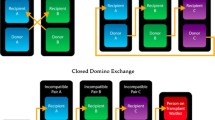
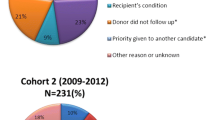
Abstract
Purpose of Review
We review the key principles of kidney paired donation (KPD) and discuss the status and unique considerations for KPD in developing countries.
Recent Findings
Despite the advantages of KPD programs, they remain rare among developing nations, and the programs that exist have many differences with those of in developed countries. There is a paucity of literature and lack of published data on KPD from most of the developing nations. Expanding KPD programs may require the adoption of features and innovations of successful KPD programs. Cooperation with national and international societies should be encouraged to ensure endorsement and sharing of best practices.
Summary
KPD is in the initial stages or has not yet started in the majority of the emerging nations. But the logistics and strategies required to implement KPD in developing nations differ from other parts of the world. By learning from the KPD experience in developing countries and adapting to their unique needs, it should be possible to expand access to KPD to allow more transplants to happen for patients in need worldwide.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable
References
Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation. WHO-ONT , 2022. http://www.transplant-observatory.org/
Kute V, Ramesh V, Shroff S, Guleria S, Prakash J. Deceased-donor organ transplantation in india: current status, challenges, and solutions. Exp Clin Transplant. 2020;18(Suppl 2):31–42. https://doi.org/10.6002/ect.rlgnsymp2020.L6.
Scurt FG, Ewert L, Mertens PR, Haller H, Schmidt BMW, Chatzikyrkou C. Clinical outcomes after ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2019;393(10185):2059–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32091-9.
Held PJ, McCormick F. ABO-incompatible kidney transplants: twice as expensive, half as good. Am J Transplant. 2016;16(5):1343–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13638.
Pankhurst L, Hudson A, Mumford L, et al. The UK National Registry of ABO and HLA antibody incompatible renal transplantation: pretransplant factors associated with outcome in 879 transplants. Transplant Direct. 2017;3(7):e181. https://doi.org/10.1097/TXD.0000000000000695.
Rapaport FT. The case for a living emotionally related international kidney donor exchange registry. Transplant Proc. 1986;18((3) Suppl. 2):5–9.
Kwak JY, Kwon OJ, Lee KS, Kang CM, Park HY, Kim JH. Exchange-donor program in renal transplantation: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 1999;31(1-2):344–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-1345(98)01655-8.
Cooper M, Leeser DB, Flechner SM, et al. Ensuring the need is met: a 50-year simulation study of the National Kidney Registry’s family voucher program. Am J Transplant. 2021;21(3):1128–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.16101.
Veale JL, Capron AM, Nassiri N, et al. Vouchers for future kidney transplants to overcome “chronological incompatibility” between living donors and recipients. Transplantation. 2017;101(9):2115–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001744.
Matas AJ. Nondirected, advanced, and voucher-based donation-the importance of terminology. JAMA Surg. 2022;157(3):280. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2021.5767.
Feizi M, Moeindarbari T. Characteristics of kidney donors and recipients in Iranian kidney market: evidence from Mashhad. Clin Transplant. 2019;33(10):e13650. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.13650.
Nizam N, Mazhar F, Abbas K, et al. Kidney swap in Pakistan: experience at the Sindh Institute of Urology and Transplantation. Exp Clin Transplant. 2017;15(Suppl 1):76–8. https://doi.org/10.6002/ect.mesot2016.O63.
Kute VB, Patel HV, Shah PR, et al. Impact of single centre kidney paired donation transplantation to increase donor pool in India: a cohort study. Transpl Int. 2017;30(7):679–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12956.
Kute VB, Patel HV, Modi PR, et al. Non-simultaneous kidney exchange cycles in resource-restricted countries without non-directed donation - a prospective single-center cohort study. Transpl Int. 2021;34(4):669–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13833.
Kute VB, Patel HV, Modi PR, et al. Paired kidney exchange in India: future potential and Challenges based on the experience at a single center. Transplantation. 2021;105(5):929–32. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000003421.
Ahmad I, Saxena S, Bansal R, et al. First successful three-way kidney exchange transplantation in North India. Indian J Nephrol. 2021;31(2):169–72. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijn.IJN_116_19.
Toews M, Giancaspro M, Richards B, Ferrari P. Kidney paired donation and the “valuable consideration” problem: the experiences of Australia, Canada, and the United States. Transplantation. 2017;101(9):1996–2002. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001778.
Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V, et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet. 2015;385(9981):1975–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61601-9.
Rees MA, Dunn TB, Kuhr CS, et al. Kidney exchange to overcome financial barriers to kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(3):782–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14106.
Minerva F, Savulescu J, Singer P. The ethics of the global kidney exchange programme. Lancet. 2019;394(10210):1775–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32474-2.
Singer P, Minerva F, Savulescu J. The global kidney exchange programme - authors’ reply. Lancet. 2020;395(10235):1485–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30619-X.
Ambagtsheer F, Haase-Kromwijk B, Dor F, et al. Global kidney exchange: opportunity or exploitation? An ELPAT/ESOT appraisal. Transpl Int. 2020;33(9):989–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13630.
Rees MA, Paloyo SR, Roth AE, et al. Global kidney exchange: financially incompatible pairs are not transplantable compatible pairs. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(10):2743–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14451.
Marino IRRA, Rees MA, Doria C. Open dialogue between professionals with different opinions builds the best policy. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(10):2749.
Roth AE, Krawiec KD, Paloyo S, et al. People should not be banned from transplantation only because of their country of origin. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(10):2747–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14485.
Roth AE, Marino IR, Ekwenna O, et al. Global kidney exchange should expand wisely. Transpl Int. 2020;33(9):985–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13656.
Lopez-Fraga M, Dominguez-Gil B. The global kidney exchange programme. Lancet. 2020;395(10235):–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30614-0.
Valera LCM. The Global Kidney Exchange programme. Lancet. 2020;395(10235):1484–5.
Danovitch GM. The Global Kidney Exchange programme. Lancet. 2020;395(10235):1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30615-2.
Roth AE, Wang SW. Popular repugnance contrasts with legal bans on controversial markets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(33):19792–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2005828117.
Baines LS, Jindal RM. Comment: kidney exchange to overcome financial barriers to kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(10):2742. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14325.
Kute V, Jindal RM, Prasad N. Kidney paired-donation program versus global kidney exchange in India. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(10):2740–1. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14324.
Bozek DN, Dunn TB, Kuhr CS, et al. Complete chain of the first global kidney exchange transplant and 3-yr Follow-up. Eur Urol Focus. 2018;4(2):190–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2018.07.021.
Rees M (Personal communication) 20 August 2023.
Stepkowski SM, Mierzejewska B, Fumo D, et al. The 6-year clinical outcomes for patients registered in a multiregional United States kidney paired donation program - a retrospective study. Transpl Int. 2019;32(8):839–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13423.
Hadaya K, Fehr T, Rusi B, Ferrari-Lacraz S, Jean V, Ferrari P. Kidney paired donation: a plea for a Swiss National Programme. Swiss Med Wkly. 2015;145:w14083. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2015.14083.
Cantwell L, Woodroffe C, Holdsworth R, Ferrari P. Four years of experience with the Australian kidney paired donation programme. Nephrology (Carlton). 2015;20(3):124–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.12369.
Cole EH, Nickerson P, Campbell P, et al. The Canadian kidney paired donation program: a national program to increase living donor transplantation. Transplantation. 2015;99(5):985–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000000455.
Malik S, Cole E. Foundations and principles of the Canadian living donor paired exchange program. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2014;1:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/2054-3581-1-6.
de Klerk M, Witvliet MD, Haase-Kromwijk BJ, Weimar W, Claas FH. A flexible national living donor kidney exchange program taking advantage of a central histocompatibility laboratory: the Dutch model. Clin Transpl. 2008:69–73. https://terasaki.org/store/CH6-deKlerk. Accessed 9 Aug 2023.
Johnson RJ, Allen JE, Fuggle SV, Bradley JA, Rudge C, Kidney Advisory Group UKTN. Early experience of paired living kidney donation in the United kingdom. Transplantation. 2008;86(12):1672–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181901a3d.
Osbun N, Thomas AG, Ronin M, et al. The benefit to waitlist patients in a national paired kidney exchange program: exploring characteristics of chain end living donor transplants. Am J Transplant. 2022;22(1):113–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.16749.
Mierzejewska B, Durlik M, Lisik W, et al. Current approaches in national kidney paired donation programs. Ann Transplant. 2013;18:112–24. https://doi.org/10.12659/AOT.889096.
Bastos J, Mankowski M, Gentry S, et al. Kidney paired donation in Brazil - a single center perspective. Transpl Int. 2021;34(8):1568–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13923.
Kher V, Jha PK. Paired kidney exchange transplantation - pushing the boundaries. Transpl Int. 2020;33(9):975–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13693.
Chandra Shrestha P, Bhandari TR, Adhikari R, Baral H, Verma RK, Shrestha KK. Living donor kidney paired exchange: an observational study. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022;78:103761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103761.
Sahay M. Transplantation of human organs and tissues Act-“Simplified”. Indian J Transplant. 2018;12(2):84.
Lucan M. Five years of single-center experience with paired kidney exchange transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(5):1371–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.02.081.
Huh KH, Kim MS, Ju MK, et al. Exchange living-donor kidney transplantation: merits and limitations. Transplantation. 2008;86(3):430–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181804a34.
McGregor TB, Sener A, Yetzer K, Gillrie C, Paraskevas S. The impact of COVID-19 on the Canadian kidney paired donation program: an opportunity for universal implementation of kidney shipping. Can J Surg. 2020;63(5):E451–3.
Treat E, Chow EKH, Peipert JD, et al. Shipping living donor kidneys and transplant recipient outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(3):632–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14597.
Treat EG, Miller ET, Kwan L, et al. Outcomes of shipped live donor kidney transplants compared with traditional living donor kidney transplants. Transpl Int. 2014;27(11):1175–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12405.
Sickand M, Cuerden MS, Klarenbach SW, et al. Reimbursing live organ donors for incurred non-medical expenses: a global perspective on policies and programs. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(12):2825–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02829.x.
Lentine KL, Kasiske BL, Levey AS, et al. KDIGO clinical practice guideline on the evaluation and care of living kidney donors. Transplantation. 2017;101(8S Suppl 1):S1–S109. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001769.
Lentine KL, Lam NN, Segev DL. Risks of living kidney donation: current state of knowledge on outcomes important to donors. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;14(4):597–608. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.11220918.
Wallis CB, Samy KP, Roth AE, Rees MA. Kidney paired donation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(7):2091–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr155.
Ellison B. A Systematic review of kidney paired donation: applying lessons from historic and contemporary case studies to improve the US model. 2014. Wharton Research Scholars Journal. Paper 107. from https://repository.upenn.edu/wharton_research_scholars/107/?utm_source=repository.upenn.edu%2Fwharton_research_scholars%2F107&utm_medium=PDF&utm_campaign=PDFCoverPages or https://www.kidneyregistry.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/A-Systematic-Review-of-Kidney-Paired-Donation_-Applying-Lessons-From-Historic-and-Contemporary-Case-Studies-to-Improve-the-US-Model.pdf. Accessed 23 Sept 2022.
The JHU Gazette. Hopkins surgical teams perform historic quintuple kidney swap 2023, Retrieved 11 June, from https://pages.jh.edu/gazette/2006/27nov06/27swap.html
de Klerk M, Keizer KM, Claas FH, Witvliet M, Haase-Kromwijk BJ, Weimar W. The Dutch national living donor kidney exchange program. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(9):2302–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01024.x.
Malik S, Cole E, et al. State of the art practices and policies in kidney paired donation. Curr Transpl Rep. 2014;1:10–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40472-013-0002-5.
Rees MA, Kopke JE, Pelletier RP, et al. A nonsimultaneous, extended, altruistic-donor chain. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(11):1096–101. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0803645.
Congress.gov. H.R.710 - 110th Congress (2007-2008): Charlie W. Norwood Living Organ Donation Act (2007) December 21 Retrieved 11 June, 2023 from https://www.congress.gov/bill/110th-congress/house-bill/710.
Flechner SM, Thomas AG, Ronin M, et al. The first 9 years of kidney paired donation through the National Kidney Registry: characteristics of donors and recipients compared with National Live Donor Transplant Registries. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(11):2730–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.14744.
Fortin MC, Williams-Jones B. Who should travel in kidney exchange programs: the donor, or the organ? Open Med. 2011;5(1):e23–5.
Johns Hopkins Medicine. Johns Hopkins leads first 16-patient, Multicenter “domino donor” kidney transplant 2023 Retrieved 11 June from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/news/media/releases/johns_hopkins_leads_first_16_patient_multicenter_domino_donor_kidney_transplant.
New York Times. 60 lives, 30 kidneys, all linked. In: New York Times; 2023. Retrieved 11 June, from https://www.nytimes.com/2012/02/19/health/lives-forever-linked-through-kidney-transplant-chain-124.html.
ABC News. Donating a kidney to a complete stranger in order to save a loved one 2023 Retrieved 11 June, from https://abcnews.go.com/Health/donating-kidney-complete-stranger-order-save-loved/story?id=30288400.
Biro P, Haase-Kromwijk B, Andersson T, et al. Building kidney exchange programmes in Europe-an overview of exchange practice and activities. Transplantation. 2019;103(7):1514–22. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002432.
European Cooperation in Science and Technology. European Network for Collaboration on Kidney Exchange Programmes (ENCKEP) 2023 Retreived 11 June, from https://www.enckep-cost.eu/
Bingaman AW, Wright FH Jr, Kapturczak M, Shen L, Vick S, Murphey CL. Single-center kidney paired donation: the Methodist San Antonio experience. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(8):2125–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04070.x.
Jan MY, Yaqub MS, Adebiyi OO, et al. Nondirected living kidney donation and recipient outcomes in the United States: a 20-year review. Kidney Int Rep. 2022;7(6):1289–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2022.03.012.
Leeser DB, Thomas AG, Shaffer AA, et al. Patient and kidney allograft survival with national kidney paired donation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;15(2):228–37. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.06660619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have made equal contributions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
KLL is a Senior Scientist of the SRTR, receives research funding related to living donation from the National Institutes of Health (NIH R01DK120551), and is also supported by the Mid-America Transplant/Jane A. Beckman Endowed Chair in Transplantation. KLL is chair of the AST LDCOP, member of the ASN Policy and Advocacy Committee, and a member of the National Kidney Foundation Transplant Advisory Committee. Unrelated to this work, KLL receives consulting fees from CareDx and speaker honoraria from Sanofi.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors. No informed consent was required as no individual patient level data was used.
Ethical Approval
We abided with the rules and regulation declaration of Helsinki and Istanbul. No institutional or any other ethical board approval was required as the data presented is retrospective, publicly available from the website.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Vivek B. Kute and Vidya A. Fleetwood are co-first authors.
Krista L. Lentine is the senior author.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kute, V.B., Fleetwood, V.A., Chauhan, S. et al. Kidney Paired Donation in Developing Countries: a Global Perspective. Curr Transpl Rep 10, 117–125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40472-023-00401-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40472-023-00401-9