stress. Nat Med 2(1):21–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0196-21
Park RJ, Godier LR, Cowdrey FA (2014) Hungry for reward: How can neuroscience inform the development of treatment for anorexia nervosa? Behav Res Ther 62:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2014.07.007
Steinglass JE, Walsh BT (2016) Neurobiological model of the persistence of anorexia nervosa. J Eat Disord 4:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40337-016-0106-2
Davis C, Woodside DB (2002) Sensitivity to the rewarding effects of food and exercise in the eating disorders. Compr Psychiatry 43(3):189–194. https://doi.org/10.1053/comp.2002.32356
Zink CF, Weinberger DR (2010) Cracking the moody brain: the rewards of self starvation. Nat Med 16(12):1382–1383. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1210-1382
Keating C (2010) Theoretical perspective on anorexia nervosa: the conflict of reward. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(1):73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.07.004
Gross JJ (1998) The emerging field of emotion regulation: an integrative review. Rev Gen Psychol 2(3):271. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.2.3.271
Gratz KL, Roemer L (2004) Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 26(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOBA.0000007455.08539.94
Sala M, Heard A, Black EA (2016) Emotion-focused treatments for anorexia nervosa: a systematic review of the literature. Eat Weight Disord 21(2):147–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0257-9
Ohmann S, Popow C, Wurzer M, Karwautz A, Sackl-Pammer P, Schuch B (2013) Emotional aspects of anorexia nervosa: results of prospective naturalistic cognitive behavioral group therapy. Neuropsychiatr Klin Diagn Ther Rehabil Organ Ges Osterreichischer Nervenarzte Psychiater 27(3):119–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40211-013-0065-7
Cook BJ, Wonderlich SA, Mitchell JE, Thompson R, Sherman R, Mccallum K (2016) Exercise in eating disorders treatment: systematic review and proposal of guidelines. Med Sci Sports Exerc 48(7):1408–1414. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000912
Diener E, Larsen RJ (1993) The experience of emotional well-being. In: Lewis M, Haviland JM, Lewis M, Haviland JM (eds) Handbook of emotions. Guilford Press, New York, pp 405–415
Myers DG, Diener E (1995) Who is happy? Psychol Sci 6(1):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.1995.tb00298.x
Kaye WH, Wierenga CE, Knatz S, Liang J, Boutelle K, Hill L et al (2015) Temperament-based treatment for anorexia nervosa. Eur Eat Disord Rev 23(1):12–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2330
Vitousek K, Manke F (1994) Personality variables and disorders in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. J Abnorm Psychol 103(1):137–147. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.103.1.137
Kaye WH, Barbarich NC, Putnam K, Gendall KA, Fernstrom J, Fernstrom M et al (2003) Anxiolytic effects of acute tryptophan depletion in anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord 33(3):257–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.10135
Fischer S, Breithaupt L, Wonderlich J, Westwater ML, Crosby RD, Engel SG et al (2017) Impact of the neural correlates of stress and cue reactivity on stress related binge eating in the natural environment. J Psychiatr Res 92:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.03.017
Monteleone AM, Cardi V, Volpe U, Fico G, Ruzzi V, Pellegrino F, Castellini G, Monteleone P, Maj M (2018) Attachment and motivational systems: relevance of sensitivity to punishment for eating disorder psychopathology. Psychiatry Res 260:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.12.002
Haynos AF, Berg KC, Cao L, Crosby RD, Lavender JM, Utzinger LM et al (2017) Trajectories of higher- and lower-order dimensions of negative and positive affect relative to restrictive eating in anorexia nervosa. J Abnorm Psychol 126(5):495–505. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000202
Selby EA, Cornelius T, Fehling KB, Kranzler A, Panza EA, Lavender JM et al (2015) A perfect storm: examining the synergistic effects of negative and positive emotional instability on promoting weight loss activities in anorexia nervosa. Front Psychol 31:6:1260. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01260
Matton A, de Jong P, Goosens L, Jonker N, Van Malderen E, Vervaet M et al (2017) Sensitivity for cues predicting reward and punishment in young women with eating disorders. Eur Eat Disorders Rev 25(6):501–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2541
Murao E, Sugihara G, Isobe M, Noda T, Kawabata M, Matsukawa N et al. Differences in neural responses to reward and punishment processing between anorexia nervosa subtypes: an f MRI study. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2017: 71(9): 647–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12537
Harney MB, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, Maldonado CR, Bardone-Cone AM (2014) Negative affective experiences in relation to stages of eating disorder recovery. Eat Behav 15(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.10.016
DeGuzman M, Shott ME, Yang TT, Riederer J, Frank GKW Association of elevated reward prediction error response with weight gain in adolescent anorexia nervosa. Am J Psychiatry 2017:174(6):557–565. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.16060671
Lavender JM, Wonderlich SA, Crosby RD, Engel SG, Mitchell JE, Crow SJ et al (2013) Personality-based subtypes of anorexia nervosa: examining validity and utility using baseline clinical variables and ecological momentary assessment. Behav Res Ther 51(8):512–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2013.05.007
Wildes JE, Marcus MD, Crosby RD, Ringham RM, Dapelo MM, Gaskill JA et al (2011) The clinical utility of personality subtypes in patients with anorexia nervosa. J Consult Clin Psychol 79(5):665. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024597
Acknowledgements
Margarita Sala is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship under Grant No. DGE-1645420. Amy H. Egbert is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship. Jason Lavender is supported by National Institute of Health (NIH) grant K23MH101342. Andrea Goldschmidt is supported by NIH grant K23DK105234. Any opinion, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NSF or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sala, M., Egbert, A.H., Lavender, J.M. et al. Affect, reward, and punishment in anorexia nervosa: a narrative overview. Eat Weight Disord 23, 731–737 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0588-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0588-9