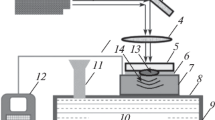
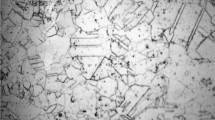
Abstract
Present work investigates the effect of laser shock peening on the microstructure and properties of alloy D9, a candidate material for the core applications in fast breeder reactors. For select peening parameter, surface and depth distribution of residual compressive stresses, microstructure, hardness, tensile properties and thermal diffusivity have been compared with a reference (annealed) material. After shock peening, using laser energy of 3J/pulse, compressive stresses were present up to a depth of 360 μm from the surface with a maximum magnitude of 330 MPa at a depth of 20-30 μm from the surface. Though the microstructure showed no appreciable change, both hardness and yield strength increased (by 32% and 63% respectively) and ductility decreased after peening. Mechanical property evaluation using miniaturized tensile testing gave a truly quantitative estimate of the change in properties due to peening. Change in thermal diffusivity measured from ambient temperature up to 700 °C suggested the superior thermal stability of laser shock peened specimen.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, X.P., Man, C.S., Shepard, M.J., Zhai, T.: Effects of shot-peening and re-shot-peening on four-point bend fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 468–470, 137–143 (2007)
Efim, S.: Statnikov, Oleg V. Korolkov, Vladimir N. Vityazev.: Physics and mechanism of ultrasonic impact. Ultrasonics. 44, e533–e538 (2006)
Prevey, P.S., Cammett, J.T.: The influence of surface enhancement by low plasticity burnishing on the corrosion fatigue performance of AA7075-T6. Int. J. Fatigue. 26, 975–982 (2004)
Anand Kumar, S., Sundar, R., Ganesh Sundar Raman, S., Gnanamoorthy, R., Kaul, R., Ranganathan, K., Bindra, K.S.: Effects of laser peening on fretting wear behavior of alloy 718 fretted against two different counter body materials. J. Eng. Tribology. 231, 1276–1288 (2017)
Sundar, R., Ganesh, P., Sunil Kumar, B., Gupta, R.K., Nagpure, D.C., Kaul, R., Ranganathan, K., Bindra, K.S., Kain, V., Oak, S.M., Singh, B.: Mitigation of stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of machined 304L stainless steel through laser peening. J. Mater. Eng. Perf. 25, 3710–3724 (2016)
Gupta, R.K., Sunil Kumar, B., Sundar, R., Ram Sankar, P., Ganesh, P., Kaul, R., Kain, V., Ranganathan, K., Bindra, K.S., Singh, B.: Enhancement of intergranular corrosion resistance of type 304 stainless steel through laser shock peening. Corr. Eng. Sci. Tech. 52, 220–225 (2017)
Montross, C.S., Wei, T., Lin, Y., Clark, G., Mai, Y.-W.: Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: A review. Int. J. Fatigue. 24, 1021–1036 (2002)
Ganesh, P., Sundar, R., Kumar, H., Kaul, R., Ranganathan, K., Hedaoo, P., Tiwari, P., Kukreja, L.M., Oak, S.M., Dasari, S., Ragvendra, G.: Studies of laser peening on spring steel for automotive applications. Opt. Lasers Eng. 50, 678–686 (2012)
Ganesh, P., Sundar, R., Kumar, H., Kaul, R., Ranganathan, K., Hedaoo, P., Ragvendra, G., Anand Kumar, S., Tiwari, P., Nagpure, D.C., Bindra, K.S., Kukreja, L.M., Oak, S.M.: Studies on fatigue life enhancement of pre-fatigued spring steel specimens using laser shock peening. Mater. Des. 54, 734–741 (2014)
Peyre, P.: Berthe. L., Scherpereel, X., Fabbro, R., Bartnicki. E.: Experimental study of laser-driven shock waves in stainless steels. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 5985–5992 (1998)
Peyre, P., Scherpereel, X., Berthe, L., Carboni, C., Fabbro, R., BeÂranger, G., Lemaitre, C.: Surface modifications induced in 316L steel by laser peening and shot-peening. Influence on pitting corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 280, 294–302 (2000)
Peyre, P., Fabbro, R., Merrien, P., Lieurade, H.P.: Laser shock processing of aluminium alloys. Application to high cycle fatigue behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 210, 102–113 (1996)
Hongchao, Q., Jibin, Z., Gongxuan, Z., Yu, G.: Effects of laser shock peening on microstructure and residual stress evolution in Ti-45Al-2Cr-2Nb-0.2B alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 276, 145–151 (2015)
Chen, L., Ren, X., Zhou, W., Tong, Z., Adu-Gyamfi, S., Ye, Y., Ren, Y.: Evolution of microstructure and grain refinement mechanism of pure nickel induced by laser shock peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 728, 20–29 (2018)
Saklakoglu, N., Irizalp, S.G., Akman, E., Demir, A.: Near surface modification of aluminum alloy induced by laser shock processing. Opt. Laser Technol. 64, 235–241 (2014)
Pant, B.K., Sundar, R., Kumar, H., Kaul, R., Pavan, A.H.V., Ranganathan, K., Bindra, K.S., Oak, S.M., Kukreja, L.M., Prakash, R., Kamaraj, M.: Studies towards development of laser peening technology for martensitic stainless steel and titanium alloys for steam turbine applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 587, 352–358 (2013)
Irizalp, S.G., Saklakoglu, N.: High strength and high ductility behavior of 6061-T6 alloy after laser shock processing. Opt. Lasers Eng. 77, 183–190 (2016)
Tong, Z., Ren, X., Ren, Y., Dai, F., Ye, Y., Zhou, W., Chen, L., Ye, Z.: Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and hot corrosion of TC11 alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 355, 32–40 (2018)
Hongchao, Q.: Experimental investigation of laser peening on Ti17 titanium alloy for rotor blade applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351, 524–530 (2015)
Salimianrizi, A., Foroozmehr, E., Badrossamay, M., Farrokhpour, H.: Effect of laser shock peening on surface properties and residual stress of Al 6061-T6. Opt. Lasers Eng. 77, 112–117 (2016)
Shadangi, Y., Chattopadhyay, K., Rai, S.B., Singh, V.: Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of interstitial free steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 280, 216–224 (2015)
Zhou, L., He, W., Luo, S., Long, C., Cheng, W., Nie, X., He, G., Shen, X.J., Li, Y.: Laser shock peening induced surface nanocrystallization and martensite transformation in austenitic stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 655, 66–70 (2016)
Luo, K.Y., Lu, J.Z., Zhang, Y.K., Zhou, J.Z., Zhang, L.F., Dai, F.Z., Zhang, L., Zhong, J.W., Cui, C.Y.: Effects of laser shock processing on mechanical properties and micro-structure of ANSI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528, 4783–4788 (2011)
Lim, H., Lee, M., Kim, P., Jeong, S.: Laser shock peening of AISI 304 stainless steel for the application to seawater desalination pump components. Desalin. Water Treat. 33, 255–260 (2011)
Huang, S., Yuan, G., Sheng, J., Tan, W., Agyenim-Boateng, E., Zhou, J., Guo, H.: Strengthening mechanism and hydrogen-induced crack resistance of AISI 316L stainless steel subjected to laser peening at different power densities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43, 11263–11274 (2018)
Rai, A.K., Biswal, R., Gupta, R.K., Singh, R., Rai, S.K., Ranganathan, K., Ganesh, P., Kaul, R., Bindra, K.S.: Study on the effect of multiple laser shock peening on residual stress and microstructural changes in modified 9Cr-1Mo (P91) steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 358, 125–135 (2019)
Rai, A.K., Biswal, R., Gupta, R.K., Rai, S.K., Singh, R., Goutam, U.K., Ranganathan, K., Ganesh, P., Kaul, R., Bindra, K.S.: Enhancement of oxidation resistance of modified P91 grade ferritic-martensitic steel by surface modification using laser shock peening Appl. Surf. Sci. 495(143611), 1–12 (2019)
Banerjee, A., Raju, S., Divakar, R., Mohandas, E.: High temperature heat capacity of alloy D9 using drop calorimetry based enthalpy increment measurements. Int. J. Thermophys. 28, 97–108 (2007)
Latha, S., Mathew, M.D., Parameswaran, P., Bhanu Sankara Rao, K., Mannan, S.L.: Thermal creep properties of alloy D9 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel fuel clad tubes. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 85, 866–870 (2008)
Latha, S., Mathew, M.D., Rao, B.S., Mannan, S.L.: Creep deformation behavior of alloy D9 cladding tubes. Trans. Ind. Inst. Metall. 53, 249–253 (2000)
Biswal, R.: Development of a 7J/10 ns Nd:YAG laser oscillator-amplifier system. RRCAT newsletter. 31, L.6 (2018) http://www.rrcat.gov.in/newsletter/NL/nl2018/issue2/pdf/L6.pdf, visited on 15.04.2019
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, Menlo Park (1978)
Suryanarayana, C., Grant Norton, M.: X-ray diffraction - A practical approach. Plenum press, NewYork (1998)
ASTM: E112-13. Standard test methods for determining average grain size. ASTM international, Pennsylvania
Kolhatkar, A.: Karthik, V., Chaitanya, G., Anish Kumar, and Divakar, R.: Development and validation of a miniature tensile specimen for determination of mechanical properties. J. Test. Eval. 47, 3417–3431 (2019)
Michael, A., Sutton, J.-J.O., Schreier, H.W.: Image correlation for shape, motion and deformation measurements - Basic concepts, theory and applications. Springer-Verlag, Boston (2009)
ASTM: E1461-13, Standard test method for thermal diffusivity by the flash method. ASTM International, Pennsylvania
Parker, W.J., Jenkins, R.J., Butler, C.P., Abbott, L.G.: Flash method for determining thermal diffusivity, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 1679–1684 (1961)
Palanichamy, P., Sivabharathy, M., Jeyadheepan, K., Kalyanasundaram, P., Ramachandran, K., Sanjeeviraja, C.: Effect of annealing on cold worked D9 alloy by photoacoustics. Mater. Sci. Forum. 699, 89–102 (2012)
Telang, A., Gill, A.S., Teysseyre, S., Mannava, S.R., Dong, Q., Vasudevan, V.K.: Effects of laser shock peening on SCC behavior of alloy 600 in tetrathionate solution. Corro. Sci. 90, 434–444 (2015)
Mordyuk, B.N., Milman, Y.V., Iefimov, M.O., Prokopenko, G.I., Silberschmidt, V.V., Danylenko, M.I., Kotko, A.V.: Characterization of ultrasonically peened and laser-shock peened surface layers of AISI 321 stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 202, 4875–4883 (2008)
Dan Wedberg: Dislocation density based material model applied in FE-simulation of material cutting. (Thesis), Lulea Univ. of Technol. ISBN: 978-91-7439-126-8 (2010).
Pierce, D.T., Jimenez, J.A., Bentley, J., Raabe, D., Wittig, J.E.: The influence of stacking fault energy on the microstructural and strain hardening evolution of Fe-Mn-Al-Si steels during tensile deformation. Acta Mater. 100, 178–190 (2015)
Llewellyn, D.T.: Work hardening effects in austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 13, 389–400 (1997)
Gerland, M., Hallouin, M.: Effect of pressure on the microstructure of an austenitic stainless steel shock-loaded by very short laser pulses. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 345–351 (1994)
Lojkowski, W., Djahanbakhsh, M., Burkle, G., Gierlotka, S., Zielinski, W., Fecht, H.J.: Nanostructure formation on the surface of railway tracks. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 303, 197–208 (2001)
Fairand, B.P., Wilcox, B.A., Gallagher, W.J., Williams, D.N.: Laser shock induced microstructural and mechanical property changes in 7075 aluminum. J. Appl. Phy. 43, 3893–3895 (1972)
Busby, J.T., Hash, M.C., Was, G.S.: The relationship between hardness and yield stress in irradiated austenitic and ferritic steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 336, 267–278 (2005)
Cahoon, J.R., Broughton, W.H., Kutsak, A.R.: The determination of yield strength from hardness measurements. Metall. Trans. 2, 1979–1983 (1971)
Takakuwa, O., Kawaragi, Y., Soyama, H.: Estimation of the yield stress of stainless steel from the Vickers hardness taking account of the residual stress. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 3, 262–268 (2013)
Tripathy, H., Rai, A.K., Hajra, R.N., Vijayashanthi, N., Raju, S., Saroja, S.: High temperature thermophysical properties of 18Cr-9Ni-2.95Cu-0.59Nb-0.1C (mass %) austenitic stainless steel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 131(3), 2749–2761 (2018)
Costanza, G., Montanari, R., Paoloni, S., Tata, M.E.: Dislocation density effect on thermal diffusivity of AISI 316 steel. Key Eng. Mater. 605, 27–30 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.605.27
Skiba, J., Kulczyk, M., Pachla, W., Wiśniewski, T.S., Smalc-Koziorowska, J., Kubiś, M., Wróblewska, M., Przybysz, M.: Effect of severe plastic deformation realized by hydrostatic extrusion on heat Transfer in cp-Ti grade 2 and 316L austenitic stainless steel. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 9, 511 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000511
Paoloni, S., Tata, M.E., Scudieri, F., Mercuri, F., Marinelli, M., Zammit, U.: IR thermography characterization of residual stress in plastically deformed metallic components. Appl. Phys. A. 98, 461–465 (2010)
Altenberger, I., Stach, E.A., Liu, G., Nalla, R.K., Ritchie, R.O.: An in situ transmission electron microscope study of the thermal stability of near-surface microstructures induced by deep rolling and laser-shock peening. Scripta Mater. 48, 1593–1598 (2003)
Tripathy, H., Raju, S., Rai, A.K., Jayakumar, T.: A calorimetric study of recovery and recrystallization in Fe-14.4Cr-15.4Ni-2.4Mo-2.36Mn-0.25Ti-0.04C-0.05P (mass %) austenitic stainless steel. Steel Research Int. 84, 1046–1059 (2013)
Acknowledgement
Authors acknowledge Dr. A.K. Bhaduri, Director IGCAR and Dr. Shaju K. Albert, Director MMG for their support and encouragement during the course of this work. Authors would like to thank Dr. V. David Vijayanand, MEG, IGCAR, for extending his facility for controlled etching of D9 specimen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundar, R., Sudha, C., Rai, A.K. et al. Effect of laser shock peening on the microstructure, tensile and heat transport properties of Alloy D9. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 7, 259–277 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-020-00118-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-020-00118-y