Abstract
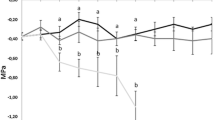
Abilities of four commercial herb species namely, Chlorophytum borivilianum, Stevia rebaudiana, Withania somnifera, and Andrographis paniculata were tested for relative drought tolerance under poly house conditions. The findings based on the quantum of data collected for growth, yield of economic parts and physiological traits reveal differential relative potential to sustain performance and cope with the conditions of water stress. Comparative performance of four herb species under stress (50% water deficit) for stress duration of 10, 20 and 30 days revealed significant adverse effects of water-deficit stress as well as stress durations. Out of the four herb species studied, adverse impact of 50% water deficit up to 30 days of stress on growth, yield, rate of photosynthesis, canopy temperature depression and chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm) ratio was significantly higher in S. rebaudiana and A. paniculata in comparison to C. borivilianum and W. somnifera. In this study, C. borivilianum and W. somnifera have exhibited greater relative drought tolerance as compared to A. paniculata and S. rebaudiana.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attia, Z., Christophe, J. D., Oren, R., Danielle, A. W., & Moshelion, M. (2015). Growth and physiological responses of isohydric and anisohydric poplars to drought. Journal of Experimental Botany. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv195.
Balaguer, L., Pugnaire, F. I., Martinez, F. E., Armass, C., Valladares, F., & Manrique, E. (2000). Ecophysiological significance of chlorophyll loss and reduced photochemical efficiency under extreme aridity in Stipa tenacissima L. Plant and Soil Journal, 240, 343–352.
Gebre, G. M., & Kuhns, M. R. (1991). Seasonal and clonal variations in drought tolerance of Populus deltoides. Canadian Journal of Forestry Research, 21, 910–916.
Guendouz, A., Guessoum, S., Maamari, K., & Hafsi, M. (2012). Predicting the efficiency of using the RGB (Red, Green and Blue) reflectance for estimating leaf chlorophyll content of Durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) genotypes under semi arid conditions. American Eurasian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 6, 102–106.
Havaux, M., & Lannoye, R. (1983). Chlorophyll fluorescence: A sensitive indicator of water stress in maize plants. Irrigation Science, 4, 147–151.
Ibaraki, Y., & Murakami, J. (2006). Distribution of chlorophyll fluorescence parameter Fv/Fm within individual plants under various stress conditions. In XXVII international horticulture congress international symposium on advances in environmental control, automation and cultivation systems for sustainable, high quality crop production under protected cultivation. ISHS Acta Horticulture, 761.
Jaimez, R. E., Vielma, O., Rada, F., & Garcia-Nunez, C. (2000). Effects of water deficit on the dynamics of flowering and fruit production in Capsicum ‘Chinense Jacq’ in a tropical semiarid region of Venezuela. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Sciences, 185, 113–119.
Jamali, M. M. (2013). Investigate the effect of drought stress and different amount of chemical fertilizers on some physiological characteristics of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.). International Journal of Farming and Allied Sciences. ISSN: 2322-4134.
Kenneth, O. T., George, N., Chemining’wa, Jane, A., & Willis, O. (2017). Effects of water stress on yield and physiological traits among selected African tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) races. International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research, 10, 78–85.
Maxwell, K., & Johnson, G. N. (2000). Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. Journal of Experimental Botany, 51, 659–668.
Moradi, P., Lloyd, B. F., & Pritchard, J. (2014). Plant water responses of different medicinal plant thyme (Thyme spp.) species to drought stress conditions. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 8, 666–673.
Parjer, K. G. (1976). Assessment of irrigation and nutrient effects on growth, yield and water use efficiency of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) in central India. Agriculture and Water Management, 85, 279–286.
Roseles, S., Sinclair, T. R., & Ludlow, M. M. (2004). Influence of soil water supply on the plant water balance of four dry beans legumes. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 13, 329–341.
Santos, D. M. S., & Alejo, O. N. (1996). Effects o c f water stress in growth, osmotic potential and solute accumulation in cell culture from chilli pepper (a mesophyte) and creosote bush (a xerophytes). Journal of Spices and Aromatic Crops, 19, 53–56.
Shah, S., Sarvanan, R., & Gajbhiye, N. A. (2010). Leaf gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, growth and root yield of ashwagandha (Withania somnefera Dunal) under soil moisture stress. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 15, 117–124.
Thakur, P. S., Chauhan, S., Thakur, A., & Dhall, S. P. (2000a). Influence of paclobutrazol and moisture stress conditioning on drought susceptibility in Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings. Journal of Tropical Forest Science, 12, 493–502.
Thakur, P. S., & Sood, R. (2005). Drought tolerance of multipurpose agroforestry tree species during first and second summer drought after transplanting. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 10, 32–40.
Thakur, P. S., & Thakur, A. (1993). Influence of triacontanol and mixtalol during plant moisture stress in Lycopersicon esculentum cultivars. Plant Physiology Biochemistry., 31, 433–439.
Thakur, A., Thakur, P. S., Attri, S., & Kanaujia, S. P. (1999a). Effect of bioextracts on growth and yield of bell pepper under water stressed conditions. Indian Journal of Horticulture, 56, 46–51.
Thakur, A., Thakur, P. S., Dhall, S. P., & Kanaujia, S. P. (1999b). Screening and evaluation of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum) varieties for drought tolerance. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 69, 234–235.
Thakur, A., Thakur, P. S., & Kanaujia, S. P. (2000b). Effect of bioregulators, bioextracts and potassium on growth and related attributes in bell pepper (Capsicum annuum) varieties under water stress. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 70, 255–258.
Thakur, A., Thakur, P. S., & Singh, R. P. (1998). Influence of paclobutrazol and triacontanol on growth and water relations in olive varieties under water stress. Indian. Journal of Plant Physiology, 3, 116–120.
Zwiazek, J. J., & Blake, T. J. (1990). Effect of preconditioning on electrolyte leakage and lipid composition in black spruce (Picea mariana) stressed with polyethylene glycol. Physiologia Plantarum, 79, 71–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, A., Thakur, C.L. Evaluation of four medicinal herb species under conditions of water-deficit stress. Ind J Plant Physiol. 23, 459–466 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0387-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0387-3