Abstract
Purpose
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a poorly understood and often chronic condition. Deviations in the gut microbiota have been reported to influence the gut–brain axis in other disorders. Therefore, if present in AN, it may impact on symptoms and illness progression. A review of the gut microbiota studies in AN is presented.
Method
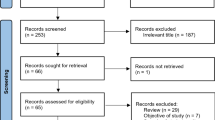
A literature search on PubMed yielded 27 articles; 14 were selected and based on relevance, 9 articles were included. The findings were interpreted in the larger context of preclinical research and clinical observations.
Results
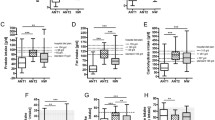
8 out of 9 included studies analysed microbiota from faeces samples, while the last analysed a protein in plasma produced by the gut. Two studies were longitudinal and included an intervention (i.e., weight restoration), five were cross-sectional, one was a case report, and the last was a case series consisting of three cases. Deviations in abundance, diversity, and microbial composition of the faecal microbiota in AN were found.
Conclusion
There are currently only a few studies on the gut microbiota in AN, all done on faeces samples, and not all describe the microbiota at the species level extensively. The Archaeon Methanobrevibacter smithii was increased in participants with a BMI < 25 in one study and specifically in AN patients in three studies. Methanobrevibacter smithii may, if detected, be a benchmark biomarker for future studies. We propose that microbiota samples could also be collected from the small intestine, where a major exchange of nutrients takes place and where the microbiota may have a biological impact on AN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keshaviah A, Edkins K, Hastings ER, Krishna M, Franko DL, Herzog DB, Thomas JJ, Murray HB, Eddy KT (2014) Re-examining premature mortality in anorexia nervosa: a meta-analysis redux. Compr Psychiatry 55(8):1773–1784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.07.017
Steinhausen HC (2009) Outcome of eating disorders. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 18(1):225–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2008.07.013
Quigley EMM (2013) Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 9(9):560–569
Claesson MJ, O’Sullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi JR, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Ross RP, O’Toole PW (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One 4(8):e6669. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006669
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, Mende DR, Li J, Xu J, Li S, Li D, Cao J, Wang B, Liang H, Zheng H, Xie Y, Tap J, Lepage P, Bertalan M, Batto JM, Hansen T, Le Paslier D, Linneberg A, Nielsen HB, Pelletier E, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Turner K, Zhu H, Yu C, Li S, Jian M, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Qin N, Yang H, Wang J, Brunak S, Dore J, Guarner F, Kristiansen K, Pedersen O, Parkhill J, Weissenbach J, Meta HITC., Bork P, Ehrlich SD, Wang J (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464(7285):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08821
Sudo N, Sawamura S, Tanaka K, Aiba Y, Kubo C, Koga Y (1997) The requirement of intestinal bacterial flora for the development of an IgE production system fully susceptible to oral tolerance induction. J Immunol 159(4):1739–1745
Guarner F, Malagelada JR (2003) Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 361(9356):512–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12489-0
Sudo N, Chida Y, Aiba Y, Sonoda J, Oyama N, Yu XN, Kubo C, Koga Y (2004) Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal system for stress response in mice. J Physiol 558(Pt 1):263–275. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063388
Clarke G, Grenham S, Scully P, Fitzgerald P, Moloney RD, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2013) The microbiome–gut–brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol Psychiatry 18(6):666–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.77
Diaz Heijtz R, Wang S, Anuar F, Qian Y, Bjorkholm B, Samuelsson A, Hibberd ML, Forssberg H, Pettersson S (2011) Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(7):3047–3052. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010529108
Cryan JF, O’Mahony SM (2011) The microbiome–gut–brain axis: from bowel to behavior. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23(3):187–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01664.x
Rogers GB, Keating DJ, Young RL, Wong ML, Licinio J, Wesselingh S (2016) From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: mechanisms and pathways. Mol Psychiatry 21(6):738–748. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.50
Godart NT, Flament MF, Lecrubier Y, Jeammet P (2000) Anxiety disorders in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: co-morbidity and chronology of appearance. Eur Psychiatry 15(1):38–45
Fernandez-Aranda F, Pinheiro AP, Tozzi F, Thornton LM, Fichter MM, Halmi KA, Kaplan AS, Klump KL, Strober M, Woodside DB, Crow S, Mitchell J, Rotondo A, Keel P, Plotnicov KH, Berrettini WH, Kaye WH, Crawford SF, Johnson C, Brandt H, La Via M, Bulik CM (2007) Symptom profile of major depressive disorder in women with eating disorders. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 41(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/00048670601057718
Kask J, Ekselius L, Brandt L, Kollia N, Ekbom A, Papadopoulos FC (2016) Mortality in women with anorexia nervosa: the role of comorbid psychiatric disorders. Psychosom Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0000000000000342
Flint HJ (2011) Obesity and the gut microbiota. J Clin Gastroenterol 45(Suppl):S128–S132. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e31821f44c4
Cox LM, Blaser MJ (2013) Pathways in microbe-induced obesity. Cell Metab 17(6):883–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.004
Aguirre M, Jonkers DM, Troost FJ, Roeselers G, Venema K (2014) In vitro characterization of the impact of different substrates on metabolite production, energy extraction and composition of gut microbiota from lean and obese subjects. PLoS One 9(11):e113864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113864
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP, Egholm M, Henrissat B, Heath AC, Knight R, Gordon JI (2009) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457(7228):480–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07540
Jesus P, Ouelaa W, Francois M, Riachy L, Guerin C, Aziz M, Do Rego JC, Dechelotte P, Fetissov SO, Coeffier M (2014) Alteration of intestinal barrier function during activity-based anorexia in mice. Clin Nutr 33(6):1046–1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2013.11.006
Pals KL, Chang RT, Ryan AJ, Gisolfi CV (1997) Effect of running intensity on intestinal permeability. J Appl Physiol (1985) 82(2):571–576
Monteleone P, Carratu R, Carteni M, Generoso M, Lamberti M, Magistris LD, Brambilla F, Colurcio B, Secondulfo M, Maj M (2004) Intestinal permeability is decreased in anorexia nervosa. Mol Psychiatry 9(1):76–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001374
Raevuori A, Haukka J, Vaarala O, Suvisaari JM, Gissler M, Grainger M, Linna MS, Suokas JT (2014) The increased risk for autoimmune diseases in patients with eating disorders. PLoS One 9(8):e104845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104845
Devkota S, Wang Y, Musch MW, Leone V, Fehlner-Peach H, Nadimpalli A, Antonopoulos DA, Jabri B, Chang EB (2012) Dietary-fat-induced taurocholic acid promotes pathobiont expansion and colitis in Il10−/− mice. Nature 487(7405):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11225
Zoetendal EG, von Wright A, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Ben-Amor K, Akkermans AD, de Vos WM (2002) Mucosa-associated bacteria in the human gastrointestinal tract are uniformly distributed along the colon and differ from the community recovered from feces. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(7):3401–3407
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308(5728):1635–1638. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1110591
Carroll IM, Ringel-Kulka T, Keku TO, Chang YH, Packey CD, Sartor RB, Ringel Y (2011) Molecular analysis of the luminal- and mucosal-associated intestinal microbiota in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301(5):G799–G807. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00154.2011
Durban A, Abellan JJ, Jimenez-Hernandez N, Ponce M, Ponce J, Sala T, D’Auria G, Latorre A, Moya A (2011) Assessing gut microbial diversity from feces and rectal mucosa. Microbial Ecol 61(1):123–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9738-y
Booijink CC, El-Aidy S, Rajilic-Stojanovic M, Heilig HG, Troost FJ, Smidt H, Kleerebezem M, De Vos WM, Zoetendal EG (2010) High temporal and inter-individual variation detected in the human ileal microbiota. Environ Microbiol 12(12):3213–3227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02294.x
Hayashi H, Takahashi R, Nishi T, Sakamoto M, Benno Y (2005) Molecular analysis of jejunal, ileal, caecal and recto-sigmoidal human colonic microbiota using 16S rRNA gene libraries and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Med Microbiol 54(Pt 11):1093–1101. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.45935-0
Wang M, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B, Molin G (2005) Comparison of bacterial diversity along the human intestinal tract by direct cloning and sequencing of 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54(2):219–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsec.2005.03.012
Morkl S, Lackner S, Muller W, Gorkiewicz G, Kashofer K, Oberascher A, Painold A, Holl A, Holzer P, Meinitzer A, Mangge H, Holasek S (2017) Gut microbiota and body composition in anorexia nervosa inpatients in comparison to athletes, overweight, obese, and normal weight controls. Int J Eat Disord 50(12):1421–1431. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22801
Kleiman SC, Watson HJ, Bulik-Sullivan EC, Huh EY, Tarantino LM, Bulik CM, Carroll IM (2015) The intestinal microbiota in acute anorexia nervosa and during renourishment: relationship to depression, anxiety, and eating disorder psychopathology. Psychosom Med 77(9):969–981. https://doi.org/10.1097/psy.0000000000000247
Mack I, Cuntz U, Gramer C, Niedermaier S, Pohl C, Schwiertz A, Zimmermann K, Zipfel S, Enck P, Penders J (2016) Weight gain in anorexia nervosa does not ameliorate the faecal microbiota, branched chain fatty acid profiles, and gastrointestinal complaints. Sci Rep 6:26752. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26752
Armougom F, Henry M, Vialettes B, Raccah D, Raoult D (2009) Monitoring bacterial community of human gut microbiota reveals an increase in Lactobacillus in obese patients and Methanogens in anorexic patients. PLoS One 4(9):e7125. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007125
Million M, Angelakis E, Maraninchi M, Henry M, Giorgi R, Valero R, Vialettes B, Raoult D (2013) Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium animalis, Methanobrevibacter smithii and Escherichia coli. Int J Obes (Lond) 37(11):1460–1466. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.20
Morita C, Tsuji H, Hata T, Gondo M, Takakura S, Kawai K, Yoshihara K, Ogata K, Nomoto K, Miyazaki K, Sudo N (2015) Gut dysbiosis in patients with anorexia nervosa. PLoS One 10(12):e0145274. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145274
Borgo F, Riva A, Benetti A, Casiraghi MC, Bertelli S, Garbossa S, Anselmetti S, Scarone S, Pontiroli AE, Morace G, Borghi E (2017) Microbiota in anorexia nervosa: the triangle between bacterial species, metabolites and psychological tests. PLoS One 12(6):e0179739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179739
Breton J, Legrand R, Akkermann K, Jarv A, Harro J, Dechelotte P, Fetissov SO (2016) Elevated plasma concentrations of bacterial ClpB protein in patients with eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord 49(8):805–808. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22531
Pfleiderer A, Lagier JC, Armougom F, Robert C, Vialettes B, Raoult D (2013) Culturomics identified 11 new bacterial species from a single anorexia nervosa stool sample. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32(11):1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-013-1900-2
Kleiman SC, Glenny EM, Bulik-Sullivan EC, Huh EY, Tsilimigras MCB, Fodor AA, Bulik CM, Carroll IM (2017) Daily changes in composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with anorexia nervosa: a series of three cases. Eur Eat Disord Rev J Eat Disord Assoc 25(5):423–427. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2524
Kishi T, Elmquist JK (2005) Body weight is regulated by the brain: a link between feeding and emotion. Mol Psychiatry 10(2):132–146. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001638
Van Wymelbeke V, Brondel L, Marcel Brun J, Rigaud D (2004) Factors associated with the increase in resting energy expenditure during refeeding in malnourished anorexia nervosa patients. Am J Clin Nutr 80(6):1469–1477
Kaye WH, Gwirtsman HE, Obarzanek E, George DT (1988) Relative importance of calorie intake needed to gain weight and level of physical activity in anorexia nervosa. Am J Clin Nutr 47(6):989–994
Moukaddem M, Boulier A, Apfelbaum M, Rigaud D (1997) Increase in diet-induced thermogenesis at the start of refeeding in severely malnourished anorexia nervosa patients. Am J Clin Nutr 66(1):133–140
Samuel BS, Gordon JI (2006) A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host–archaeal–bacterial mutualism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(26):10011–10016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602187103
Gottlieb K, Wacher V, Sliman J, Pimentel M (2016) Review article: inhibition of methanogenic archaea by statins as a targeted management strategy for constipation and related disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(2):197–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13469
Triantafyllou K, Chang C, Pimentel M (2014) Methanogens, methane and gastrointestinal motility. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 20(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2014.20.1.31
Lapage SP, Sneath PHA, Lessel EF et al (1992) International code of nomenclature of bacteria: bacteriological code. ASM Press, Washington (DC)
Claesson MJ, Clooney AG, O’Toole PW (2017) A clinician’s guide to microbiome analysis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.97
Johansson ME, Hansson GC (2011) Microbiology. Keeping bacteria at a distance. Science 334(6053):182–183. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1213909
Belkaid Y, Grainger J (2013) Immunology. Mucus coat, a dress code for tolerance. Science 342(6157):432–433. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1246252
Zoetendal EG, Raes J, van den Bogert B, Arumugam M, Booijink CC, Troost FJ, Bork P, Wels M, de Vos WM, Kleerebezem M (2012) The human small intestinal microbiota is driven by rapid uptake and conversion of simple carbohydrates. ISME J 6(7):1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.212
Vandeputte D, Falony G, Vieira-Silva S, Tito RY, Joossens M, Raes J (2016) Stool consistency is strongly associated with gut microbiota richness and composition, enterotypes and bacterial growth rates. Gut 65(1):57–62. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309618
Finegold SM, Sutter VL, Boyle JD, Shimada K (1970) The normal flora of ileostomy and transverse colostomy effluents. J Infect Dis 122(5):376–381
Rangel I, Sundin J, Fuentes S, Repsilber D, de Vos WM, Brummer RJ (2015) The relationship between faecal-associated and mucosal-associated microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients and healthy subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 42(10):1211–1221. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13399
Rooks MG, Garrett WS (2016) Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 16(6):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.42
Cebra JJ (1999) Influences of microbiota on intestinal immune system development. Am J Clin Nutr 69(5):1046 s-1051 s
Singeap AM, Stanciu C, Trifan A (2016) Capsule endoscopy: the road ahead. World J Gastroenterol 22(1):369–378. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.369
Neufeld KA, Foster JA (2009) Effects of gut microbiota on the brain: implications for psychiatry. J Psychiatry Neurosci 34(3):230–231
O’Mahony SM, Marchesi JR, Scully P, Codling C, Ceolho AM, Quigley EM, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2009) Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses. Biol Psychiatry 65(3):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.06.026
Whitehead WE, Palsson O, Jones KR (2002) Systematic review of the comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome with other disorders: what are the causes and implications? Gastroenterology 122(4):1140–1156
Grenham S, Clarke G, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2011) Brain–gut–microbe communication in health and disease. Front Physiol 2:94. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2011.00094
Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2012) Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(10):701–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3346
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y, Fischbach MA, Biddinger SB, Dutton RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505(7484):559–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12820
Leibbrand R, Cuntz U, Hiller W (2002) Assessment of functional gastrointestinal disorders using the Gastro-Questionnaire. Int J Behav Med 9(2):155–172
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Psychiatric Center Ballerup and the Capitol Region of Denmark, for providing support for this study.
Funding
No funding was received in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, no formal consent is required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwensen, H.F., Kan, C., Treasure, J. et al. A systematic review of studies on the faecal microbiota in anorexia nervosa: future research may need to include microbiota from the small intestine. Eat Weight Disord 23, 399–418 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0499-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0499-9