Abstract
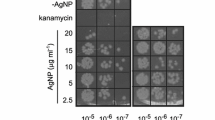
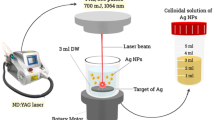
Bacterial resistance to antibiotic treatment raises serious public health-related concerns, in parallel with increasing efforts to develop efficient and safe therapeutic alternatives. Silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) have been synthesized and enhanced to increase their antibacterial properties using two primary types of lasers. These include the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser and the 405 nm diode laser. The former was used to prepare Ag-NPs colloidal solutions that shown effectiveness against sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, whereas the latter was utilized to activate Ag-NPs against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The approach of this work is to enhance the antibacterial potential of Q-switched Nd:YAG synthesized Ag-NPs against both normal and resistant strains of S. aureus, once by using them in combination with antibiotics and another time by exposing them to 405 nm diode laser. The synthesized silver nanoparticles were characterized by different methods such as UV–Visible, TEM, AFM and zeta potential. These characterizations revealed the formation of AgNPs with sizes in the range from 10 to 30 nm in response to pulsed laser ablation of pure Ag metal plates. The NPs efficiently deactivated S. aureus. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of AgNPs was 60 µg/ml, which caused a growth inhibition zone with a diameter of 12 mm. A remarkable improvement in antibacterial activity was achieved upon the irradiation of AgNPs with 405 nm laser light, causing a reduction of the MIC to the half (30 µg/ml), even when the treated strain is known to be resistant (MRSA). It is concluded that further enhancement of laser-synthesized AgNPs leads to more powerful antimicrobial impacts that even involve antibiotic-resistant bacteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelghany, A., Menazea, A., Abd-El-Maksoud, M., Khatab, T.: Pulsed laser ablated zeolite nanoparticles: A novel nano-catalyst for the synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthene and N-aryl-1,8-dioxodecahydroacridine with molecular docking validation. ApplOrganometal. Chem. 34, e5250 (2020)
Abderrafi, K., Jimenez, E., et al.: Production of Nanometer-Size GaAs Nanocrystals by Nanosecond Laser Ablation in Liquid. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 12, 6774–6778 (2012)
Agnihotri, S., Mukherji, S., Mukherji, S.: Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv 4, 3974–3983 (2014)
Ahmed, M., Meera Moydeen, A., Ismail, A., El-Naggar, M., Menazea, A., El-Newehy, M.: Wound dressing properties of functionalized environmentally biopolymer loaded with selenium nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struc. 1225, 129–138 (2021)
Ahmed, M., El-Naggar, M., Aldalbahi, A., El-Newehy, M., Menazea, A.: Methylene blue degradation under visible light of metallic nanoparticles scattered into graphene oxide using laser ablation technique in aqueous solutions. J. Molec. Liquids 315 (2020)
Ahmed, M., Menazea, A., Mansour, S., Al-Wafi, R.: Differentiation between cellulose acetate and polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous scaffolds containing magnetite nanoparticles/graphene oxide via pulsed laser ablation technique for tissue engineering applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 11629–11640 (2020)
Ahmed, M., Mansour, S., Al-wafi, R., Menazea, A.: Composition and design of nanofibrous scaffolds of Mg/Se- hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide @ ε-polycaprolactone for wound healing applications. J. Market. Res. 9, 7472–7485 (2020)
Akram, F., El-Tayeb, T., Abou-Aisha, K., El-Azizi, M.: A combination of silver nanoparticles and visible blue light enhances the antibacterial efficacy of ineffective antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Comb. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 15, 48 (2016)
Alamro, F., Toghan, A., Ahmed, H., Mostafa, A., Alakhras, A., Mwafy, E.: Multifunctional leather surface embedded with zinc oxide nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation method. Microsc. Res. Tech. 85, 1611–1617 (2021)
Alamro, F., Mostafa, A., Abu Al-Ola, K., Ahmed, H., Toghan, A.: Synthesis of ag nanoparticles-decorated cnts via laser ablation method for the enhancement the photocatalytic removal of naphthalene from water. Nanomaterials 11(8), 2142 (2021)
Ash, R., Mauck, B., Morgan, M.: Antibiotic resistance of Gram-Negative bacteria in rivers. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 7, 8 (2002)
Astuti, S., Kharisma, D., Kholimatussa, S., Zaidan, H.: An in vitro antifungal efficacy of silver nanoparticles activated by diode laser to Candida albicans. AIP Conf. Proc. 1888, 020016 (2007)
Ayman, M., Mostafa, A.: Menazea: Laser-assisted for preparation ZnO/CdO thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition for catalytic degradation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 176, (2020)
Bruna, T., Maldonado-Bravo, F., Jara, P., Caro, N.: Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7202 (2021)
Catalina, M.J., Eric, M., Hoek, V.: A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart, Res. 12, 1531–1551 (2010)
Czaplewski, L., Bax, R., Clokie, M., Dawson, M., Fairhead, H., Fischetti, V., et al.: Alternatives to antibiotics-a pipeline portfolio review. Lancet Infect Dis. 16, 239–251 (2016)
Dong, P., Ha, C., Binh, L., Kasbohm, J.: Chemical synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel-shaped silver nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett 2, 1–9 (2012)
El Faham, M., Mostafa, A., Toghan, A.: Facile synthesis of Cu2O nanoparticles using pulsed laser ablation method for optoelectronic applications. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 630, 127562 (2021)
El-Kheshen, A., El-Rab, S.: Effect of reducing and protecting agents on size of silver nanoparticles and their anti-bacterial activity. Pharma Chem 4, 53–65 (2012)
El-Saied, H., Mostafa, A., Hasanin, M., Mwafy, E., Mohammed, A.: Synthesis of Antimicrobial Cellulosic Derivative and its Catalytic Activity. J King Saud Univ.-Sci. 32(1), 436–442 (2020)
Fayaz, A., Balaji, K., GirilalM, Y.R., Kalaichelvan, P., Venketesan, R.: Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: a study against gram-positive and gram negative bacteria. Nanomed.: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 61, 103–109 (2010)
Friedman, N.D., Temkin, E., Carmeli, Y.: The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 22, 416–422 (2016)
Georgios, A., Sotiriou, E., Pratsinis: Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ. Sci. Tech. 44, 5649 (2010)
Gurunathan, S., Han, J., Kwon, D., Kim, J.: Enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res Lett. 9, 373 (2014)
Ilic, V., Saponjic, Z., et al.: Bactericidal efficiency of silver nanoparticles deposited onto radio frequencyplasma pretreated polyester fabrics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 7287 (2010)
Jeevanandam, J., Barhoum, A., Chan, Y.S., Dufresne, A., Danquah, M.K.: Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 9, 1050–1074 (2018)
Kim, H.S., Ryu, J.H., Jose, B., Lee, B.G., Ahn, B.S., Kang, Y.S.: Formation of silver nanoparticles induced by poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide). Langmuir 17, 5817–5820 (2001)
Kim, J., Kuk, E., et al.: Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3, 95 (2007)
Li, Y., Lu, W., Huang, Q., Huang, M., Li, C., Chen, W.: Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for photothermal ablation of tumor cells. Nanomedicine 5, 1161–1171 (2010)
Li, Y., Hindi, K., Watts, K., Taylor, J., Zhan, Z., Li, Z., Hunstad, D., Cannon, C., Young, W., Wooley, K.: Shell crosslinked nanoparticles carrying silver antimicrobials as therapeutics. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 46, 121–123 (2010)
Li, W., Xie, X., Shi, Q., Zeng, H., Ou-Yang, Y., Chen, Y.: Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85, 1115–1122 (2010)
Liu, W., Wu, Y., Wang, C., et al.: Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: Effect of particle size. Nanotoxicology 4, 319–330 (2010)
Mafuné, F., Kohno, J., Takeda, Y., Kondow, T., Sawabe, T.: J. Phys. Chem. B 104(39), 9111–9117 (2000)
Mannaa, D., Mandal, A., Sen, I., et al.: Antibacterial and DNA degradation potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized via green route. Int J Biol Macromol. 80, 455–459 (2015)
Matthews, K., Roberson, J., Gillespie, B., Luther, D., Oliver, S.: Identification and differentiation of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction. J. Food Prot. 60, 686–688 (1997)
Menazea, A., Mostafa, A.: Ag doped CuO thin film prepared via pulsed laser deposition for 4-nitrophenol degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 5 (2020)
Mizajani, F., Ghassempour, A., Aliahmadi, A., Esmaeli, M.: Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Staphyloccus aureus. Res Microbiol 162, 542–549 (2011)
Mlalila, N., Shaidi, H., Hilonga, A., Kadam, D.: Antimicrobial dependence of silver nanoparticles on surface plasmon resonance bands against Escherichia coli. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 10, 1–9 (2017)
Mostafa, A., Mwafy, E.: Effect of dual-beam laser radiation for synthetic SnO2/Au nanoalloy for antibacterial activity. J. Mol. Struct. 1222, 128913 (2020)
Mostafa, A., Mwafy, E.: The effect of laser fluence for enhancing the antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation in liquid media. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monitor. Manag. 14, 100382 (2020)
Mostafa, A., Mwafy, E., Hasanin, M.: One-pot synthesis of nanostructured CdS, CuS, and SnS by pulsed laser ablation in liquid environment and their antimicrobial activity. Opt. Laser Technol. 121, 105824 (2020)
Mostafa, A., Mwafy, E., Awwad, N., Ibrahium, H.: Synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with silver metallic nanoparticles as a catalytic degradable material via pulsed laser ablation in liquid media. Colloids Surf., A 626, 126992 (2021)
Mwafy, E., Hasanin, M., Mostafa, A.: Cadmium Oxide/ TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanocomposites produced by pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid Environment: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Activity. Opt. Laser Technol. 120, 105744 (2019)
Pal, S., Tak, Y., Song, J.: Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle? A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 1712–1720 (2007)
Paramelle, D., Sadovoy, A., Gorelik, S., Free, P., Hobley, J., Fernig, D.: A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst, R. Soc. Chem. 139, 0003–2654 (2014)
Rudramurthy, G., Swamy, M., Sinniah, U., Ghasemzadeh, A.: Nanoparticles: alternatives against drug-resistant pathogenic microbes. Molecules 21, 836 (2016)
Sadeghi, B., Garmaroudi, F., Hashemi, M., Nezhad, H., Nasrollahi, A., Ardalan, S., Ardalan, S.: Comparison of the anti-bacterial activity on the nanosilver shapes: Nanoparticles, nanorods and nanoplates. Adv. Powder Technol 23, 22–26 (2012)
Salleh, A., Naomi, R., Utami, N.D., Mohammad, A.W., Mahmoudi, E., Mustafa, N., Fauzi, M.B.: The Potential of Silver Nanoparticles for Antiviral and Antibacterial Applications: A Mechanism of Action. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 10, 1566 (2020)
Sharma, V.K., Yngard, R.A., Lin, Y.: Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 145, 83–96 (2009)
Shuai, C., Liu, G., Yang, Y., Qi, F., Peng, S., Yang, W., He, C., Wang, G., Qian, G.: A strawberry-like Ag-decorated barium titanate enhances piezoelectric and antibacterial activities of polymer scaffold. Nano Energy 74, 104825 (2020)
Smejkal, P., Pfleger, J., Vlckova, B., Dammer, O.: Laser ablation of silver in aqueous ambient: effect of laser pulse wavelength and energy on efficiency of the process. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 59, 185–188 (2007)
Soo-Hwan, K., Lee, H., Ryu, D., Choi, S., Lee, D.: Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against Staphyloccus aureus and Escherichia coli. Korean J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39, 77–85 (2011)
Torres, L., Gmez-Quintero, T., Padron, G., Santana, F., Hernandez, J., Castano, V.: Silver nanoprisms and nanospheres for prosthetic biomaterials. IADR/AADR/CADR General Session and Exhibition, San Francisco (2013)
Velusamy, P., Kumar, G.V., Jeyanthi, V., Das, J., Pachaiappan, R.: Bio-inspired green nanoparticles:synthesis, mechanism, and antibacterial application. Toxicol. Res. 32, 95–102 (2016)
Vogt, R., Dippold, L.: Escherichia coli O157:H7 outbreak associated with consumption of ground beef. Public Health Rep. 120, 174 (2005)
Wei, Q., Fu, J., Shen, J.: Norvancomycin-capped silver nanoparticles: synthesis and antibacterial activities against E. coli. Sci. China, Ser. B: Chem. 50, 418–424 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest / Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ogaidi, M.A.Z., Rasheed, B.G. Enhancement of Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Using Lasers. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 9, 610–621 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-022-00192-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-022-00192-4