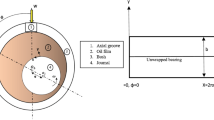
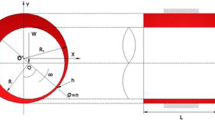
Abstract
The current study addresses the influence of thermo-elasto effects on performance parameters of the journal bearing lubricated with biodegradable nanolubricants. It is assumed that the non-Newtonian nature of the biodegradable nanolubricants follows the power law model. The analysis is done by simultaneous numerical solutions of the modified Reynolds equation, adiabatic energy equation, and the deformation equation. The finite difference method is adopted to solve the Reynolds and energy equations with suitable iterative scheme. Simulated results reveal that the deviation in performance parameters due to thermo-elasto effects is observed differently for different power law indexes. Moreover, biodegradable nanolubricants enhance the load carrying capacity and friction force, while the attitude angle and side leakage remain unchanged in comparison with the base biolubricant.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(U\) :
-
Tangential velocity of the journal, m/s
- \(\omega\) :
-
Angular velocity of the journal (\(\omega\) = U/R), rad/s
- \(N\) :
-
Rotational speed, rpm
- \(h\) :
-
Film thickness, m
- \(e\) :
-
Eccentricity, m
- \(O_{{{\rm b}}}\) :
-
Bearing center
- \(O_{{{\rm J}}}\) :
-
Journal center
- \(h_{\min }\) :
-
Minimum fluid film thickness, m
- \(\mu\) :
-
Apparent viscosity, Pa s
- \(\mu_{0}\) :
-
Reference viscosity of the lubricant, Pa s
- \(\mu_{{{{\rm nf}}}}\) :
-
Viscosity of nanolubricant, Pa s
- x, y, z :
-
Bearing coordinates, x measures along circumferential direction, y measures along the radial direction, z measures along the axial direction, m
- \(\theta\) :
-
Angular coordinate, rad
- R :
-
Journal radius, m
- D :
-
Journal diameter, m
- L :
-
Bearing length, m
- \(c\) :
-
Radial clearance, m
- \(\theta_{{{\rm c}}}\) :
-
Cavitation angle, rad
- \(\varphi\) :
-
Nanoparticles volume fraction, %
- \(\varphi_{{{\rm m}}}\) :
-
Maximum particle packing fraction, %
- [η]:
-
Intrinsic viscosity
- \(n\) :
-
Power law index
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Eccentricity ratio
- \(C_{0}\) :
-
Elastic coefficient
- \(t\) :
-
Bearing liner thickness, m
- \(E\) :
-
Modulus of elasticity of the bearing
- \(\nu\) :
-
Poisson ratio
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of oil, kg/m3
- \(\rho_{{{\rm p}}}\) :
-
Density of nanoparticles, kg/m3
- \(\rho_{0} { }\) :
-
Density of base oil, kg/m3
- \(\rho_{{{{\rm nf}}}}\) :
-
Density of nanolubricant, kg/m3
- \(C_{{{{\rm pp}}}} ,C_{{{{\rm p}}0}} , C_{{{{\rm pnf}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of nanoparticles, base oil, and nanolubricant (J/kg°C)
- \(\beta\) :
-
Thermoviscosity coefficient, °C−1
- \(u, v\) :
-
Oil velocity components in x and y directions (m/s)
- \(q_{x} ,q_{y}\) :
-
Discharge in x and y directions, m3/s
- \(\phi\) :
-
Attitude angle, degree
- \(p\) :
-
Lubricant film pressure, N/m2
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Aspect ratio
- \(W\) :
-
Load carrying capacity, N
- \(Q_{{{\rm S}}}\) :
-
Total lubricant side leakage, m3/s
- \(W_{\theta }\) :
-
Tangential component of load carrying capacity, N
- \(W_{{{\rm r}}}\) :
-
Radial component of load carrying capacity, N
- \(C_{{{\rm f}}}\) :
-
Coefficient of friction
- \(f\) :
-
Friction force, N
- \(\dot{\gamma }\) :
-
Shear strain rate, s−1
- \(D_{e}\) :
-
Dissipation number
- THD:
-
Thermohydrodynamic
- TEHD:
-
Thermo-elasto-hydrodynamic
References
Duvedi RK, Garg HC, Jadon VK (2006) Analysis of hybrid journal bearing for non-Newtonian lubricants. Lubr Sci 18:187–207. https://doi.org/10.1002/ls.17
Garg HC, Kumar V, Sharda HB (2010) Performance of slot-entry hybrid journal bearings considering combined influences of thermal effects and non-Newtonian behavior of lubricant. Tribol Int 43:1518–1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.02.013
Khatak P, Garg HC (2017) Performance analysis of capillary compensated hybrid journal bearing by considering combined influence of thermal effects and micropolar lubricant. J Tribol 139:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4033715
Boncompain R, Fillon M, Frene J (1986) Analysis of thermal effects in hydrodynamic bearings. J Tribol 108:219–224. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261166
Sinhasan R, Chandrawat HN (1989) Analysis of two-axial groove journal bearing including thermoelasto-hydrodynamic effects. Tribol Int 22:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-679X(89)90151-5
Zhang C (2002) TEHD behaviour of non-Newtonian dynamically loaded journal bearings in mixed lubrication for direct problem. J Tribol 124:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1396342
Bouyer J, Fillon M (2004) Relevance of the thermoelastohydrodynamic model in the analysis of a plain journal bearing subjected to severe operating conditions. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 218:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1243/1350650042128058
Bouyer J, Fillon M (2004) On the significance of thermal and deformation effects on a plain journal bearing subjected to severe operating conditions. J Tribol 126:819–822. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1792678
Pierre I, Bouyer J, Fillon M (2004) Thermohydrodynamic behavior of misaligned plain journal bearings: theoretical and experimental approaches. Tribol Trans 47:594–604. https://doi.org/10.1080/05698190490513974
Bouyer J, Fillon M (2005) Influence of deformation effects on a misaligned plain journal bearing. In: Proceedings of third world tribology congress, pp 105–106
Kuznetsov E, Glavatskih S, Fillon M (2011) THD analysis of compliant journal bearings considering liner deformation. Tribol Int 44:1629–1641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.05.013
Linjamaa A, Lehtovaara A, Larsson R, Kallio M, Sochting S (2018) Modelling and analysis of elastic and thermal deformations of a hybrid journal bearing. Tribol Int 118:451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.02.029
Nair KP, Ahmed MS, Al-qahtani ST (2009) Static and dynamic analysis of hydrodynamic journal bearing operating under nano lubricants. Int J Nanoparticles 2:251–262. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJNP.2009.028757
Shenoy BS, Binu KG, Pai R, Rao DS, Pai RS (2012) Effect of nanoparticles additives on the performance of an externally adjustable fluid film bearing. Tribol Int 45:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.10.004
Phuoc TX, Massoudi M, Chen RH (2011) Viscosity and thermal conductivity of nanofluids containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes stabilized by chitosan. Int J Therm Sci 50:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2010.09.008
Kotia A, Ghosh SK (2015) Experimental analysis for rheological properties of aluminium oxide (Al2O3)/gear oil (SAE EP-90) nanolubricant used in HEMM. Ind Lubr Tribol 67:600–605. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-03-2015-0029
Sajeeb A, Rajendrakumar PK (2019) Investigation on the rheological behavior of coconut oil based hybrid CeO2/Cuo nanolubricants. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 233:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650118772149
Swamy S, Prabhu B, Rao B (1975) Calculated load capacity of non-Newtonian lubricants in finite width journal bearings. Wear 31:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(75)90162-3
Jang JY, Khonsari MM (2001) On the thermohydrodynamic analysis of a Bingham fluid in slider bearings. Acta Mech 148:165–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183676
Ma YY, Wang WH, Cheng XH (2004) A study of dynamically loaded journal bearings lubricated with non-Newtonian couple stress fluids. Tribol Lett 17:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRIL.0000017420.44627.63
Kumar P, Khonsari M (2009) On the role of lubricant rheology and piezo-viscous properties in line and point contact EHL. Tribol Int 42:1522–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.11.006
Garg HC, Kumar V (2010) Analysis of thermal effects in capillary compensated hole-entry hybrid journal bearings lubricated with a non-Newtonian lubricant. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 224:317–334. https://doi.org/10.1243/13506501JET683
Williams P, Symmons G (1987) Analysis of hydrodynamic slider thrust bearings lubricated with non-Newtonian fluids. Wear 117:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301679X(87)90041-7
Bhattacharjee R, Das N (1996) Power law fluid model incorporated into elastohydrodynamic lubrication theory of line contact. Tribol Int 29:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-679X(95)00096-M
Safar ZS (1979) Journal bearing operating with non- Newtonian lubricant films. Wear 53:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(79)90220-5
Singh C, Sinha P (1981) Non-newtonian squeeze films in journal bearings. Wear 70:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(81)90351-3
Tanner RI (1964) Short bearing solution for pressure distribution in a non-Newtonian lubricant. J Appl Mech 31:350–351. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3629618
Dien IK, Elrod HG (1983) A generalized steady-state Reynolds equation for non-Newtonian fluids, with applications to journal bearings. J Lubr Technol 105:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3254619
Jain D, Sharma SC (2015) Two-lobe geometrically imperfect hybrid journal bearing operating with power law lubricant. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 229:30–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650114541252
Das BJ, Roy L (2018) Analysis and comparison of steady-state performance characteristics of two-axial groove and multilobe hydrodynamic bearings lubricated with non-Newtonian fluids. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 232:1581–1596. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650118758087
Jang J, Chang C (1988) Adiabatic analysis of finite width journal bearings with non-Newtonian lubricants. Wear 122:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(88)90007-5
Mahbubul IM, Saidur R, Amalina MA (2012) Latest developments on the viscosity of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.10.021
Kole M, Dey TK (2011) Effect of aggregation on the viscosity of copper oxide e gear oil nano fluids. Int J Therm Sci 50:1741–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.03.027
Hooke CJ, Brighton DK, O’Donoghue JP (1966) The effect of elastic distortions on the performance of thin shell bearing. Proc I Mech Eng 181:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1243/PIME_CONF_1966_181_033_02
Jain SC, Sinhasan R (1983) Performance of flexible shell journal bearings with variable viscosity lubricants. Tribol Int 16:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-679X(83)90043-9
Chetti B, Zouggar H (2019) Steady-state performance of a circular journal bearing lubricated with a non-Newtonian fluid considering the elastic deformation of the liner. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 233:1389–1396. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650119836616
Ferron J, Ferene J, Boncompain R (1983) A study of the thermohydrodynamic performance of a plain journal bearing comparison between theory and experiments. J Lubr Technol 105:422–428. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3254632
Pak BC, Cho Y (1998) Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxides particles. Exp Heat Transf 11:151–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916159808946559
Funding
No funding to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author (s) acknowledged that there are no conflicts of interest corresponding to the research, authorship and publication of this research.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Roney Leon Thompson.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanola, A., Garg, H.C. Thermo-elasto-hydrodynamic (TEHD) study of journal bearing lubricated with biodegradable nanolubricant. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 43, 69 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02801-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02801-3