Abstract
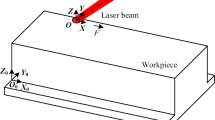
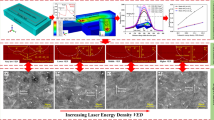
Laser polishing is a surface finishing operation in which a superficial layer of material is being redistributed in a controlled manner, typically to achieve a better surface quality. In this study, three-dimensional numerical model has been developed to investigate the formation of remelted line during the laser polishing (LP) of H13 tool steel. To closely mimic the thermophysics of laser line formation, several different heat transfer mechanisms have been included in the simulation. Furthermore, to enhance model accuracy and applicability, experimental calibrations were conducted to determine more accurate representations of material absorptivity, a parameter that is typically assumed as constant in the literature. The experimental validations performed have proved that the model can constitute a reliable alternative to time and cost consuming trial-and-error physical LP experiments that are commonly used to analyze the effect of various process parameters on post-polished surface quality.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρ :
-
Density
- k :
-
Conductivity
- T :
-
Temperature of the workpiece
- H :
-
Enthalpy
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity in constant pressure
- q ” :
-
Applied heat flux
- A :
-
Absorptivity
- r :
-
Radial position
- w :
-
Gaussian laser beam spot radius
- P :
-
Total laser power
- I :
-
Laser intensity
- h :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient
- ε :
-
Surface emissivity ε ∈ [0, 1]
- σ :
-
Stefan-Boltzman constant = 5.56×10-8 W/m2K4
- L :
-
Latent heat of fusion
- ref :
-
reference
- s :
-
surface
- ∞ :
-
surrounding
- rad:
-
emitted radiation
- liq:
-
liquidous
- sol:
-
solidus
References
ASME/ANSI B46.1 surface texture. In. American National standard, New York, (1985)
Bordatchev, E.V., Hafiz, A.M.K., Tutunea-Fatan, O.R.: Performance of laser polishing in finishing of metallic surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 73(1–4), 35–52 (2014). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5761-3
Temmler, A., Willenborg, E., Wissenbach, K.: Laser polishing. Proceedings of SPIE 8243, paper 82430W: (2012). doi:https://doi.org/10.1117/12.906001
Willenborg, E.: Polishing with laser radiation. In: Poprawe, R. (ed.) Tailored Light 2: Laser Application Technology. pp. 196–202. Springer, (2011)
Kiedrowski, T., Wissenbach, K.: Laser-beam polishing of injection-molded tools. Fraunhofer ILT Annual Report, 72: (2003)
Vega, F., Cebrian, A., Lupon, J., Laguarta, N.B., F.: Surface dynamics during laser polishing of glass. Proceedings of SPIE 3822, 92–102: (1999)
Nüsser, C., Kumstel, J., Kiedrowski, T., Diatlov, A., Willenborg, E.: Process- and material-induced surface structures during laser polishing. Adv. Eng. Mater. 17(3) (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4027433
Shen, Z.H., Zhang, S.Y., Lu, J., Ni, X.W.: Mathematical modeling of laser induced heating and melting in solids. Opt. Laser Technol. 33(8), 533–537 (2001). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0030-3992(01)00005-6
Ramos, J.A., Bourell, D.L., Beaman, J.J.: Surface over-melt during laser polishing of indirect-SLS metal parts. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 758, 53–61 (2003)
Liu, S.Y., Hu, J.D., Yang, Y., Guo, Z.X., Wang, H.Y.: Microstructure analysis of magnesium alloy melted by laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(5), 1723–1731 (2005). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.03.110
Dutto, C., Fogarassy, E., Mathiot, D.: Numerical and experimental analysis of pulsed excimer laser processing of silicon carbide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 184(1–4), 362–366 (2001). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(01)00518-9
Shao, T.M., Hua, M., Tam, H.Y., Cheung, E.H.M.: An approach to modelling of laser polishing of metals. Surf. Coat. Technol. 197(1), 77–84 (2005). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.01.010
Mai, T.A., Lim, G.C.: Micromelting and its effects on surface topography and properties in laser polishing of stainless steel. J. Laser Appl. 16(4), 221–228 (2004). doi:https://doi.org/10.2351/1.1809637
Yilbas, B.S., Shuja, S.Z., Khan, S.M.A., Aleem, A.: Laser melting of carbide tool surface: Model and experimental studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(23), 9396–9403 (2009). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.07.042
Marimuthu, S., Triantaphyllou, A., Antar, M., Wimpenny, D., Morton, H., Beard, M.: Laser polishing of selective laser melted components. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 95, 97–104 (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.05.002
Perry, T.L., Werschmoeller, D., Li, X.C., Pfefferkorn, F.E., Duffie, N.A.: The effect of laser pulse duration and feed rate on pulsed laser polishing of microfabricated Nickel samples. ASME J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 131(3), paper 031002: (2009). doi:https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3106033
Ma, C., Vadali, M., Duffie, N.A., Pfefferkorn, F.E., Li, X.: Melt pool flow and surface evolution during pulsed laser micro polishing of Ti6Al4V. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 135(6), 061023–061023 (2013). doi:https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4025819
Morrow, J.D., Wang, Q., Duffie, N.A., Pfefferkorn, F.E.: A hybrid surface processing method using surface alloying and pulsed laser micro melting on S7 tool steel. Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference MSEC2015, paper MSEC2015-9446 (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1115/MSEC2015-9446
Pfefferkorn, F.E., Duffie, N.A., Morrow, J.D., Wang, Q.: Effect of beam diameter on pulsed laser polishing of S7 tool steel. CIRP Ann. 63(1), 237–240 (2014). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.055
Vadali, M., Ma, C., Duffie, N.A., Li, X., Pfefferkorn, F.E.: Pulsed laser micro polishing: Surface prediction model. J. Manuf. Process. 14(3), 307–315 (2012). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2012.03.001
Wang, Q.H., Morrow, J.D., Ma, C., Duffie, N.A., Pfefferkorn, F.E.: Surface prediction model for thermocapillary regime pulsed laser micro polishing of metals. J. Manuf. Process. 20, 340–348 (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2015.05.005
Ukar, E., Lamikiz, A., Martinez, S., Tabernero, I., de Lacalle, L.N.L.: Roughness prediction on laser polished surfaces. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 212(6), 1305–1313 (2012). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.01.007
Mohajerani, S., Bordatchev, E.V., Tutunea-Fatan, O.R.: Recent developments in modeling of laser polishing of metallic materials. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 5(4), 395–429 (2018). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-018-0071-5
Mohajerani, S., Miller, J.D., Tutunea-Fatan, O.R., Bordatchev, E.V.: Thermo-physical modelling of track width during laser polishing of H13 tool steel. Proc. Manuf. 10, 708–719 (2017). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.07.026
Bergström, D., Kaplan, A., Powell, J.: Mathematical modelling of laser absorption mechanisms in metals: A review. Paper presented at the The M4PL16 Workshop, Igls, Austria, January 2003
Bergström, D., Powell, J., Kaplan, A.F.H.: The absorptance of steels to Nd:YLF and Nd:YAG laser light at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(11), 5017–5028 (2007). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.11.018
Bergström, D.: The absorption of laser light by rough metal surfaces. PhD thesis. Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden: (2008)
ANSYS Fluent Theory Guide. Release 16. In. (2015)
Lin, Y.J., McHugh, K.M., Park, Y.S., Zhou, Y.Z., Lavernia, E.J.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of spray-formed H13 steel tooling. MPMD Sixth Global Innovations Proceedings - Trends in Materials and Manufacturing Technologies for Transportation Industries and Powder Metallurgy Research and Development in the Transportation Industry - Proceedings of Symposium, 45–50: (2005)
Benedyk, J.C.: High performance alloys database. In. CINDAS, LLC., (2008)
Bohler-Uddeholm: H13 Tool Steel datasheet. http://www.bucorp.com/media/H13_data_sheet_09032013.pdf (2013)
Wilthan, B., Schutzenhofer, W., Pottlacher, G.: Thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of five different steel alloys in the solid and liquid phases. Int. J. Thermophys. 36(8), 2259–2272 (2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-015-1850-2
OMEGA: Table of total emissivity. http://www.omega.com/techref/Z-section.html
Indhu, R., Vivek, V., Sarathkumar, L., Bharatish, A., Soundarapandian, S.: Overview of laser absorptivity measurement techniques for material processing. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 5(4), 458–481 (2018). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-018-0075-1
Naeem, M.: Laser Processing of Reflective Materials. Laser Tech. J. 10(1), 18–20 (2013). doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/latj.201390001
Yung, K.C., Zhang, S.S., Duan, L., Choy, H.S., Cai, Z.X.: Laser polishing of additive manufactured tool steel components using pulsed or continuous-wave lasers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105(1–4), 425–440 (2019). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04205-z
Zhou, J., Liao, C., Shen, H., Ding, X.: Surface and property characterization of laser polished Ti6Al4V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 380, 125016 (2019). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.125016
Acknowledgments
The work presented in this study is the result of the collaboration between Western University (London, Ontario, Canada) and National Research Council of Canada (London, Ontario, Canada). Partial financial support was also provided by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada. The authors would also like to acknowledge CMC Microsystems for the provision of the CFD simulation software that has been used in this research. Note: All three authors have contributed equally to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohajerani, S., Bordatchev, E.V., Tutunea-Fatan, O.R. et al. Thermophysical Simulation and Experimental Verification of Remelting Lines During Laser Polishing of H13 Tool Steel. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 7, 317–337 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-020-00120-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-020-00120-4