Abstract
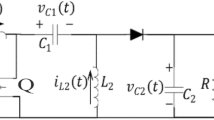
In this paper, an adaptive nonlinear method is proposed for both Maximum Power Point Traking Control and output voltage regulation of a Single-Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC). The main objective of this adaptive synergetic controller is to maintain a constant switching frequency of the converter and to stabilize the output voltage under uncertain weather conditions in real time. A hybrid control scheme has been derived and a Radial Basis function neural network used for approximation of unmeasurable or unmeasured variables. The effect of the controller to provide a maximum power transfer from PV side to SEPIC converter under unpredictable weather conditions and load variations has been verified through simulations. The stability of the close-loop system is insured by Lyapunov’s theory and the proposed algorithm gives good results compared to the Sliding Mode Controller used in the same context.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaramillo-Lopez F, Kenne G, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F (2017) Maximum power extraction on wind turbine systems using block-backstepping with gradient dynamics control. Int J Adapt Control Signal Process 31:835–858
Pedro P, Vergara M, Salazar Tam T, Mai Phuong H, Slootweg Nguyen H (2020) A comprehensive assessment of PV inverters operating with droop control for overvoltage mitigation in lv distribution networks. Renew Energy 159:172–183
Qian J, Li K, Wu H, Yang J, Li X (2017) Synergetic control of grid-connected photovoltaic systems. Hindawi Int J Photoenergy 1–11
Attoui H, Khaber F, Melhaoui M, Kassmi K, Essounbouli N (2016) Development and experimentation of a new MPPT synergetic control for photovoltaic systems. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 18:165–173
Ozsoy E, Sanjeevikumar P, Blajerg F, Ionel DM, Kalla U, Bhaskar MS (2018) Control of high gain modified SEPIC converter: a constant switching frequency modulation sliding mode controlling technique. In: Proceedings of 2018 IEEE international power electronics and application conference and exposition (PEAC), Shenzhen, China, Nov, pp 1–6
Verma D, Nema S, Shandilya AM, Dash SK (2016) Maximun power point traking (MPPT) techniques: recapitulation in solar photovoltaic systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:1018–1034
Femia N, Petrone G, spagnuolo G, Vitelli M (2005) Optimization of perturb and observe maximum power tracking method. IEEE Trans Power Electron 20:963–973
Desai HP, Patel HK (2007) Maximum power point algorithm in PV generation: an overview. Power Electron Drive Syst 624–630
Xiao L, Seem JE, Lei P (2011) Maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic systems using adaptive extremum seeking control. In: Proceedings of 50th IEEE conference on decision and control and European control conference-CDC-ECC, pp 1503–1508
Messai A, Mellit A, Guessoum A, Kologirou SA (2011) Maximum power point tracking using a GA optimized fuzzy logic controller and its FPGA implementation. Sol Energy 85:265–277
Kulaksiz AA, Akkaya R (2012) A genetic algorithm optimized ANN-based MPPT algorithm for a stand-alone PV system with induction motor drive. Sol Energy 86:2366–2375
Tsang KM, Chan WL (2012) Fast acting regenerative dc electronic load based on a SEPIC converter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27:269–275
Kircioglu O, Unlu M, Mur S (2016) Modeling and analysis of DC–DC SEPIC converter with coupled inductors. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference international symposium on industrial electronics (INDEL), pp 1–5
Ayachit A, Reatti A, Kazimierczuk MK (2016) Small-signal modeling of PWM dual-SEPIC DC-DC converter by circuit averaging technique. In: Proceedings IEEE conference international symposium on industrial electronics (INDEL), pp 3606–3611
Santi E, Monti A, Li D, Proddutur K, Dougal R (2004) Synergetic control for power electronics applications: a comparison with sliding mode approach. J Circuits Syst Comput 13:737–760
Mars N, Crouz F, Essounbouli N, Sbita L (2017) Synergetic MPPT controller for photovoltaic system. J Electr Electr Syst 6:232
Moshksar E, Ghanbari T, Samet H, Guay M (2019) Estimation-based extremum-seeking control: a real-time approach for improving energy efficiency in photovoltaic systems. IEEE Syst J 13:3141–3152
Chiu HJ, Lo YK, Chen JT (2010) A high-efficiency dimmable led driver for low-power lighting applications. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 57:735–743
Middlebrook RD, Cuk S (1976) A general unified approach to modelling swiching converter power stages. In: IEEE power electronics specialists conference, pp 18–34
Kolesnikov A et al (2000) Modern applied control theory: synergetic approach in control theory, vol 2. TSURE-Press, Moscow-Taganrog
Kolesnikov A, Veselov G, Monti A, Ponci F, Santi F, Dougal R (2002) Synergetic synthesis of DC-DC boost converter controllers: theory and experimental analysis. In: Annual IEEE applied power electronics conference and exposition (Cat. No. 02CH37335)
Padhi BK, Padhy SN (2016) Controller design for reduced order model of SEPIC converter. In: Proceedings of the 2016 international conference on signal processing, vol 1. Communication, Power Embedded Systems (SCOPES). Paralakhemundi, India, pp 1533–1538
Rosa Arthur H, de Souza Thiago M, Morals Lenin MF, Seleme Seleme I (2018) Adaptive and nonlinear control techniques applied to SEPIC converter in DC-DC, PFC, CCM, DCM modes using HIL simulation. Energies MDPI 11:1–22
Rodriguez H, Ortega R, Escobar G (2001) A new family of energy-based nonlinear controllers for switched power converters. In: Proceedings of ISIE 2001 IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, Pusan, Korea, June, pp 723–727
Meghnous AR, Pham MT, Lin-Shi X (June 2013) Nonlinear observer and lyapunov-based control for sepic converter: design and experimental results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE American control conference (ACC). vol. 2. Washington, DC, USA, pp 5833–5838
Jiang Z, Dougal Roger A (2004) Synergetic control of power converters for pulse current charging of advanced batteries from a fuel cell power source. IEEE Trans Power Electron 19:1140–1150
Ahmed-Ali T, Kenne G, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F (2009) Identification of nonlinear systems with time-varying parameters using a sliding-neural network observer. Neurocomputing 72:1611–1620
Kenne G, Simo Fotso A, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F (2016) A new adaptive control strategy for a class of nonlinear system using RBF neuro-sliding-mode technique: application to SEIG wind turbinecontrol system. Int J Control 90:855–872
Jaramillo-Lopez F, Kenne G, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F (2017) Adaptive control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems: application to photovoltaic control systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 62:393–398
Jain AK, Dubes RC (1988) Algorithms for clustering data, vol 2. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Jaramillo-Lopez F, Kenne G, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F (2016) A novel online training neural network-based algorithm for wind speed estimation and adaptive control of PMSG wind turbine system for maximum power extraction. Renew Energy 86:38–48
Kenne G, Nguimfack-Ndongmo J d D, Kuate RF, Fotsin HB (2015) An online simplified nonlinear controller for transient stabilization enhancement of DFIG in multi-machine power systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 60(9):2464–2469
Nguimfack-Ndongmo J d D, Kenne G, Mbaka-Nfah E (2016) Design of synergetic nonlinear controller for transient stabilization enhancement of DFIG in multi-machine wind power systems. Energy Procedia 93:125–132
Levant A (2003) Higher order sliding modes, differentiation and output feedback control. Int J Control 76:924–941
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguimfack-Ndongmo, J.d.D., Kenné, G., Kuate-Fochie, R. et al. Adaptive neuro-synergetic control technique for SEPIC converter in PV systems. Int. J. Dynam. Control 10, 203–216 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-021-00808-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-021-00808-1