Abstract
So far, few empirical studies have tried to investigate the relationship of bilateral causality between entrepreneurial motivations and institutions. Indeed, researchers have not paid due attention to complexities such as the subsystems of entrepreneurship, institutional factors, and feedbacks within and between them. Similarly, the dynamics, or the changes in the variables of the two subsystems in the long run, and the uncertainties of the entrepreneurial ecosystem have remained neglected. Considering these gaps, this research seeks to detect the institutional factors that influence the index of entrepreneurial motivation (i.e., opportunity/necessity-based entrepreneurship ratio) in possible futures through strategic scenarios derived from the key uncertainties in the Iranian entrepreneurial ecosystem. To achieve the goal, this study utilizes system dynamics as a method to provide a systemic model for the Iranian entrepreneurial ecosystem and its effects on the motivation index. The data required for the model are collected from various international reports in the period of 2008–2018. After the key uncertainties are identified through scenario planning, the causal relationships between the variables are designed and simulated by the Vensim DSS software. Once the model performance is ensured, it is simulated in four strategic scenarios obtained from a combination of corruption and country risk as two possible situations of uncertainty. Then, in more probable scenarios, the factors with long-term effects on the motivation index are identified. As the results suggest, institutional factors such as business freedom, technology transfer, competition quality, and government effectiveness can improve the index of entrepreneurial motivation. Moreover, this index is involved in the process of institutional changes.


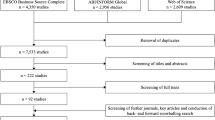
Source: The authors of this manuscript



Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript

Source: The authors of this manuscript
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used during the current study have been identified and extracted from the following data sites: https://www.gemconsortium.org/, https://www.weforum.org/, https://info.worldbank.org/governance/wgi/, http://www.heritage.org/index/explore, http://data.uis.unesco.org/index.aspx?queryid=74, https://www.doingbusiness.org/, https://kof.ethz.ch/en/forecasts-and-indicators/indicators/kof-globalisation-index.html, atlas.media.mit.edu/en/resources/economic_complexity/. https://guides.tricolib.brynmawr.edu/icrg, https://atlas.cid.harvard.edu/rankings. In addition, researchers can use soft systems dynamics methodology (a combination of soft systems methodology and the system dynamics) to identify the factors influencing the entrepreneurial motivations.
References
Acs, Z. J., Autio, E., & Szerb, L. (2014). National systems of entrepreneurship: Measurement issues and policy implications. Research Policy, 43(3), 476–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2013.08.016
Acs, Z. J., & Varga, A. (2005). Entrepreneurship, agglomeration and technological change. Small Business Economics, 24(3), 323–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-1998-4
Acs, Z. J., Desai, S., & Hessels, J. (2008). Entrepreneurship, economic development and institutions. Small Business Economics, 31, 219–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-008-9135-9
Aidis, R., Estrin, S., & Mickiewicz, T. (2008). Institutions and entrepreneurship development in Russia: A comparative perspective. Bus Ventur, 23(6), 656–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2008.01.005
Amorós JE, Cristi O, Minniti M (2009) Driving forces behind entrepreneurship: Differences on entrepreneurship rate level and its volatility across countries. Front Entrep Res 29(16): 1–20. Available at: http://digitalknowledge.babson.edu/fer/vol29/iss16/2
Amorós, J. E., Ciravegna, L., Mandakovic, V., & Stenholm, P. (2019). Necessity or opportunity? The effects of state fragility and economic development on entrepreneurial efforts. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 43(4), 725–750. https://doi.org/10.1177/1042258717736857
Anokhin, S., & Wincent, J. (2012). Start-up rates and innovation: A cross-country examination. Journal International Business Stuies, 43(1), 41–60. https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2011.47
Aparicio, S., Urbano, D., & Audretsch, D. (2016). Institutional factors, opportunity entrepreneurship and economic growth: Panel data evidence. Technology Forecasting Social Change, 102(1), 45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.04.006
Baumol, W. J. (1990). Entrepreneurship: Productive, unproductive, and destructive. Journal Political Economy, 98(5), 893–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-9026(94)00014-X
Belt, J. E., & Bashore, E. (2000). Managed care strategic planning: The reality of uncertainty. Healthcare Financial Management, 54(5), 38–42.
Bianchi, C. G., Borini, F. M., & Ogasavara, M. H. (2015). Creative industry internationalization: The impact of regulative, normative and cognitive institutions in developed and developing economies. Journal Global Business Advance, 8(4), 451–468. https://doi.org/10.1504/JGBA.2015.074031
Bjerregaard, T., & Lauring, J. (2012). Entrepreneurship as institutional change: Strategies of bridging institutional contradictions. European Management Review, 9(1), 31–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1740-4762.2012.01026.x
Block, J. H., Kohn, K., Miller, D., & Ullrich, K. (2015). Necessity entrepreneurship and competitive strategy. Small Business Economics, 44(1), 37–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-014-9589-x
Block, J., & Sandner, P. (2009). Necessity and opportunity entrepreneurs and their duration in self-employment: Evidence from German micro data. Industry Competition Trade, 9(2), 117–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10842-007-0029-3
Bosma N, Wennekers S, Amorós JE (2012) Global Entrepreneurship Monitor. 2011 extended report: Entrepreneurs and entrepreneurial employees across the globe. Babson Park, MA: Babson College. Available at: https://www.gemconsortium.org/file/open?fileId=48326
Bowen, H. P., & De Clercq, D. (2008). Institutional context and the allocation of entrepreneurial effort. International Business Studies, 39(4), 747–767. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8400343
Bruton, G. D., Ahlstrom, D., & Li, H. L. (2010). Institutional theory and entrepreneurship: Where are we now and where do we need to move in the future? Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 34(3), 421–440. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2010.00390.x
Bylund, P. L., & McCaffrey, M. (2017). A theory of entrepreneurship and institutional uncertainty. Business Venture, 32(5), 461–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2017.05.006
Dau, L. A., & Cuervo-Cazurra, A. (2014). To formalize or not to formalize: Entrepreneurship and pro-market institutions. Business Venture, 29(5), 668–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2014.05.002
Dean, BV., Nagel, BI., Osland, A .(2005). Entrepreneurial system: Application to Silicon Valley nanotechnology companies. In A Unifying Discipline for Melting the Boundaries Technology Management, 433–443. https://doi.org/10.1109/PICMET.2005. 1509722
Elert, N., & Henrekson, M. (2017). Entrepreneurship and institutions: A bidirectional relationship. Found Trends Entrep, 13(3), 191–263. https://doi.org/10.1561/0300000073
El Harbi, S., & Anderson, A. R. (2010). Institutions and the shaping of different forms of entrepreneurship. Socio-Economics, 39(3), 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2010.02.011
Estrin, S., Korosteleva, J., & Mickiewicz, T. (2016). Which institutions encourage entrepreneurial growth aspirations? Business Venture, 28(4), 564–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2012.05.001
Fuentelsaz, L., González, C., Maícas, J. P., & Montero, J. (2015). How different formal institutions affect opportunity and necessity entrepreneurship. Business Research Quarterly, 18(4), 246–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brq.2015.02.001
Fuentelsaz, L., González, C., & Maicas, J. P. (2018). Formal institutions and opportunity entrepreneurship. The contingent role of informal institutions. Business Research Quarterly, 22(1), 5–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brq.2018.06.002
Gartner, W. B. (1988). Who is an entrepreneur? Is the wrong question. Am J Small Bus, 12(4), 11–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/104225878801200401
Gartner, W. B. (1990). What are we talking about when we talk about entrepreneurship? Business Venture, 5(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-9026(90)90023-M
GEM. (2012). Global Entrepreneurship Monitor 2012 Executive Report. Available at: https://www.gemconsortium.org/file/open?fileId=48576
GEM. (2018). Global Entrepreneurship Monitor 2018 Executive Report. Available at: https://www.gemconsortium.org/file/open?fileId=50012
GEM. (2019). Global Entrepreneurship Monitor 2019 Executive Report. Available at: https://www.gemconsortium.org/file/open?fileId=50213
Greenwood, R., & Suddaby, R. (2006). Institutional entrepreneurship in mature fields: The big five accounting firms. Academy Management, 49(1), 27–48. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMJ.2006.20785498
Ilevbare, I. M., Probert, D., & Phaal, R. (2014). Towards risk-aware road mapping: Influencing factors and practical measures. Technovation, 34(8), 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2014.05.006
Henrekson, M., & Sanandaji, T. (2011). The interaction of entrepreneurship and institutions. Institutional Economy, 7, 47–75. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1744137410000342
Henrekson, M .(2007). Entrepreneurship and institutions. In Research Institute of Industrial Economics (IFN), Paper No. 707 https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.996807
Hessels, J., Van Gelderen, M., & Thurik, R. (2008). Entrepreneurial aspirations, motivations, and their drivers. Small Business Economics, 31(3), 323–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-008-9134-x
Hidayatno, A., Destyanto, AR., Moeis, AO., Iman, MRN .(2017). Scenario planning using system dynamics for reducing uncertainty on managing employee turnover. In 2nd Asia-Pacific Region System Dynamics Conference.
Kalantaridis, C., & Fletcher, D. (2012). Entrepreneurship and institutional change: A research agenda. Entrepreneur Regional Development, 24(3/4), 199–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2012.670913
Kelley, D., Bosma, N., Amorós, JE .(2011). Global Entrepreneurship Monitor 2010 report. Wellesley Mass., Santiago, Chile: Babson College & Universidad del Desarrollo.
Knight, F. H. (1921). Risk, uncertainty and profit. Houghton Mifflin.
Laffineur, C., Barbosa, S. D., Fayolle, A., & Nziali, E. (2017). Active labor market programs’ effects on entrepreneurship and unemployment. Small Business Economics, 49(4), 889–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9857-7
Lange, K., Müller-Seitz, G., Sydow, J., & Windeler, A. (2013). Financing innovations in uncertain networks: Filling in roadmap gaps in the semiconductor industry. Research Policy, 42(3), 647–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2012.12.001
Low, M. B., & MacMillan, I. C. (2007). Entrepreneurship: Past research and future challenges. Journal of Management, 14(2), 139–161. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920638801400202
Mavaddaty, M., Torabi, T., Memaenejad, A., & Mahmodzadeh, M. (2018). Formal and informal institutional factors, opportunity entrepreneurship and economic growth by GMM method. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship, 11(3), 521–539. https://doi.org/10.22059/jed.2019.265932.652728
McMullen, J. S., & Shepherd, D. A. (2006). Entrepreneurial action and the role of uncertainty in the theory of the entrepreneur. Academy Management Review, 31(1), 132–152. https://doi.org/10.2307/20159189
Morris, M. H., Miyasaki, N. N., Watters, C. E., & Coombes, S. M. (2006). The dilemma of growth: Understanding venture size choices of women entrepreneurs. Small Business Management, 44(2), 221–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-627X.2006.00165.x
Mrożewski, M., & Kratzer, J. (2017). Entrepreneurship and country-level innovation: Investigating the role of entrepreneurial opportunities. Technology Transfer, 42(5), 1125–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9479-2
North, D. C. (1990). Institutions, institutional change and economic performance. Cambridge University Press.
Oliver, C. (1991). Strategic responses to institutional processes. Academy of Management Review, 16(1), 145–179. https://doi.org/10.2307/258610
Petrakis, P. E. (2014). The construction of opportunity entrepreneurship function. Technology Forecasting Society Change, 10(2), 207–230.
Reynolds, P., Camp, M., Bygrave, W., Autio, E., & Hay, M. (2002). Global Entrepreneurship Monitor 2001 executive report. Global Entrepreneurship Research Association, Babson College.
Ricciardi, F., De Bernardi, P., & Cantino, V. (2020). System dynamics modeling as a circular process: The smart commons approach to impact management. Technol Forecast Soc Change, 151(C), 119799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119799
Samadi, AH .(2018). Institutions and entrepreneurship in MENA countries. In N. Faghih & M. R. Zali (Eds.), Entrepreneurship ecosystem in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), Springer International Publishing AG (part of Springer Nature). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75913-5_3
Samadi, A. H. (2019). Institutions and entrepreneurship: Unidirectional or bidirectional causality? Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 9(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40497-018-0129-z
Schoemaker, P. (1995). Scenario planning: A tool for strategic thinking. MIT Sloan Management Review, 36(2), 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-6301(95)91604-0
Schumpeter, J. A. (1934). The theory of economic development: An inquiry into profits, capital, credits, interest, and the business cycle. Transaction Publishers.
Sobel, R. S. (2008). Testing Baumol: Institutional quality and the productivity of entrepreneurship. Business Venture, 23(6), 641–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2008.01.004
Stenholm, P., Acs, Z. J., & Wuebker, R. (2013). Exploring country-level institutional arrangements on the rate and type of entrepreneurial activity. Business Venture, 28(1), 176–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2011.11.002
Sterman, J. D. (2000). Business dynamics: Systems thinking and modeling for a complex world. Irwin McGraw-Hill.
Suchart, T. (2017). Factors influencing opportunity driven nascent entrepreneurs in Europe and Asia. Europe Research Studies, 20(3A), 774. https://doi.org/10.35808/ersj/745
Terjesen, S., & Szerb, L. (2008). Dice thrown from the beginning? An empirical investigation of determinants of firm level growth expectations. Estudio De Economia, 35(2), 153–178. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-52862008000200003
Theil, H. (1966). Applied economic forecasting. North Holland Publishing.
Udimal, T. B., Luo, M., Liu, E., & Mensah, N. O. (2020). How has formal institutions influenced opportunity and necessity entrepreneurship? The case of brics economies. Heliyon, 6(9), e04931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04931
Valdez, M. E., & Richardson, J. (2013). Institutional determinants of macro-level entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 37(5), 1149–1175. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12000
Valliere, D., & Peterson, R. (2009). Entrepreneurship and economic growth: Evidence from emerging and developed countries. Entrepreneur Regional Development, 21(5–6), 459–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985620802332723
Van der Zwan, P., Thurik, R., Verheul, I., & Hessels, J. (2016). Factors influencing the entrepreneurial engagement of opportunity and necessity entrepreneurs. Eurasian Business Review, 6(3), 273–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40821-016-0065-1
Van de Ven, H. (1993). The development of an infrastructure for entrepreneurship. Business Venture, 8(3), 211–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-9026(93)90028-4
Wennekers, S., Van Stel, A. J., Thurik, A. R., & Reynolds, P. (2005). Nascent entrepreneurship and the level of economic development. Small Business Economy, 24, 293–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-1994-8
Williams, C. C., Martinez-Perez, A., & Kedir, A. M. (2016). Does bribery have a negative impact on firm performance? A firm level analysis across 132 developing countries. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior Research, 22(3), 398–415. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-01-2016-0002
Yu, T. F. (2001). An entrepreneurial perspective of institutional change. Constitutional Political Economy, 12(3), 217–236. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011607927754
Zali, M., Najafian, M., & Colabi, A. (2014). System dynamics modeling in entrepreneurship research: A review of the literature. International Journal of Supply Operator Management, 1(3), 347–370. https://doi.org/10.22034/2014.3.06
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. A. Ranaei Kordshouli presented the main idea of this article. B. Maleki reviewed the research literature and designed a systematic conceptual model of the research. H. A. Ranaei Kordshouli has reviewed and evaluated the conceptual model. B. Maleki was responsible for holding the focus group meeting and conducting interviews. Questionnaire data collection was done by B. Maleki. The simulation of the system model has been done by B. Maleki and then the evaluation of the simulation results has been done by H. A. Ranaei Kordshouli. All authors contributed to writing the manuscript and analyzed data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Duplicate publication policy
The authors declare and confirm that the content of the manuscript has not been published or submitted for publication elsewhere.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ranaei Kordshouli, H.A., Maleki, B. Entrepreneurship motivation and institutions: system dynamics and scenario planning. J Glob Entrepr Res 13, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40497-023-00348-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40497-023-00348-2
Keywords
- Entrepreneurship motivation index
- Necessity motivation
- Opportunity motivation
- Scenario planning
- System dynamics