Abstract
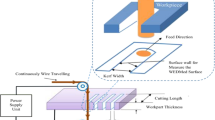
The present study analyzed the effects of cold treated brass wire electrode for the machining of hardened high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel on wire electric discharge machine. Cold treatment of brass wire at − 70 °C for 24 h has refined its microstructure which results in an increase in electrical conductivity by 24.5%. The experimental work is designed using fractional factorial design to determine the relationship of input variables including servo voltage (SV), pulse on time (Ton), pulse off time (Toff), wire type (Wt), wire tension (Tw), and flushing pressure (Fp) and response measures including cutting speed (CS), surface roughness (Ra), and kerf width (Kf). In Wt, two kinds of brass wires including cold treated (CT) and non-cold treated (NCT) have been used. Empirical models for cutting speed (CS), surface roughness (Ra), and kerf width (Kf) are developed, and their contribution is analyzed through the analysis of variance (ANOVA) technique. Desirability function offers the best combination of input variables to maximize CS and minimize both Ra and Kf simultaneously. Ton is observed as the most effective input variable for all response measures, followed by Wt and Toff. CT brass wire has been observed as the best alternative in multi-objective optimization.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WEDM:
-
Wire electric discharge machining
- ECM:
-
Electric chemical machining
- WJM:
-
Water jet machining
- HSLA:
-
High-speed low alloy
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- SV:
-
Servo voltage
- T on :
-
Pulse on time
- T off :
-
Pulse off time
- W t :
-
Wire type
- T w :
-
Wire tension
- F p :
-
Flushing pressure
- CT:
-
Cold treated
- NCT:
-
Non-cold treated
- CS:
-
Cutting speed
- Ra:
-
Surface roughness
- Kf:
-
Kerf width
- I :
-
Discharge current
- C :
-
Capacitance
- MRR:
-
Material removal rate
- SS:
-
Sum of square
- df :
-
Degree of freedom
- MS:
-
Mean square
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- C.V:
-
Coefficient of variation
References
Show B et al (2010) Effect of vanadium and titanium modification on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a microalloyed HSLA steel. Mater Sci Eng A 527(6):1595–1604
Lu P et al (2017) Microstructure and failure analysis of flash butt welded HSLA 590CL steel joints in wheel rims. JOM 69(2):135–143
Rashid M (1980) High-strength, low-alloy steels. Science 208(4446):862–869
Pandey PC, Shan H (1980) Modern machining processes. Tata McGraw-Hill Education, New York
Manikandan N, Kumanan S, Sathiyanarayanan C (2017) Optimisation of electrochemical drilling process using Taguchi method and regression analysis. Int J Mach Mach Mater 19(2):136–159
Manikandan N, Kumanan S, Sathiyanarayanan C (2017) Multiple performance optimization of electrochemical drilling of Inconel 625 using Taguchi based grey relational analysis. Eng Sci Technol Int J 20(2):662–671
Manikandan N et al (2019) Influence of wire-EDM textured conventional tungsten carbide inserts in machining of aerospace materials (Ti–6Al–4V alloy). Mater Manuf Process 34(1):103–111
Soni H, Sannayellappa N, Rangarasaiah RM (2017) An experimental study of influence of wire electro discharge machining parameters on surface integrity of TiNiCo shape memory alloy. J Mater Res 32(16):3100–3108
Raju R et al (2018) Optimization of process parameters in electrical discharge machining of haste alloy C276 using Taguchi’s method. Mater Today Proc 5(6, Part 2):14432–14439
Das AK et al (2016) Influence of process parameters on the surface integrity of micro-holes of SS304 obtained by micro-EDM. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 38(7):2029–2037
Meshram DB, Puri YM (2017) Review of research work in die sinking EDM for machining curved hole. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 39(7):2593–2605
Ikram A et al (2013) Parametric optimization for surface roughness, kerf and MRR in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) using Taguchi design of experiment. J Mech Sci Technol 27(7):2133–2141
Shah A et al (2011) Material removal rate, kerf, and surface roughness of tungsten carbide machined with wire electrical discharge machining. J Mater Eng Perform 20(1):71–76
Singh V, Pradhan S (2014) Optimization of WEDM parameters using Taguchi technique and response surface methodology in machining of AISI D2 steel. Proc Eng 97:1597–1608
Rao PS, Ramji K, Satyanarayana B (2014) Experimental investigation and optimization of wire EDM parameters for surface roughness, MRR and white layer in machining of aluminium alloy. Proc Mater Sci 5:2197–2206
Saha P et al (2008) Soft computing models based prediction of cutting speed and surface roughness in wire electro-discharge machining of tungsten carbide cobalt composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39(1):74–84
Mahapatra SS, Patnaik A (2007) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(9):911–925
Azam M et al (2016) Modeling of cutting speed (CS) for HSLA steel in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) using moly wire. J Chin Inst Eng 39(7):802–808
Bobbili R, Madhu V, Gogia A (2015) Modelling and analysis of material removal rate and surface roughness in wire-cut EDM of armour materials. Eng Sci Technol Int J 18(4):664–668
Shakeri S et al (2016) Investigation of material removal rate and surface roughness in wire electrical discharge machining process for cementation alloy steel using artificial neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(1–4):549–557
Reitz W, Pendray J (2001) Cryoprocessing of materials: a review of current status. Mater Manuf Process 16(6):829–840
Isaak CJ, Reitz W (2007) The effects of cryogenic treatment on the thermal conductivity of GRCop-84. Mater Manuf Process 23(1):82–91
Jafferson J, Hariharan P (2013) Machining performance of cryogenically treated electrodes in microelectric discharge machining: a comparative experimental study. Mater Manuf Process 28(4):397–402
Gill SS et al (2010) Cryoprocessing of cutting tool materials—a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 48(1–4):175–192
Gill SS, Singh J (2010) Effect of deep cryogenic treatment on machinability of titanium alloy (Ti-6246) in electric discharge drilling. Mater Manuf Process 25(6):378–385
Arockia Jaswin M, Mohan Lal D (2010) Optimization of the cryogenic treatment process for En 52 valve steel using the Grey-Taguchi method. Mater Manuf Process 25(8):842–850
Smol’nikov E, Kossovich G (1980) Cold treatment of cutting tools. Met Sci Heat Treat 22(10):704–705
Kapoor J, Singh S, Khamba JS (2012) Effect of cryogenic treated brass wire electrode on material removal rate in wire electrical discharge machining. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 226(11):2750–2758
Goyal A (2017) Investigation of material removal rate and surface roughness during wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) of Inconel 625 super alloy by cryogenic treated tool electrode. J King Saud Univ Sci 29(4):528–535
Nayak BB, Mahapatra SS (2016) Optimization of WEDM process parameters using deep cryo-treated Inconel 718 as work material. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19(1):161–170
Kapoor J, Khamba JS, Singh S (2012) Effect of shallow cryogenic treated brass wire electrode on workpiece surface roughness in wire-EDM. Int J Mater Eng Innov 3(3–4):190–203
Kapoor J, Khamba JS, Singh S (2011) Effects of cryogenic treated wire electrode on the surface of an EN-31 steel machined by WEDM. Int J Surf Eng Mater Technol 1(1):43–47
Tarng Y, Ma S, Chung L (1995) Determination of optimal cutting parameters in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 35(12):1693–1701
Azam M et al (2016) Parametric analysis of recast layer formation in wire-cut EDM of HSLA steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(1–4):713–722
Sharma N et al (2013) Modeling and multiresponse optimization on WEDM for HSLA by RSM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(9):2269–2281
Tosun N, Cogun C, Tosun G (2004) A study on kerf and material removal rate in wire electrical discharge machining based on Taguchi method. J Mater Process Technol 152(3):316–322
Manton RB (1988) High strength weldable seamless tube of low alloy steel. Google Patents
Azam M et al (2016) Parametric analysis of recast layer formation in wire-cut EDM of HSLA steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(1):713–722
Ishfaq K et al (2018) Investigation of wire electric discharge machining of stainless-clad steel for optimization of cutting speed. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96(1):1429–1443
Akhtar MU, Raza MH, Shafiq M (2019) Role of batch size in scheduling optimization of flexible manufacturing system using genetic algorithm. J Ind Eng Int 15(1):135–146
Alidoosti A et al (2013) Electrical discharge machining characteristics of nickel–titanium shape memory alloy based on full factorial design. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 24(13):1546–1556
Jung JH, Kwon WT (2010) Optimization of EDM process for multiple performance characteristics using Taguchi method and Grey relational analysis. J Mech Sci Technol 24(5):1083–1090
Lin C, Lin J, Ko T (2002) Optimisation of the EDM process based on the orthogonal array with fuzzy logic and grey relational analysis method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 19(4):271–277
Bal KS, Dutta Majumdar J, Roy Choudhury A (2018) Minimization of bead geometry by optimization of regression equations for laser-beam bead-on-plate welded Hastelloy C-276 sheet. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(9):451
Montgomery DC (2017) Design and analysis of experiments. Wiley, New York
Abellan-Nebot JV, Subirón FR (2010) A review of machining monitoring systems based on artificial intelligence process models. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(1–4):237–257
Yu J et al (2017) Multi-objective optimizations of multidirectional forming mold based on fractional factorial design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88(1–4):1151–1160
Patil NG, Brahmankar PK (2010) Some studies into wire electro-discharge machining of alumina particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 48(5):537–555
Singh V, Bhandari R, Yadav VK (2017) An experimental investigation on machining parameters of AISI D2 steel using WEDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1):203–214
Aggarwal V, Khangura SS, Garg RK (2015) Parametric modeling and optimization for wire electrical discharge machining of Inconel 718 using response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(1):31–47
Manikandan N et al (2019) Investigations on wire spark erosion machining of aluminum-based metal matrix composites. Springer, Singapore
Tahir W et al (2019) Surface morphology evaluation of hardened HSLA steel using cryogenic-treated brass wire in WEDM process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04301-0
Raza MH et al (2019) Modeling of the mechanical properties of directionally solidified Al–4.3% Cu alloy using response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(9–12):3913–3925
Raza MH et al (2018) Investigating the effects of different electrodes on Al6061-SiC-7.5 wt% during electric discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 99(9–12):3017–3034
Ali MA et al (2018) Evaluating the effects of as-casted and aged overcasting of Al–Al joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96(1):1377–1392
Chalisgaonkar R, Kumar J (2016) Investigation of the machining parameters and integrity of the work and wire surfaces after finish cut WEDM of commercially pure titanium. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 38(3):883–911
Kumar H, Manna A, Kumar R (2018) Modeling and desirability approach-based multi-response optimization of WEDM parameters in machining of aluminum metal matrix composite. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(9):458
Sarfraz S et al (2017) Investigating the effects of as-casted and in situ heat-treated squeeze casting of Al–3.5% Cu alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 89(9–12):3547–3561
Patil NG, Brahmankar P (2010) Some studies into wire electro-discharge machining of alumina particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 48(5–8):537–555
Sharma P, Chakradhar D, Narendranath S (2015) Evaluation of WEDM performance characteristics of Inconel 706 for turbine disk application. Mater Des 88:558–566
Rao TB, Krishna AG (2014) Selection of optimal process parameters in WEDM while machining Al7075/SiCp metal matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(1):299–314
Khan MAR, Rahman M, Kadirgama K (2015) An experimental investigation on surface finish in die-sinking EDM of Ti–5Al–2.5 Sn. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77(9–12):1727–1740
Abbasi JA et al (2017) Effects of wire-Cut EDM process parameters on surface roughness of HSLA steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(5–8):1867–1878
Rao TB, Krishna AG (2014) Selection of optimal process parameters in WEDM while machining Al7075/SiCp metal matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(1–4):299–314
Yang RT et al (2012) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters for cutting tungsten. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60(1–4):135–147
Okada A et al (2010) Evaluations of spark distribution and wire vibration in wire EDM by high-speed observation. CIRP Ann 59(1):231–234
Prasad D, Krishna AG (2015) Empirical modeling and optimization of kerf and wire wear ratio in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77(1–4):427–441
Rajyalakshmi G, Ramaiah PV (2013) Multiple process parameter optimization of wire electrical discharge machining on Inconel 825 using Taguchi grey relational analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(5–8):1249–1262
Derringer G, Suich R (1980) Simultaneous optimization of several response variables. J Qual Technol 12(4):214–219
Devarajaiah D, Muthumari C (2018) Evaluation of power consumption and MRR in WEDM of Ti–6Al–4 V alloy and its simultaneous optimization for sustainable production. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(8):400
El-Taweel T (2009) Multi-response optimization of EDM with Al–Cu–Si–TiC P/M composite electrode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(1–2):100–113
Natarajan U, Periyanan P, Yang S (2011) Multiple-response optimization for micro-endmilling process using response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 56(1–4):177–185
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Marcelo Areias Trindade.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahir, W., Jahanzaib, M. Multi-objective optimization of WEDM using cold treated brass wire for HSLA hardened steel. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41, 525 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-2028-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-2028-9