Abstract
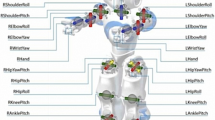
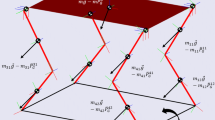
This work proposes a simple technique to implement in real-time a nonlinear robust controller on a humanoid NAO robot that does not have direct drive joints. The key trick consists of designing a time delay estimation based sliding mode controller without any prior knowledge of the robot’s dynamics to alleviate the heavy computations since the on-board processor has low computational power and to deal with the effect of the uncertainties. Then, the calculated torque inputs will be converted to position controller for the servo actuated NAO robot using an appropriate transformer. The proposed method will ensure in addition to high precision tracking a fast convergence during the reaching phase. The proposed control architecture is validated through experimental results on a real NAO robot.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldebaran robotics: Nao documentation. http://doc.aldebaran.com/2-1/family/nao_dcm/actuator_sensor_names.html. (Accessed on 08 April 2019)
Boiko I, Fridman L (2005) Analysis of chattering in continuous sliding-mode controllers. IEEE Trans Autom Control 50(9):1442–1446. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2005.854655
Fallaha CJ, Saad M, Kanaan HY, Al-Haddad K (2011) Sliding-mode robot control with exponential reaching law. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 58(2):600–610. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2045995
Gelin R (2019) NAO. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 147–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6046-2_14
Gouaillier D, Collette C, Kilner C (2010) Omni-directional closed-loop walk for nao. In: 2010 10th IEEE-RAS international conference on humanoid robots, pp 448–454. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICHR.2010.5686291
Hashemi E, Khajepour A (2017) Kinematic and three-dimensional dynamic modeling of a biped robot. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part K J Multi-body Dyn 231(1):57–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464419316645243
Kali Y, Rodas J, Gregor R, Saad M, Benjelloun K (2018) Attitude tracking of a tri-rotor UAV based on robust sliding mode with time delay estimation. In: ICUAS, international conference on unmanned aircraft systems
Khatib O, Thaulad P, Yoshikawa, Taizo, Park J (2008) Torque-position transformer for task control of position controlled robots. In: 2008 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 1729–1734. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2008.4543450
Moosavian SAA, Takhmar A, Alghooneh M (2007) Regulated sliding mode control of a biped robot. In: 2007 international conference on mechatronics and automation, pp 1547–1552. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMA.2007.4303779
Orozco-Soto SM, Ibarra-Zannatha JM (2017) Motion control of humanoid robots using sliding mode observer-based active disturbance rejection control. In: 2017 IEEE 3rd colombian conference on automatic control (CCAC), pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCAC.2017.8276383
Sanchez-Magos M, Ballesteros-Escamilla M, Cruz-Ortiz D, Salgado I, Chairez I (2019) Terminal sliding mode control of a virtual humanoid robot. In: 2019 6th international conference on control, decision and information technologies (CoDIT), pp 726–731. https://doi.org/10.1109/CoDIT.2019.8820326
Swikir A, Utkin V (2016) Chattering analysis of conventional and super twisting sliding mode control algorithm. In: 2016 14th international workshop on variable structure systems (VSS), pp 98–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/VSS.2016.7506898
Utkin V (1992) Sliding mode in control and optimization. Springer, Berlin
Utkin V, Guldner J, Shi J (1999) Sliding mode control in electromechanical systems. Taylor-Francis, Oxford
Yoshikawa T, Khatib O (2009) Compliant humanoid robot control by the torque transformer. In: 2009 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, pp 3011–3018. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2009.5353907
Youcef-Toumi K, Ito O (1990) A time delay controller for systems with unknown dynamics. ASME J Dyn Syst Meas Control 112:133–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kali, Y., Saad, M., Boland, JF. et al. Walking task space control using time delay estimation based sliding mode of position Controlled NAO biped robot. Int. J. Dynam. Control 9, 679–688 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00696-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00696-x