Abstract
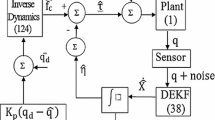
This paper proposes a stochastic model predictive control using the Laguerre function with optimal Kalman filter state estimation. The controller design uses an ARMAX state-space model, incorporating moving average into the stochastic formulation by a state disturbance matrix in innovation form, which calculates a stochastic term introduced in the control law. Then, reducing the output variance and preserving a better trade-off between the control effort and closed-loop performance. The optimal Kalman filter gain design copes with the minimum variance case, where the Kalman filter weighting matrices are tuned based on the state disturbance matrix and the covariance of estimated states of an ARMAX model. Hildreth’s quadratic programming solves the constrained optimization problem in a stochastic scenario, and it is used with the Laguerre function, simplifying finding the optimal problem in constrained cases. Moreover, we present a highly oscillatory mechanical system, a robotic joint benchmark used for numerical examples, and an experimental test using a circuit representing an under-damped coupled multivariable system with two inputs and two outputs. The proposed strategy results are compared to the Laguerre deterministic MPC approach and the classic MPC approach.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicated.
Code Availability
Not applicated.
Notes
References
Payri F, Guardiola C, Pla B, Blanco-Rodriguez D (2014) A stochastic method for the energy management in hybrid electric vehicles. Control Eng Pract 29:257–265
Alvarez-Mendoza F, Bacher P, Madsen H, Angeles-Camacho C (2017) Stochastic model of wind-fuel cell for a semi-dispatchable power generation. Appl Energy 193:139–148
Zhang Y, Meng F, Wang R, Zhu W, Zeng XJ (2018) A stochastic mpc based approach to integrated energy management in microgrids. Sustain Cities Soc 41:349–362
Tsai CC, Lin SC, Wang TY, Teng FJ (2009) Stochastic model reference predictive temperature control with integral action for an industrial oil-cooling process. Control Eng Pract 17(2):302–310
Kou P, Liang D, Gao L (2016) 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), IEEE, pp 1–5
From PJ, Gravdahl JT, Lillehagen T, Abbeel P (2011) Motion planning and control of robotic manipulators on seaborne platforms. Control Eng Pract 19(8):809–819
Grosso JM, Velarde P, Ocampo-Martinez C, Maestre JM, Puig V (2017) Stochastic model predictive control approaches applied to drinking water networks. Opt Control Appl. Methods 38(4):541–558
Wang Y, Ocampo-Martinez C, Puig V (2016) Stochastic model predictive control based on gaussian processes applied to drinking water networks. IET Control Theory Appl 10(8):947–955
Yang Y, Chen Y, Tang C, Chai L (2017) 2017 Australian and New Zealand Control Conference (ANZCC) (IEEE), pp 166–171
Tan Y, Cai G, Li B, Teo KL, Wang S (2019) Stochastic model predictive control for the set point tracking of unmanned surface vehicles. IEEE Access 8:579–588
Mesbah A (2016) Stochastic model predictive control: an overview and perspectives for future research. IEEE Control Syst Mag 36(6):30–44
Kouvaritakis B, Cannon M (2016) Model predictive control: classical, robust, and stochastic. Springer, New York
Cannon M, Cheng Q, Kouvaritakis B, Raković SV (2012) Stochastic tube mpc with state estimation. Automatica 48(3):536–541
Oldewurtel F, Jones C.N, Morari M (2008) 2008 47th IEEE conference on decision and control (IEEE), pp 4731–4736
Shang C, You F (2019) A data-driven robust optimization approach to scenario-based stochastic model predictive control. J Process Control 75:24–39
Jørgensen J.B, Huusom J.K, Rawlings J.B (2011) 2011 50th IEEE conference on decision and control and European control conference (IEEE), pp 1896–1903
Watanabe K, Ikeda K, Fukuda T, Tzafestas S.G (1991) Proceedings IROS’91: IEEE/RSJ international workshop on intelligent robots and systems’ 91 (IEEE), pp 1609–1614
Liu S, Jing Q (2011) 2011 international conference on electrical and control engineering (IEEE), pp 4670–4673
Ono M, Topcu U, Yo M, Adachi S (2013) 52nd IEEE conference on decision and control (IEEE), pp 4949–4956
Silveira A, Trentini R, Coelho A, Kutzner R, Hofmann L (2016) Generalized minimum variance control under long-range prediction horizon setups. ISA Trans 62:325–332
Trentini R, Silveira A, Kutzner R, Hofmann L (2016) 2016 European control conference (ECC) (IEEE), pp 1322–1327
Silveira A, Silva A, Coelho A, Real J, Silva O (2020) Design and real-time implementation of a wireless autopilot using multivariable predictive generalized minimum variance control in the state-space. Aerosp Sci Technol 105:106053
Evans MA, Cannon M, Kouvaritakis B (2015) Robust mpc tower damping for variable speed wind turbines. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 23(1):290–296
Manwell JF, McGowan JG, Rogers AL (2010) Wind energy explained: theory, design and application. Wiley, Hoboken
Abdullah M, Rossiter JA (2016) 2016 UKACC 11th international conference on control (CONTROL) (IEEE), pp 1–6
Rossiter JA, Wang L, Valencia-Palomo G (2010) Efficient algorithms for trading off feasibility and performance in predictive control. Int J Control 83(4):789–797
Pinheiro TCF, Silveira AS (2021) Constrained discrete model predictive control of an arm-manipulator using Laguerre function. Opt Control Appl Methods 42(1):160–179
Wang L (2001) Continuous time model predictive control design using orthonormal functions. Int J Control 74(16):1588–1600
Wang L (2009) Model predictive control system design and implementation using MATLAB®. Springer, New York
Khashirunnisa S, Chand BK, Kumari BL (2016) 2016 2nd international conference on communication control and intelligent systems (CCIS) (IEEE), pp 170–174
Humpherys J, Redd P, West J (2012) A fresh look at the Kalman filter. SIAM Rev 54(4):801–823
Seban L, Kirubakaran V, Roy B, Radhakrishnan T (2015) Gobf-arma based model predictive control for an ideal reactive distillation column. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 121:110–115
Silveira AS, Coelho AA (2011) Generalised minimum variance control state-space design. IET Control Theory Appl 5(15):1709–1715
Unbehauen H (2009) Control systems, robotics and automation-volume III: system analysis and control: classical approaches-III. EOLSS Publications
Bitmead RR, Gevers M, Wertz V (1990) Adaptive optimal control: the thinking man’s GPC. Prentice Hall, New York
Lewis FL, Xie L, Popa D (2008) Optimal and robust estimation, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton)
Wahlberg B (1991) System identification using Laguerre models. IEEE Trans Autom Control 36(5):551–562
Wang L (2004) Discrete model predictive controller design using Laguerre functions. J Process Control 14(2):131–142
Hildreth C (1957) A quadratic programming procedure. Naval Res Logist (NRL) 4(1):79–85
Jamil N, Chen X, Cloninger A (2015) Hildreths algorithm with applications to soft constraints for user interface layout. J Comput Appl Math 288:193–202
Åström KJ, Wittenmark B (2013) Adaptive control. Courier Corporation, North Chelmsford
Van Donkelaar ET, Bosgra OH, Van den Hof PM (1999) Proceedings of the 38th IEEE conference on decision and control (Cat. No. 99CH36304), vol 4 (IEEE), pp 3718–3721
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge the financial support of the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) under Grant 142414/2018-2 and the project 408559/2016-0.
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) under grant Grant 142414/2018-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicated.
Ethical statements
I hereby declare that this manuscript is the results of my independent creation under the reviewers’ comments. Except for the quoted contents, this manuscript does not contain any research achievements that have been published or written by other individuals or groups. I am the only author of this manuscript. The legal responsibility of this statement shall be borne by me.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pinheiro, T.C.F., Silveira, A.d.S. Stochastic model predictive control using Laguerre function with minimum variance Kalman filter estimation. Int. J. Dynam. Control 11, 1330–1350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-022-01029-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-022-01029-w