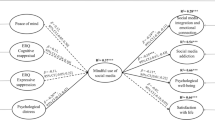
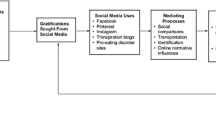
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Social media use is widespread. Because social media can yield both positive and negative mental health effects, it is critical for clinicians to consider how their clients use social media. The purpose of this review is to examine the extant experimental literature on the positive and negative effects of social media, with an eye towards how clinicians can (1) assess use, (2) educate on harmful use, and (3) promote skills that encourage healthier use.
Recent Findings
The existing literature suggests that active social media use that promotes positive connection, reminiscing, or warmth can be beneficial, whereas social media use that involves exposure to and production of highly idealized content, a focus on physical appearance, or a reliance on feedback can be harmful. To encourage healthier social media use, clinicians can encourage the building of intrapersonal skills, including reappraising comparison-inducing content, self-compassion, and mindfulness.
Summary
Although additional experimental work is needed to thoroughly inform treatment plans, findings suggest avenues that may be effective for clinicians when treating clients who struggle with their social media use. Changing how clients approach social media, rather than encouraging abstinence from use, may be more effective and practical in this digitally saturated age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Auxier B, Anderson M. Social media use in 2021. Pew Res Cent. 2021.
Anderson M, Faverio M, Gottfried J. Teens, social media and technology 2023. Pew Res Cent. 2023.
Twenge JM, Haidt J, Lozano J, Cummins KM. Specification curve analysis shows that social media use is linked to poor mental health, especially among girls. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022;224:103512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2022.103512.
Nesi J, Choukas-Bradley S, Prinstein MJ. Transformation of adolescent peer relations in the social media context: part 1—a theoretical framework and application to dyadic peer relationships. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2018;21:267–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-018-0261-x.
Granic I, Morita H, Scholten H. Beyond screen time: identity development in the digital age. Psychol Inq. 2020;31(3):195–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047840X.2020.1820214.
Radtke T, Apel T, Schenkel K, Keller J, Von Lindern E. Digital detox: an effective solution in the smartphone era? A systematic literature review. Mob Media Commun. 2022;10(2):190–215. https://doi.org/10.1177/205015792110286. Review of existing literature examining effectiveness of digital detox interventions, including social media abstinence studies.
Bronfenbrenner U. The ecology of human development: experiments by nature and design. Harv Univ Press. 1979.
Lehman BJ, David DM, Gruber JA. Rethinking the biopsychosocial model of health: understanding health as a dynamic system. Soc Pers Psychol Compass. 2017;11:e12328. https://doi.org/10.1111/spc3.12328.
Sommers-Flanagan J, Sommers-Flanagan R. Counseling and psychotherapy theories in context and practice: skills, strategies, and techniques. John Wiley Sons. 2018.
O’Neill MM, Nakash O. Uncovering the intricacies of the clinical intake assessment: how clinicians prioritize information in complex contexts. J Soc Soc Work Res. 2021;12(4):803–29. https://doi.org/10.1086/715439.
Rifkin-Zybutz R, Turner N, Derges J, Bould H, Sedgewick F, Gooberman-Hill R, et al. Digital technology use and mental health consultations: survey of the views and experiences of clinicians and young people. JMIR Ment Health. 2023;10:e44064. https://doi.org/10.2196/44064.
Boer M, Stevens GWJM, Finkenauer C, Van Den Eijnden RJJM. The course of problematic social media use in young adolescents: a latent class growth analysis. Child Dev. 2022;93(2):e168–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13712.
Griffioen N, Van Rooij MMJW, Lichtwarck-Aschoff A, Granic I. A stimulated recall method for the improved assessment of quantity and quality of social media use. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(1):e15529. https://doi.org/10.2196/15529.
Weinstein E, James C. School-based initiatives promoting digital citizenship and healthy digital media use. In: Nesi J, Telzer EH, Prinstein MJ, editors. Handbook of adolescent digital media use and mental health. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK. 2022. Review of interventions that have been employed in schools in promoting healthy digital technology use.
Valkenburg PM, Peter J. The differential susceptibility to media effects model: differential susceptibility to media effects model. J Commun. 2013;63(2):221–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119011071.iemp0122.
Heffer T, Good M, Daly O, MacDonell E, Willoughby T. The longitudinal association between social-media use and depressive symptoms among adolescents and young adults: an empirical reply to Twenge et al. (2018). Clinical Psychological Science. 2019;7(3):462–70. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702618812727.
Appel H, Crusius J, Gerlach AL. Social comparison, envy, and depression on Facebook: a study looking at the effects of high comparison standards on depressed individuals. J Soc Clin Psychol. 2015;34(4):277–89. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2015.34.4.277.
Marciano L, Schulz PJ, Camerini AL. Cyberbullying perpetration and victimization in youth: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Comput-Mediat Commun. 2020;25(2):163–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcmc/zmz031.
Choukas-Bradley S, Kilic Z, Stout CD, Roberts SR. Perfect storms and double-edged swords: recent advances in research on adolescent social media use and mental health. Adv Psychiatry Behav Health. 2023;3(1):149–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypsc.2023.03.007.
Bhattacharjee D, Rai AK, Singh NK, Kumar P, Munda SK, Das B. Psychoeducation: a measure to strengthen psychiatric treatment. Delhi Psychiatry J. 2011;14(1):33–9.
Gordon CS, Rodgers RF, Slater AE, McLean SA, Jarman HK, Paxton SJ. A cluster randomized controlled trial of the SoMe social media literacy body image and wellbeing program for adolescent boys and girls: study protocol. Body Image. 2020;33:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2020.02.003.
Gordon CS, Jarman HK, Rodgers RF, McLean SA, Slater A, Fuller-Tyszkiewicz M, et al. Outcomes of a cluster randomized controlled trial of the SoMe social media literacy program for improving body image-related outcomes in adolescent boys and girls. Nutrients. 2021;13(11):3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113825.
McLean SA, Wertheim EH, Masters J, Paxton SJ. A pilot evaluation of a social media literacy intervention to reduce risk factors for eating disorders. Intl J Eating Disord. 2017;50(7):847–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22708.
Bell BT, Taylor C, Paddock D, Bates A. Digital bodies : a controlled evaluation of a brief classroom-based intervention for reducing negative body image among adolescents in the digital age. Brit J of Edu Psychol. 2022;92(1):280–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12449.
Stiff C, Cutts M. The effectiveness of an Instagram intervention targeted at men to reduce body dissatisfaction. Curr Psychol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05060-8.
Galla BM, Choukas-Bradley S, Fiore HM, Esposito MV. Values-alignment messaging boosts adolescents’ motivation to control social media use. Child Dev. 2021;92(5):1717–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13553.
Fitz N, Kushlev K, Jagannathan R, Lewis T, Paliwal D, Ariely D. Batching smartphone notifications can improve well-being. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;101:84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.07.016.
Dekker CA, Baumgartner SE. Is life brighter when your phone is not? The efficacy of a grayscale smartphone intervention addressing digital well-being. Mob Media Commun. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20501579231212062.
Marengo D, Longobardi C, Fabris MA, Settanni M. Highly-visual social media and internalizing symptoms in adolescence: the mediating role of body image concerns. Comput Hum Behav. 2018;82:63–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.01.003.
Choukas-Bradley S, Roberts SR, Maheux AJ, Nesi J. The perfect storm: a developmental–sociocultural framework for the role of social media in adolescent girls’ body image concerns and mental health. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2022;25:681–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-022-00404-5. Developmental framework describing how adolescent girls’ social media use can be harmful for their body image.
Roberts SR, Maheux AJ, Hunt RA, Ladd BA, Choukas-Bradley S. Incorporating social media and muscular ideal internalization into the tripartite influence model of body image: towards a modern understanding of adolescent girls’ body dissatisfaction. Body Image. 2022;41:239–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.03.002.
McCrory A, Best P, Maddock A. The relationship between highly visual social media and young people’s mental health: a scoping review. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2020;115:105053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105053.
Saiphoo AN, Vahedi Z. A meta-analytic review of the relationship between social media use and body image disturbance. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;101:259–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.07.028.
Engeln R, Loach R, Imundo MN, Zola A. Compared to Facebook, Instagram use causes more appearance comparison and lower body satisfaction in college women. Body Image. 2020;34:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2020.04.007.
Mills JS, Musto S, Williams L, Tiggemann M. “Selfie” harm: effects on mood and body image in young women. Body Image. 2018;27:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2018.08.007.
Salomon I, Brown CS. That selfie becomes you: examining taking and posting selfies as forms of self-objectification. Media Psychol. 2021;24(6):847–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2020.1817091.
Burnell K, Kurup AR, Underwood MK. Snapchat lenses and body image concerns. New Media Soc. 2022;24(9):2088–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444821993038.
Wick MR, Keel PK. Posting edited photos of the self: increasing eating disorder risk or harmless behavior? Intl J Eating Disorders. 2020;53(6):864–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.23263.
Ferguson CJ. In the eye of the beholder: thin-ideal media affects some, but not most, viewers in a meta-analytic review of body dissatisfaction in women and men. Psychol Pop Media Cult. 2013;2(1):20–37. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030766.
Fioravanti G, Bocci Benucci S, Ceragioli G, Casale S. How the exposure to beauty ideals on social networking sites influences body image: a systematic review of experimental studies. Adolescent Res Rev. 2022;7:419–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-022-00179-4. Review of the effects of social media use on body image.
Pryde S, Prichard I. TikTok on the clock but the #fitspo don’t stop: the impact of TikTok fitspiration videos on women’s body image concerns. Body Image. 2022;43:244–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.09.004.
Seekis V, Kennedy R. The impact of #beauty and #self-compassion TikTok videos on young women’s appearance shame and anxiety, self-compassion, mood, and comparison processes. Body Image. 2023;45:117–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2023.02.006.
Rodgers RF, Wertheim EH, Paxton SJ, Tylka TL, Harriger JA. #Bopo: enhancing body image through body positive social media- evidence to date and research directions. Body Image. 2022;41:367–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.03.008.
Cohen R, Fardouly J, Newton-John T, Slater A. #BoPo on Instagram: an experimental investigation of the effects of viewing body positive content on young women’s mood and body image. New Media Soc. 2019;21(7):1546–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444819826530.
Fardouly J, Slater A, Parnell J, Diedrichs PC. Can following body positive or appearance neutral Facebook pages improve young women’s body image and mood? Testing novel social media micro-interventions. Body Image. 2023;44:136–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.12.008.
Dhadly PK, Kinnear A, Bodell LP. #BoPo: does viewing body positive TikTok content improve body satisfaction and mood? Eat Behav. 2023;50:101747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2023.101747.
Graham S, Newell E, Phillips JB, Pritchard M, Scarf D. Curating a body-positive feed? An attempt to mitigate the negative impacts of thin-ideal content on Instagram. Body Image. 2023;46:168–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2023.06.002.
Seekis V, Lawrence RK. How exposure to body neutrality content on TikTok affects young women’s body image and mood. Body Image. 2023;47:101629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2023.101629.
Cohen R, Newton-John T, Slater A. The case for body positivity on social media: perspectives on current advances and future directions. J Health Psychol. 2021;26(13):2365–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105320912450.
Verduyn P, Ybarra O, Résibois M, Jonides J, Kross E. Do social network sites enhance or undermine subjective well-being? A critical review. Soc Issues Policy Rev. 2017;11(1):274–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/sipr.12033.
Kleemans M, Daalmans S, Carbaat I, Anschütz D. Picture perfect: the direct effect of manipulated Instagram photos on body image in adolescent girls. Media Psychol. 2018;21(1):93–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2016.1257392.
Verduyn P, Lee DS, Park J, Shablack H, Orvell A, Bayer J, et al. Passive Facebook usage undermines affective well-being: experimental and longitudinal evidence. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2015;144(2):480–8. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000057.
Yuen EK, Koterba EA, Stasio MJ, Patrick RB, Gangi C, Ash P, et al. The effects of Facebook on mood in emerging adults. Psychol Pop Media Cult. 2019;8(3):198–206. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000178.
de Vries DA, Möller AM, Wieringa MS, Eigenraam AW, Hamelink K. Social comparison as the thief of joy: emotional consequences of viewing strangers’ Instagram posts. Media Psychol. 2018;21(2):222–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2016.1267647.
Weinstein E. Adolescents’ differential responses to social media browsing: exploring causes and consequences for intervention. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;76:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.07.038.
Valkenburg PM, Van Driel II, Beyens I. The associations of active and passive social media use with well-being: a critical scoping review. New Media Soc. 2022;24(2):530–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448211065425. Review describing the inconsistencies in relations between active and passive use with well-being.
Verduyn P, Gugushvili N, Kross E. Do social networking sites influence well-being? The extended active-passive model. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2022;31(1):62–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/09637214211053637. Theoretical framework describing how active and passive use can differentially affect well-being, and under what circumstances each may have an influence.
Burnell K, George MJ, Underwood MK. Browsing different Instagram profiles and associations with psychological well-being. Front Hum Dyn. 2020;2:585518. https://doi.org/10.3389/fhumd.2020.585518.
Khoo SS, Yang H, Toh WX. Leveraging Instagram to enhance self-esteem: a self-affirmative intervention study and multilevel mediation analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;150:107972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2023.107972.
Liu J, Li C, Carcioppolo N, North M. Do our Facebook friends make us feel worse? A study of social comparison and emotion: Facebook social comparison and emotion. Hum Commun Res. 2016;42(4):619–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/hcre.12090.
Alfasi Y. The grass is always greener on my friends’ profiles: the effect of Facebook social comparison on state self-esteem and depression. Personality Individ Differ. 2019;147:111–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2019.04.032.
Hogue JV, Mills JS. The effects of active social media engagement with peers on body image in young women. Body Image. 2019;28:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2018.11.002.
Pit IL, Veling H, Karremans JC. Does passive Facebook use promote feelings of social connectedness? Media Commun. 2022;10(2):119–29. https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.v10i2.5004.
Smoktunowicz E, Białobrzeska O, Jakubik Z. Posting photos that reflect positive aspects of everyday life on Instagram increases appreciation, life satisfaction, and happiness. New Media Soc. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444823119309.
Walsh LC, Regan A, Twenge JM, Lyubomirsky S. What is the optimal way to give thanks? Comparing the effects of gratitude expressed privately, one-to-one via text, or publicly on social media. Affec Sci. 2022;4:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42761-022-00150-5.
Jungselius B, Weilenmann A. Keeping memories alive: a decennial study of social media reminiscing, memories, and nostalgia. Social Media + Society. 2023;9(4):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/20563051231207850.
Kushlev K, Leitao MR. The effects of smartphones on well-being: theoretical integration and research agenda. Curr Opin Psychol. 2020;36:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.05.001.
Sacco DF, Ismail MM. Social belongingness satisfaction as a function of interaction medium: face-to-face interactions facilitate greater social belonging and interaction enjoyment compared to instant messaging. Comput Hum Behav. 2014;36:359–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.04.004.
Yau JC, Reich SM. “It’s Just a Lot of Work”: adolescents’ self-presentation norms and practices on Facebook and Instagram. J Res Adolesc. 2019;29(1):196–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12376.
Burrow AL, Rainone N. How many likes did I get?: Purpose moderates links between positive social media feedback and self-esteem. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2017;69:232–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2016.09.005.
Sherman LE, Payton AA, Hernandez LM, Greenfield PM, Dapretto M. The power of the Like in adolescence: effects of peer influence on neural and behavioral responses to social media. Psychol Sci. 2016;27(7):1027–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797616645673.
Lee HY, Jamieson JP, Reis HT, Beevers CG, Josephs RA, Mullarkey MC, et al. Getting fewer “Likes” than others on social media elicits emotional distress among victimized adolescents. Child Dev. 2020;91(6):2141–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13422.
Reich S, Schneider FM, Zwillich B. No likes – no control? Examining the role of coping deprivation and social anxiety in social media ostracism. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2023;1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2022.2161938.
Seo M, Kim J, Yang H. Frequent interaction and fast feedback predict perceived social support: using crawled and self-reported data of Facebook users. J Comput-Mediat Commun. 2016;21(4):282–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12160.
Diefenbach S, Anders L. The psychology of likes: relevance of feedback on Instagram and relationship to self-esteem and social status. Psychology of Popular Media. 2021;11(2):196–207. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000360.
Nesi J, Prinstein MJ. In search of likes: longitudinal associations between adolescents’ digital status seeking and health-risk behaviors. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2018;48(5):740–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2018.1437733.
Sabik NJ, Falat J, Magagnos J. When self-worth depends on social media feedback: associations with psychological well-being. Sex Roles. 2020;82:411–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-019-01062-8.
Prichard I, O’Toole S, Wu Y, Harford J, Tiggemann M. No likes, no problem? Users’ reactions to the removal of Instagram number of likes on other people’s posts and links to body image. Body Image. 2021;38:72–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.03.007.
Sheldon KM, Abad N, Hinsch C. A two-process view of Facebook use and relatedness need-satisfaction: disconnection drives use, and connection rewards it. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2011;100(4):766–75. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022407.
Reinecke L, Trepte S. Authenticity and well-being on social network sites: a two-wave longitudinal study on the effects of online authenticity and the positivity bias in SNS communication. Comput Hum Behav. 2014;30:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.07.030.
Midgley C, Thai S, Lockwood P, Kovacheff C, Page-Gould E. When every day is a high school reunion: social media comparisons and self-esteem. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2021;121(2):285–307. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspi0000336. Series of studies examining social comparison as it occurs on social media.
Collins RL. For better or worse: the impact of upward social comparison on self-evaluations. Psychol Bull. 1996;119(1):51–69. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.119.1.51.
Schreurs L, Meier A, Vandenbosch L. Exposure to the positivity bias and adolescents’ differential longitudinal links with social comparison, inspiration and envy depending on social media literacy. Curr Psychol. 2022;42:28221–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03893-3.
Vimalakanthan K, Kelly AC, Trac S. From competition to compassion: a caregiving approach to intervening with appearance comparisons. Body Image. 2018;25:148–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2018.03.003.
Andrade FC, Erwin S, Burnell K, Jackson J, Storch M, Nicholas J, Zucker N. Intervening on social comparisons on social media: electronic daily diary pilot study. JMIR Mental Health. 2023;10(1):e42024. https://doi.org/10.2196/42024.
Weber S, Messingschlager T, Stein JP. This is an Insta-vention! Exploring cognitive countermeasures to reduce negative consequences of social comparisons on Instagram. Media Psychol. 2021;25(3):411–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2021.1968440.
Neff K. Self-compassion: an alternative conceptualization of a healthy attitude toward oneself. Self and Identity. 2003;2(2):85–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309032.
Barron AM, Krumrei-Mancuso EJ, Harriger JA. The effects of fitspiration and self-compassion Instagram posts on body image and self-compassion in men and women. Body Image. 2021;37:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.01.003.
Slater A, Varsani N, Diedrichs PC. #fitspo or #loveyourself? The impact of fitspiration and self-compassion Instagram images on women’s body image, self-compassion, and mood. Body Image. 2017;22:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2017.06.004.
Rutter H, Campoverde C, Hoang T, Goldberg SF, Berenson KR. Self-compassion and women’s experience of social media content portraying body positivity and appearance ideals. Psychol Pop Media. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000453.
Lonergan AR, Bussey K, Mond J, Brown O, Griffiths S, Murray SB, et al. Me, my selfie, and I: the relationship between editing and posting selfies and body dissatisfaction in men and women. Body Image. 2019;28:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2018.12.001.
Mahon C, Hevey D. Pilot trial of a self-compassion intervention to address adolescents’ social media-related body image concerns. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2023;28(1):307–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591045221099215.
De Valle MK, Wade TD. Targeting the link between social media and eating disorder risk: a randomized controlled pilot study. Intl J Eating Disord. 2022;55(8):1066–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.23756.
Gobin KC, McComb SE, Mills JS. Testing a self-compassion micro-intervention before appearance-based social media use: implications for body image. Body Image. 2022;40:200–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2021.12.011.
Seekis V, Bradley GL, Duffy AL. Does a Facebook-enhanced mindful self-compassion intervention improve body image? An evaluation study. Body Image. 2020;34:259–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2020.07.006.
Bishop SR, Lau M, Shapiro S, Carlson L, Anderson ND, Carmody J, et al. Mindfulness: a proposed operational definition. Clin Psychol Sci Pract. 2004;11(3):230–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy.bph077.
Johnson BT, Acabchuk RL, George EA, Nardi W, Sun S, Salmoirago-Blotcher E, et al. Mental and physical health impacts of mindfulness training for college undergraduates: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mindfulness. 2023;14(9):2077–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-023-02212-6.
Poon KT, Jiang Y. Getting less likes on social media: mindfulness ameliorates the detrimental effects of feeling left out online. Mindfulness. 2020;11:1038–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01313-w.
Weaver JL, Swank JM. A mindfulness-based intervention for adolescent social media users: a quasi-experimental study. J Child Adolesc Couns. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/23727810.2023.2266895.
Funding
The production of this article was supported by generous funds from the Winston Family Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KB drafted the manuscript. KF and AM provided critical revisions. KF drafted Table 1. All authors reviewed the final manuscript and provided final feedback.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Burnell, K., Fox, K.A., Maheux, A.J. et al. Social Media Use and Mental Health: A Review of the Experimental Literature and Implications for Clinicians. Curr Treat Options Psych 11, 1–16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40501-024-00311-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40501-024-00311-2