Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the psychometric properties and scoring pattern of the Brazilian version of the three-factor eating questionnaire-r21 (TFEQ-R21).
Methods
Data were collected from 410 undergraduate students. Confirmatory factor analysis was conducted to examine the factor structure of the TFEQ-R21. Convergent and discriminant validity also was assessed. Cluster analysis was performed to investigate scoring patterns.
Results
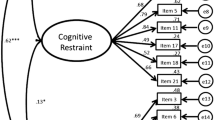
In assessing the quality setting, the model was considered satisfactory (χ 2/gl = 2.24, CFI = 0.97, TLI = 0.96, RMSEA = 0.05). The instrument was also considered appropriate in relation to the discriminant and convergent validity. There was a positive correlation between body mass index and the dimensions of cognitive restraint (r s = 0.449, p < 0.001) and emotional eating (r s = 0.112, p = 0.023). Using cluster analysis three respondent profiles were identified. The profile “A” was associated with appropriate weight, the “B” was characterized by high scores in cognitive restraint dimension, and the cluster “C” focused individuals who had higher scores on the uncontrolled eating and emotional eating dimensions.
Conclusions
The Brazilian version of TFEQ-R21 has adequate psychometric properties, and the identified response profiles offer a promising prospect for its use in clinical practice, in weight loss interventions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde, Departamento de Análise da Situação de Saúde (2011) Plano de ações estratégicas para o enfrentamento das doenças crônicas não transmissíveis (DCNT) no Brasil/2011–2022. Editora MS, Brasília
Associação Brasileira para o Estudo da Obesidade e da Síndrome Metabólica (2009) Diretrizes Brasileiras de Obesidade, 3rd edn. AC Farmacêutica, São Paulo
Stunkard AJ, Messick S (1985) The three-factor eating questionnaire to measure dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger. J Psychosom Res 29:71–83
Cappelleri JC, Bushmakin AG, Gerber RA, Leidy NK, Sexton CC, Lowe MR, Karlsson J (2009) Psychometric analysis of the three-factor eating questionnaire-R21: results from a large diverse sample of obese and non-obese participants. Int J Obes 33:611–620. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.74
Tholin S, Rasmussen F, Tynelius P, Karlsson J (2005) Genetic and environmental influences on eating behavior: the Swedish Young Male Twins Study. Am J Clin Nutr 81:564–569
Löffler A, Luck T, Then FS, Sikorski C, Kovacs P, Böttcher Y, Breitfeld J, Tönjes A, Horstmann A, Löffler M, Engel C, Thiery J, Villringer A, Stumvoll M, Riedel-Heller SG (2015) Eating behaviour in the general population: an analysis of the factor structure of the German version of the Three-Factor-Eating-Questionnaire (TFEQ) and its association with the body mass index. PLoS One 10:e0133977. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133977
Preedy VR, Watson RR, Martin CR (2011) Handbook of behavior, food and nutrition. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-92271-3
Gibson EL (2012) The psychobiology of comfort eating. Behav Pharmacol 23:442–460. doi:10.1097/FBP.0b013e328357bd4e
Lesdéma A, Fromentin G, Daudin JJ, Arlotti A, Vinoy S, Tome D, Marsset-Baglieri A (2012) Characterization of the three-factor eating questionnaire scores of a young French cohort. Appetite 59:385–390. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2012.05.027
Keskitalo K, Tuorila H, Spector TD, Cherkas LF, Knaapila A, Kaprio J, Silventoinen K, Perola M (2008) The three-factor eating questionnaire, body mass index, and responses to sweet and salty fatty foods: a twin study of genetic and environmental associations. Am J Clin Nutr 88:263–271
Ismail R, Zali M, Noh M, Ismail NH, Tamil AM (2015) A tale of two construct validation analysis: rasch model and exploratory factor analysis approach for Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ-R21) among Malaysian male. Med J Malaysia 70:169–176
Jáuregui-Lobera I, García-Cruz P, Carbonero-Carreño R, Magallares A, Ruiz-Prieto I (2014) Psychometric properties of spanish version of the three-factor eating questionnaire-R18 (Tfeq-Sp) and its relationship with some eating and body image-related variables. Nutrients 6:5619–5635. doi:10.3390/nu6125619
Chearskul S, Pummoung S, Vongsaiyat S, Janyachailert P, Phattharayuttawat S (2010) Thai version of three-factor eating questionnaire. Appetite 54:410–413. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2010.01.005
Kavazidou E, Proios M, Liolios I, Doganis G, Petrou K, Tsatsoulis A, Fachantidou-Tsiligiroglou A (2012) Structure validity of the three-factor eating questionnaire-R18 in Greek population. J Hum Sport Exerc 7:218–226. doi:10.4100/jhse.2012.71.01
Natacci LC, Ferreira Júnior M (2011) The three factor eating questionnaire—R21: tradução para o português e aplicação em mulheres brasileiras. Rev Nutr 24:383–394
Ministério da Saúde do Brasil, Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde, Departamento de Atenção Básica, Coordenação-Geral da Política de Alimentação e Nutrição (2008) Protocolos do Sistema de Vigilância Alimentar e Nutricional SISVAN. Editora MS, Brasília
Yeomans MR, Leitch M, Mobini S (2008) Impulsivity is associated with the disinhibition but not restraint factor from the three factor eating questionnaire. Appetite 50:469–476. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2007.10.002
Poínhos R, Oliveira BMPM, Correia F (2013) Eating behaviour patterns and BMI in Portuguese higher education students. Appetite 71:314–320. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2013.08.024
Brown TA (2015) Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research, 2nd edn. The Guilford Press, New York
Schreiber JB, Stage FK, King J, Nora A, Barlow EA (2006) Modeling and confirmatory factor analysis results: a review. J Educ Res 99:323–337
Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE, Tatham RL (2009) Análise Multivariada de Dados, 6th edn. Bookman, Porto Alegre
Feinstein AR (2002) Principles of medical statistics. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Mooi E, Sarstedt M (2011) Cluster analysis. A concise guid. to mark. res. Springer, Berlin, pp 237–284
Desgraupes B (2013) The Comprehensive R Archive Network: CRAN Package. In: Clustering indices, Paris. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/clusterCrit
Wang K, Wang B, Peng L (2009) CVAP: validation for cluster analyses. Data Sci J 8:88–93. doi:10.2481/dsj.007-020
Lowe MR, Doshi SD, Katterman SN, Feig EH (2013) Dieting and restrained eating as prospective predictors of weight gain. Front Psychol 4:1–7. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00577
Van Gucht D, Soetens B, Raes F, Griffith JW (2014) The attitudes to chocolate questionnaire. Psychometric properties and relationship with consumption, dieting, disinhibition and thought suppression. Appetite 76:137–143. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2014.01.078
Delinsky SS, Wilson GT (2008) Weight gain, dietary restraint, and disordered eating in the freshman year of college. Eat Behav 9:82–90. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2007.06.001
Chacko SA, Chiodi SN, Wee CC (2015) Recognizing disordered eating in primary care patients with obesity. Prev Med (Baltim) 72:89–94. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.12.024
Löffler A, Luck T, Then FS, Luppa M, Sikorski C, Kovacs P, Tönjes A, Böttcher Y, Breitfeld J, Horstmann A, Löffler M, Engel C, Thiery J, Stumvoll M, Riedel-Heller SG (2015) Age- and gender-specific norms for the German version of the Three-Factor Eating-Questionnaire (TFEQ). Appetite 91:241–247. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2015.04.044
Nasser M (2009) Eating disorders across cultures. Psychiatr Disord 8:347–350. doi:10.1016/j.mppsy.2009.06.009
Anglé S, Engblom J, Eriksson T, Kautiainen S, Saha MT, Lindfors P, Lehtinen M, Rimpelä A (2009) Three factor eating questionnaire-R18 as a measure of cognitive restraint, uncontrolled eating and emotional eating in a sample of young Finnish females. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 6:41. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-6-41
Jaakkola J, Hakala P, Isolauri E, Poussa T, Laitinen K (2013) Eating behavior influences diet, weight, and central obesity in women after pregnancy. Nutrition 29:1209–1213. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2013.03.008
Danielsen KK, Svendsen M, Mæhlum S, Sundgot-Borgen J (2013) Changes in body composition, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and eating behavior after an intensive lifestyle intervention with high volume of physical activity in severely obese subjects: a prospective clinical controlled trial. J Obes 2013:325464. doi:10.1155/2013/325464
Svensson M, Hult M, van der Mark M, Grotta A, Jonasson J, von Hausswolff-Juhlin Y, Rössner S, Trolle Lagerros Y (2014) The change in eating behaviors in a Web-based weight loss program: a longitudinal analysis of study completers. J Med Internet Res 16:e234. doi:10.2196/jmir.3131
Bernardi F, Cichelero C, Vitolo R (2005) Comportamento de restrição alimentar e obesidade. Rev Nutr 18:85–93
Gravel K, Deslauriers A, Watiez M, Dumont M, Dufour Bouchard AA, Provencher V (2014) Sensory-based nutrition pilot intervention for women. J Acad Nutr Diet 114:99–106. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2013.06.354
Batra P, Das SK, Salinardi T, Robinson L, Saltzman E, Scott T, Pittas AG, Roberts SB (2013) Eating behaviors as predictors of weight loss in a 6 month weight loss intervention. Obesity (Silver Spring) 21:2256–2263. doi:10.1002/oby.20404
Miller CK, Kristeller JL, Headings A, Nagaraja H (2014) Comparison of a mindful eating intervention to a diabetes self-management intervention among adults with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Heal Educ Behav 41:145–154. doi:10.1177/1090198113493092
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kirill Orlov, Wallisen Tadashi Hattori and Antonio G. Oliveira, who kindly discussed some issues about statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The research was approved by the Ethic in Research Committee from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte and all procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent in writing was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Medeiros, A.C.Q., Yamamoto, M.E., Pedrosa, L.F.C. et al. The Brazilian version of the three-factor eating questionnaire-R21: psychometric evaluation and scoring pattern. Eat Weight Disord 22, 169–175 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0256-x