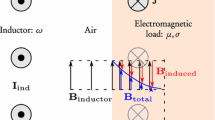
Abstract
Efficient computation for thermal conduction is particularly important for analyzing the plate forming induced by induction line heating. Coupled magneto-thermal model is time-consuming while the existing alternative heat source models are mainly based on empirical assumptions. This paper introduces an equivalent volumetric heat source model to enable the rapid estimation of thermal conduction in plate forming for a linear inductor. First, the distribution features of induced heat sources were investigated with a local yet accurate coupling model. Second, according to these features, an equivalent volumetric heat source (EVHS) model was proposed. Third, the relationship between the proposed EVHS model and the heating parameters was determined. Finally, the proposed model was applied to perform the thermal conduction analysis for a large-scale plate. The results reveal that the proposed model can be used to considerably reduce the calculation time while maintaining the same level of engineering precision.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Lee K, Hwang B (2014) An approach to triangular induction heating in final precision forming of thick steel plates. J Mater Process Tech 214:1008–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.11.002
Wang J, Yi B, Zhang C, Zhou H, Shu Y (2019) Experiments of double curvature plate bending with induction heating and processing parameters investigation by computational analysis. Ocean Eng 192:106596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106596
Yi B, Zhou H, Wang J (2019) Study on typical out-of-plane bending deformation of hull plate by high frequency induction heating. In: Proceedings of the 29th international ocean and polar engineering conference, Honolulu, Hawaii, p 8
Xiao Y, Han Y, Mk C, Wang L, Xu D (2022) Spatial matching relationship of dual heat sources in electromagnetic heating of pipes. Appl Therm Eng 202:117858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117858
Luo Y, Ishiyama M, Murakawa H (2004) Study of temperature field and inherent strain produced by high frequency induction heating on flat plate (mechanics, strength and structural design). Trans JWRI 33:59–63
Bae K, Yang Y, Hyun C (2012) Analysis of triangle heating technique using high frequency induction heating in forming process of steel plate. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0069-4
Zhu Y, Luo Y (2018) A simplified heat source model for thick plate bending via high-frequency induction line heating. Ships Offshore Struc 14:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445302.2018.1475883
Zhu Y, Luo Y, Ma N (2019) Relationship between equivalent surface heat source and induction heating parameters for analysis of thermal conduction in thick plate bending. Ships Offshore Struc 14:921–928. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445302.2019.1589762
Dong H, Zhao Y, Yuan H, Hu X, Yang Z (2019) A simplified calculation method of heat source model for induction heating. Materials 12:2938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182938
Chang L, Zhao Y, Yuan H, Hu X, Yang Z, Zhang H (2020) Effect of plate curvature on heat source distribution in induction line heating for plate forming. Appl Sci 10:2304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072304
Ueda K, Murakawa H, Rashwan AM, Neki I, Kamichika R, Ishiyama M, Ogawa J (1993) Development of computer-aided process planning system for plate bending by line-heating (report 3)—relation between heating condition and deformation. TRANS JWRI 22:145–156
Osawa N, Hashimoto K, Sawamura J, Kikuchi J, Deguchi Y, Yamaura T (2007) Development of heat input estimation technique for simulation of shell forming by line-heating. CMES-Comp Model Eng 20:43
Tango Y, Ishiyama M, Osawa N, Hashimoto K, Sawamura J (2010) Method of estimating temperature distribution history. US 9271336 B2, 2010
Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang Y, Ji Z, Deng Y (2011) Technical parameter analysis of high-frequency induction heating applied to steel plate bending. J Ship Prod Des 27:99–110. https://doi.org/10.5957/jspd.2011.27.3.99
Cheng DK (1989) Field and wave electromagnetics. Pearson education India, Beijing
Guru BS, Hiziroglu HR (2004) Electromagnetic field theory fundamentals, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ishimaru A (2017) Electromagnetic wave propagation, radiation, and scattering: from fundamentals to applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52001174), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. LQ21E090005), and the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (Grant No. 202003N4090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ did the methodology, investigation, and writing of original manuscript. ZL, ML, and AD did the conceptualization, methodology, editing, and supervision of the study. YL and ZL did the conceptualization, methodology, review, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competitive economic interests or personal relationships that could affect the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Daniel Onofre de Almeida Cruz.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Li, Z., Li, M. et al. An equivalent volumetric heat source model for thermal conduction of plate forming by inducted line heating. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 45, 412 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04219-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-023-04219-5